Quick Facts
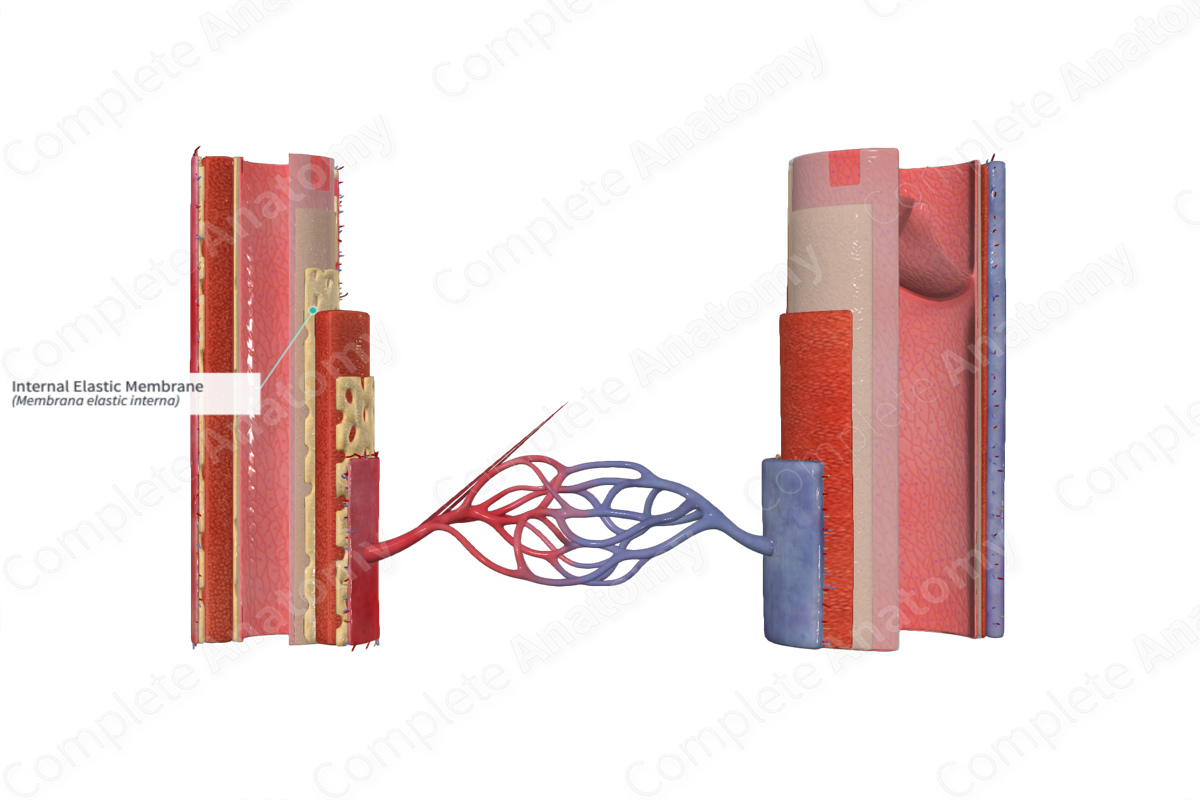
The internal elastic membrane is a fenestrated elastic membrane that constitutes the outermost component of the tunica intima of arteries (Dorland, 2011).
Related parts of the anatomy
Structure
The internal elastic membrane (or lamina) is a layer found in the tunica intima of the blood vessel. This thin elastic layer separates the tunica intima and the tunica media.
The internal elastic membrane is composed of an elastic covering with numerous openings, known as fenestrae, along its surface.
Anatomical Relations
The internal elastic membrane is found separating the tunica media from the tunica intima.
Function
The internal elastic membrane acts as a physical barrier. The fenestrae within the laminas sheath are thought to act as low-resistance pathways for heightened communication between vascular endothelial and smooth muscle cell layers.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Chronic allograft nephropathy
- Fungal rhinosinusitis
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
