Making the best use of Find Reviewers
Finding willing and suitable reviewers remains the backbone of the editorial process. Due to the increase in submissions many journals are experiencing, however, this is often a source of frustration for editors. This is why we developed the Find Reviewers tool, accessed through Editorial Manager (EM), to help you with this vital task.
Find Reviewers can be used to help validate and expand your existing reviewer pool to ensure you invite the most up-to-date experts while also diversifying requests across a broader range of potential referees.
Find Reviewers’ search sections
You can access Find Reviewers by selecting “Find Reviewers using Scopus” on the Reviewer Selection Summary page in EM. Note: if you receive an error message containing a reference to Reviewer Recommender, make sure to disable the pop-up blocker opens in new tab/window for this page.

The System Recommendations section generates up to 100 reviewer candidates based on Scopus data. You can further refine the results by filtering on, for example, h-index, research expertise or examine candidates who have a special connection with the journal and might therefore be more likely to accept an invitation.
The Keyword Search section allows you to search using self-chosen research keywords, and now includes an automated conflict of interest check.
The Author Search section lets you search for specific candidates by name, email address or affiliation.
The Interested Reviewers section displays candidates that have actively indicated their interest to review for the journal via our Reviewer Hub platform opens in new tab/window. You can now refine your candidate list using various filters that have been added since this section was introduced in 2021.
The Editorial Board member section allows you to search for and invite suitable Editorial Advisory Board members (EBMs) from your journal – these tend to be loyal and motivated to review! Note: In order to be displayed here, EBMs will need to have linked their Elsevier account to their Scopus profile, and the email address(es) associated with their Elsevier account must match the email address we have for them in our editor contact system.
In addition to the above, there are two search sections in beta stage:
The Referenced Authors section allows you to browse authors of articles referenced in the manuscript. Candidates are listed alongside additional insights, such as the referenced article(s), published matching articles, their reviewing history, and whether they have a special connection with the journal.
In the Journal Reviewers section, youfind active reviewers from your journal’s database in EM, offering better insights into referees who are more likely to accept requests to review. The list shows available reviewers, ordered based on the best match of manuscript keywords and a wide range of signals that will help you find an optimal referee.
Tips & tricks to increase the success of your searches
Enable pop-ups on Editorial Manager (EM)
When you have reached the point of sending a manuscript forward for peer review, you can launch Find Reviewers by selecting “Invite Reviewers” within the Editorial Main Menu and then selecting “Find Reviewers Using Scopus”.
Selecting this link will open Find Reviewers in a new window but if this does not work, you may have pop-ups blocked on Editorial Manager – find instructions on how to disable these for the main browsers here:
Keyword search
Keyword search allows you to home in on potential reviewers by entering one or multiple keywords related to the manuscript in question.
Upon arrival on this page, you will be see two sections with suggestions to guide you in finding your ideal reviewer:
Suggested manuscript keywords entered by the author
Manuscript classifications selected by the author
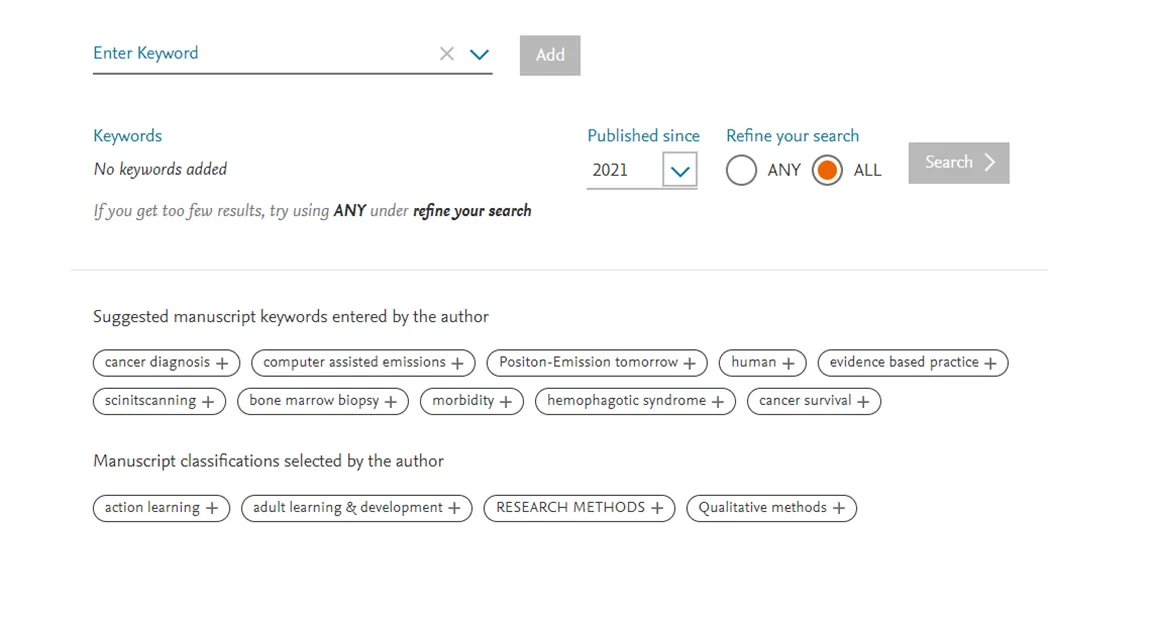
These keywords are an excellent starting point, but they might need further refinement and combinations to see results specifically relating to the manuscript in question. Within Find Reviewers, editors can view the manuscript title and abstract which can act as a resource for additional keywords (see Manuscript Details on the Find Reviewer tool).
To further refine the search, you are also able to:
Adjust the years of publication since (this may aid in identifying reviewers who have recent activity within the keywords of interest)
Adjust whether ALL keywords must be present in the reviewer’s activity or if ANY of the key terms can be present (If there are limited results, ANY is recommended to widen the pool)
Once your keywords have been selected and you have selected “Search”, Find Reviewers will then perform a Scopus search of these key terms and present you potential reviewer candidates.
NOTE: This is a keyword matching Boolean search. There is no additional intelligence for looking at plurals or synonyms.

