Description
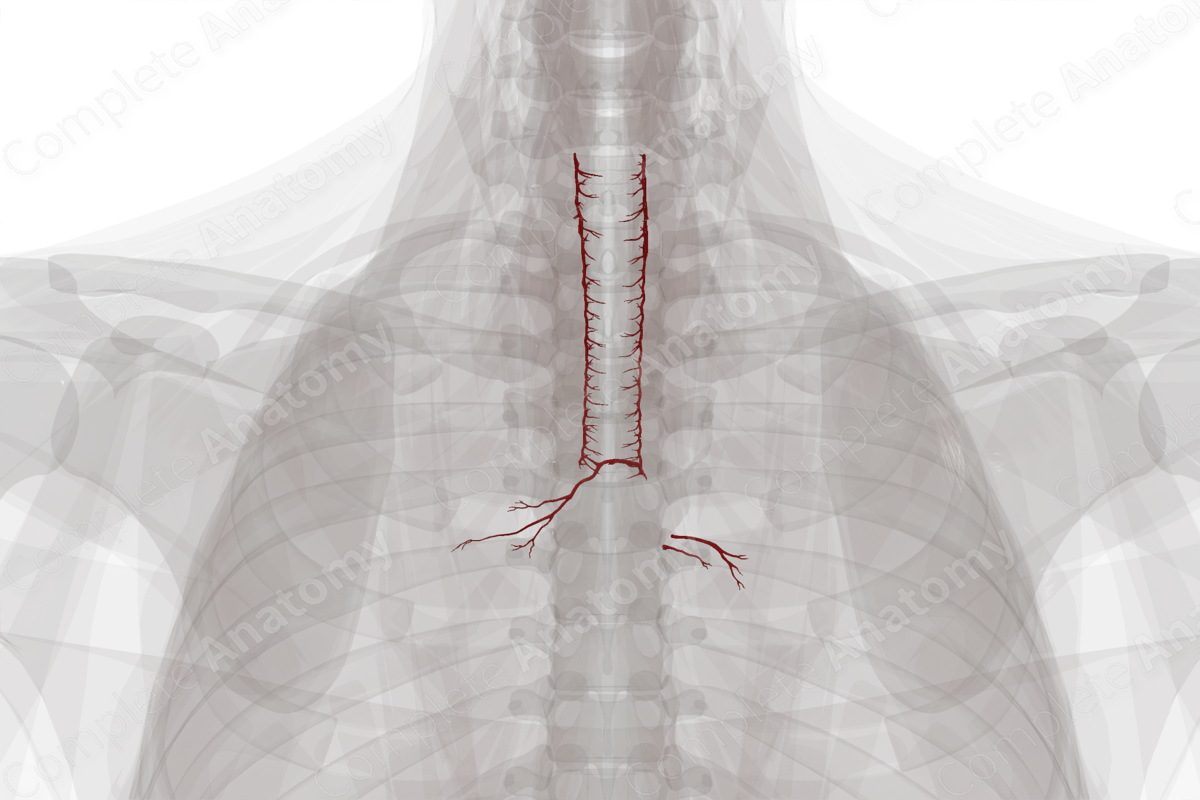
The arteries of the respiratory system do not refer to the pulmonary system, but to the systemic system that provides oxygenated blood and nutrition to the connective tissue of the lungs. These include the highly variable bronchial arteries.
A paired group of left bronchial branches arise directly from the descending thoracic aorta, the superior and inferior bronchial branches. The right bronchial branch arises indirectly from the descending thoracic aorta via the right-sided posterior intercostal artery, usually the third right posterior intercostal artery.
Much of the blood supplied by the bronchial arteries is returned to the heart via the pulmonary veins, and not the bronchial veins. See our micro-anatomy model of the bronchial tree.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





