Quick Facts
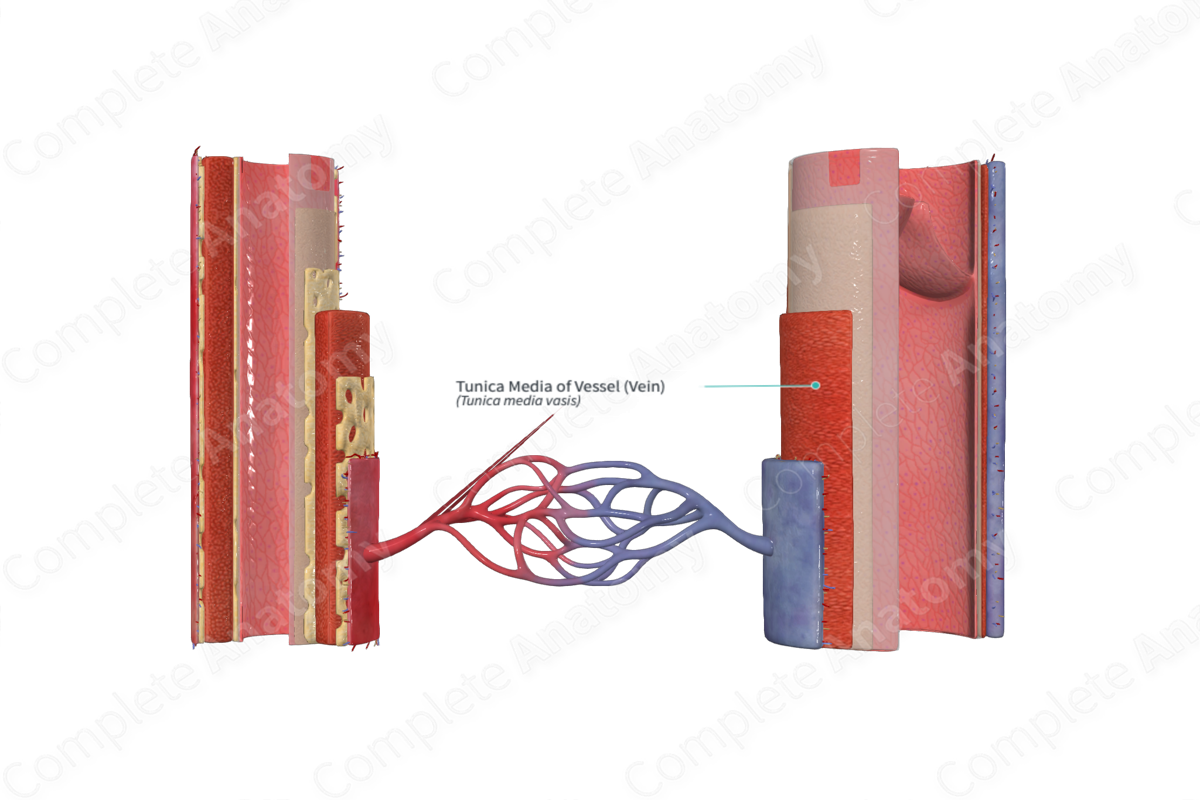
The tunica media a blood vessel is made up of transverse elastic fibers and smooth muscle cells (Dorland, 2011).
Structure
The tunica media lies deep to the tunica externa superficial to the tunica intima of the blood vessel. The external elastic lamina separates the tunica media from the tunica externa. Dividing the tunica media from the tunica intima is the internal elastic lamina.
The tunica media consists of layers of smooth muscle supported by connective tissue that is primarily made up of elastin and collagen. This smooth muscle is predominantly arranged in a helical manner surrounding the layer below it. These smooth muscle cells can also synthesize and secrete elastin, collagen and other extracellular components. Towards the outer portion of the tunica media there are also some layers of longitudinal muscle found.
Anatomical Relations
The tunica media is found between the tunica externa and the tunica intima. The elastin, collagen, and other extracellular components secreted by the smooth muscle cells of the tunica media contribute to the mechanical properties of the vessel (Pawlina, 2016).
Function
The tunica media provides the mechanical strength of the blood vessel. In addition, when the circular muscles contract or relax the diameter of the vessels' lumen decreases or increases respectively (vasoconstriction or vasodilation).
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Pawlina, W. 2016. Histology: A text and atlas with correlated cell and molecular biology. 7th ed. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer.