Matching works
Within the matching works section, you will find the specific publications of the reviewer that match the keyword terms you have entered. These keywords can be present in the:
Title
Abstract
Author keywords (of publication)
Indexed keywords (of publication)
Clicking on these publications will open a Scopus link to view the full publication where you will be able to see where your key terms are present within the publication.
Author keywords
This section highlights the reviewer candidate’s keywords present in the publications matching with your keywords. Selecting these terms will apply an additional filter on your search results (you can view these terms being added to the “Filter on expertise” section).
Scopus subject areas
This section will highlight the review candidate’s subject areas that align with the candidate’s matching works with your search terms. In a similar fashion to author keywords above, selecting these terms applies an additional filter in the “Filter on expertise” section.

NOTE: These terms will not be added to your keyword search terms, but instead will act as a filter on your existing search
To add new keywords to your search, please select “Edit Search” and you will be taken back to the Keyword Search page where you can then add any additional terms, ANY/ALL function and year filtering to begin to home in on your desired candidates.

Session preferences
You can improve matching works results across these sections by tweaking these keywords to your preferences by selecting the “Session Preferences” link on the left-hand navigation bar which in turn will open the pop up below.

Within this window, you will be able to refine the keywords used to conduct this search to your preferences, which in turn will assist you in finding candidates with the specific expertise you require for the manuscript you are handling. You can remove keywords currently selected as well as add new keywords that you feel are relevant.
Conflicts of interest
When Find Reviewers is initially launched, the tool will analyse both the corresponding and co-authors of the manuscript and flag potential candidates as having a potential conflict of interest (COI) if they share activities and/or institutions - (this relates to activity within the last three years). This information is presented to you within the “Session Preferences” and “Conflict of Interest” tab where you can view who the tool was successfully able to identify and who was not (cases where we are unable to identify a COI might be due to inability to locate a Scopus profile based on the details provided).
Throughout the tool, we will flag these individuals to you to help you avoid selecting a potentially conflicted referee. If you discover any further individuals through your use of the Find Reviewer tool who also have a potential conflict of interest, you can increase this list by selecting the “Add to Conflict of Interest” button next to a candidate’s profile.

Filters
Within each search avenue of Find Reviewers, you are presented with filters that can assist you in refining the list of candidates you view within each tab. These filters are labelled as:
Filter on h-index
Filter on expertise
Filter on connections
Filter on review history

H-index
This filter allows you to refine your search within a cohort of selected h-index intervals. The default mechanism is presented as the range of lowest to highest of all candidates in view. While candidates with a high h-index are likely active and highly knowledgeable researchers, it might also be that these researchers are simply too busy to commit to reviewing.
It is therefore highly recommended to utilize these individuals with a high h-index by viewing their co-author network within their matching publications. Alternatively, we also recommend avoid focusing too much on high h-index individuals for the purpose of peer review and instead widen your search across the h-index range, including those candidates with lower h-index figures.

