Quick Facts
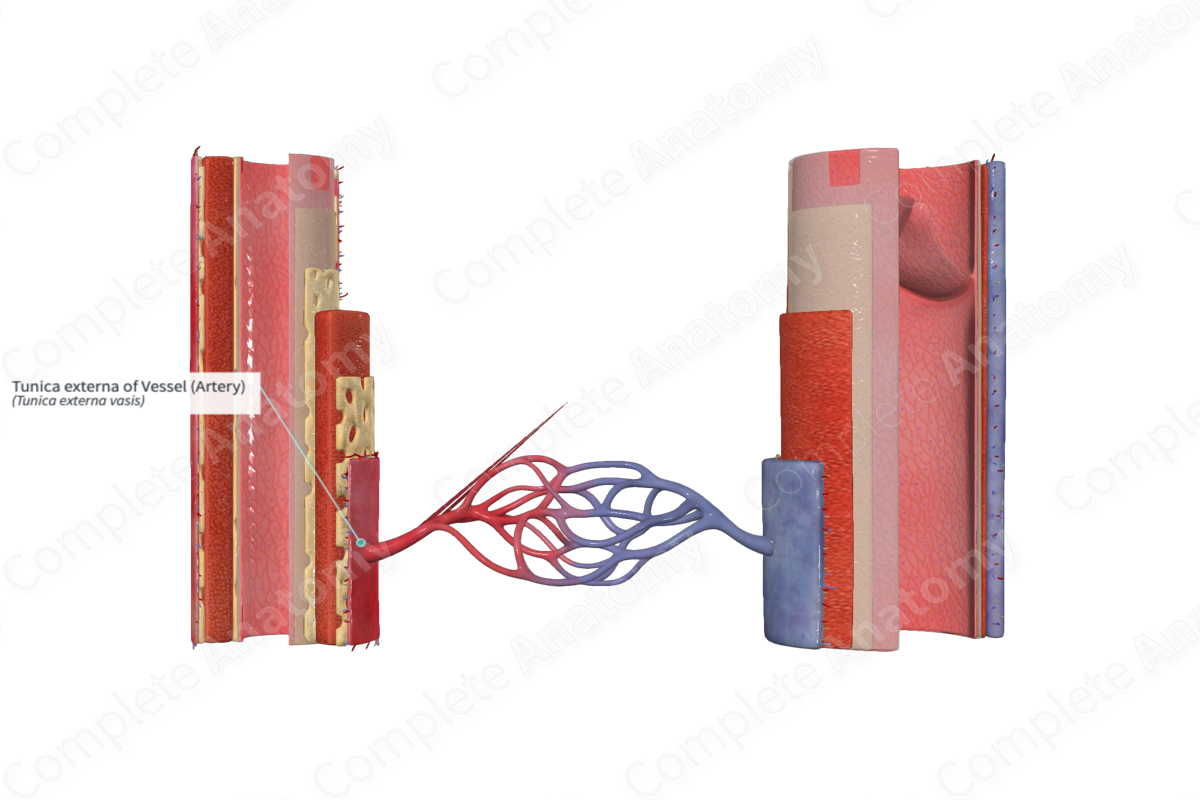
The tunica externa of a blood vessel is the outer, fibroelastic coat of vessels, usually in contact with surrounding tissues (Dorland, 2011).
Structure
The tunica externa is the outermost layer of the artery wall. It possesses its own network of smaller blood vessels, known as the vasa vasorum, which provide the blood vessel with the molecules and nutrients necessary for cellular activity (Pawlina, 2016). Along with this small network of supportive blood vessels, the tunica externa is innervated by unmyelinated autonomic nerve fibers, the nervi vasorum (Mescher, 2013). The nervi vasorum are efferent autonomic fibers that play a role in vasodilation and vasoconstriction.
The tunica externa is composed of fibroblasts, scarce smooth muscle cells, and connective tissue, typically elastin and type I collagenous fibers. Recent studies have suggested that the tissue arrangement of tunica externa is not a densely packed wall like-structure, commonly seen in alcohol fixed tissue. In fact, it is composed of a collagen lattice surrounded by fluid filled interstitial spaces (Benias et al., 2018). This has also been described in other tissues, such as lung, renal, dermis, and fascia.
Anatomical Relations
The external elastic lamina, a layer of elastic tissue, separates the tunica externa from the tunica media.
Function
The tunica externa serves to anchor the blood vessel in place in the body tissue. Furthermore, the tunica externa acts as a protective layer restricting sudden expansion of the artery and therefore preventing damage to the artery wall.
References
Benias, P. C., Wells, R. G., Sackey-Aboagye, B., Klavan, H., Reidy, J., Buonocore, D., Miranda, M., Kornacki, S., Wayne, M., Carr-Locke, D. L. and Theise, N. D. (2018) 'Structure and Distribution of an Unrecognized Interstitium in Human Tissues', Scientific Reports, 8(1), pp. 4947.
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Mescher, A. (2013) Junqueira's Basic Histology: Text and Atlas. 13th edn.: McGraw-Hill Education.
Pawlina, W. 2016. Histology: A text and atlas with correlated cell and molecular biology. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer.