Connections
Filter on connections, allows you to identify candidate relationships, both with your journal and the manuscript you are currently handling. This functionality can be employed to identify candidates that may already have a relationship with your journal (either having recently reviewed or published).
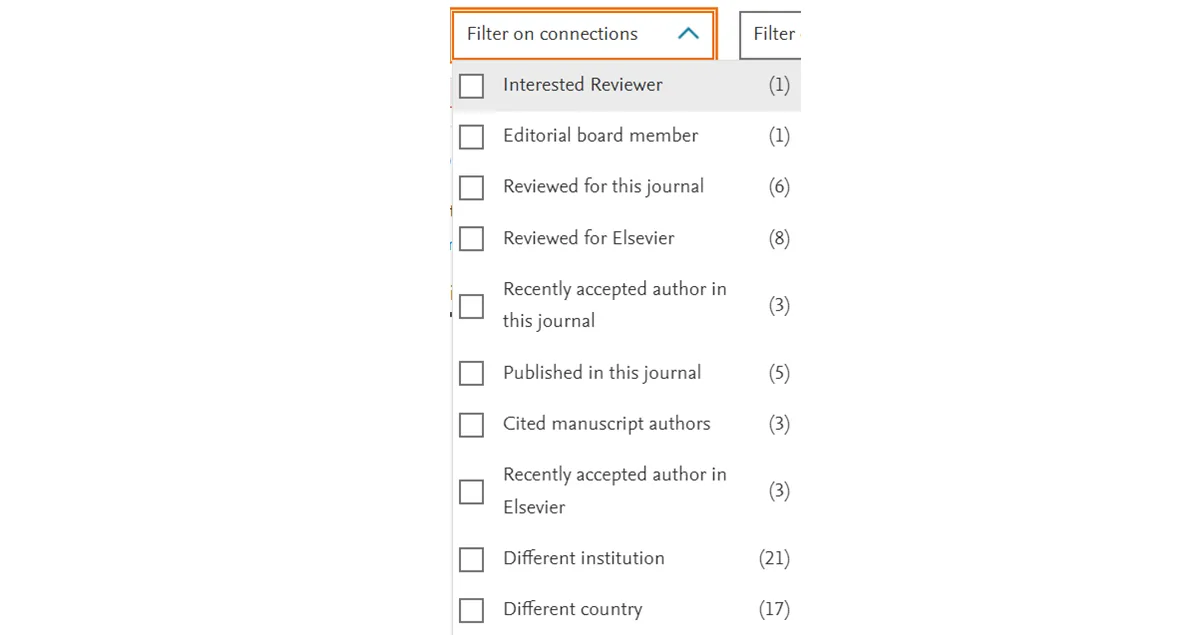
Recently accepted authors are (up to 75%) more likely to accept peer review invitations from journals which have accepted their publications. Candidates who also have reviewed for journal previously can increase your chance of success by up to 50%. These candidates can be easily identified via the search listings by the “Engaged Reviewer” label here:

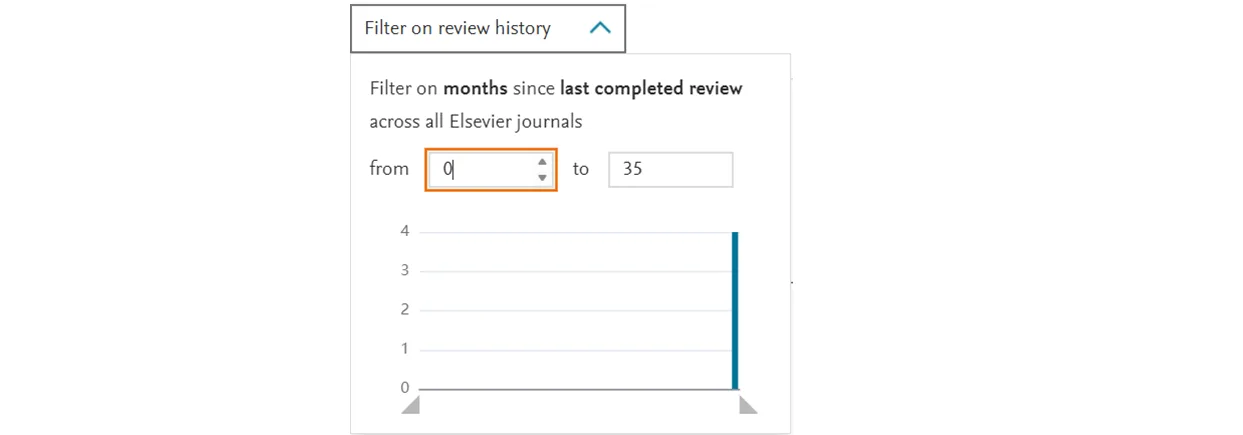
Filter on Reviewer History
Filtering on reviewer activity allows you to identify candidates who have completed peer review activities within your designated timeframe. On the left-hand side, you will be shown a scale presenting the number of eligible candidates. On the bottom of the chart, this scale indicates the timeframe of their activity.
We recommend using this filter alongside candidates’ recent publication activity. We have noted that authors who have had their papers published within a recent timeframe tend to be more willing to accept peer review invitations to pay back the service from which they have benefited and this filter, alongside the publication data we provide, may help guide you to more successful outcomes.
We hope you found the above tips useful. Should you have any questions or suggestions for further features in Find Reviewers, please feel free to contact us at: findreviewers@elsevier.com opens in new tab/window.