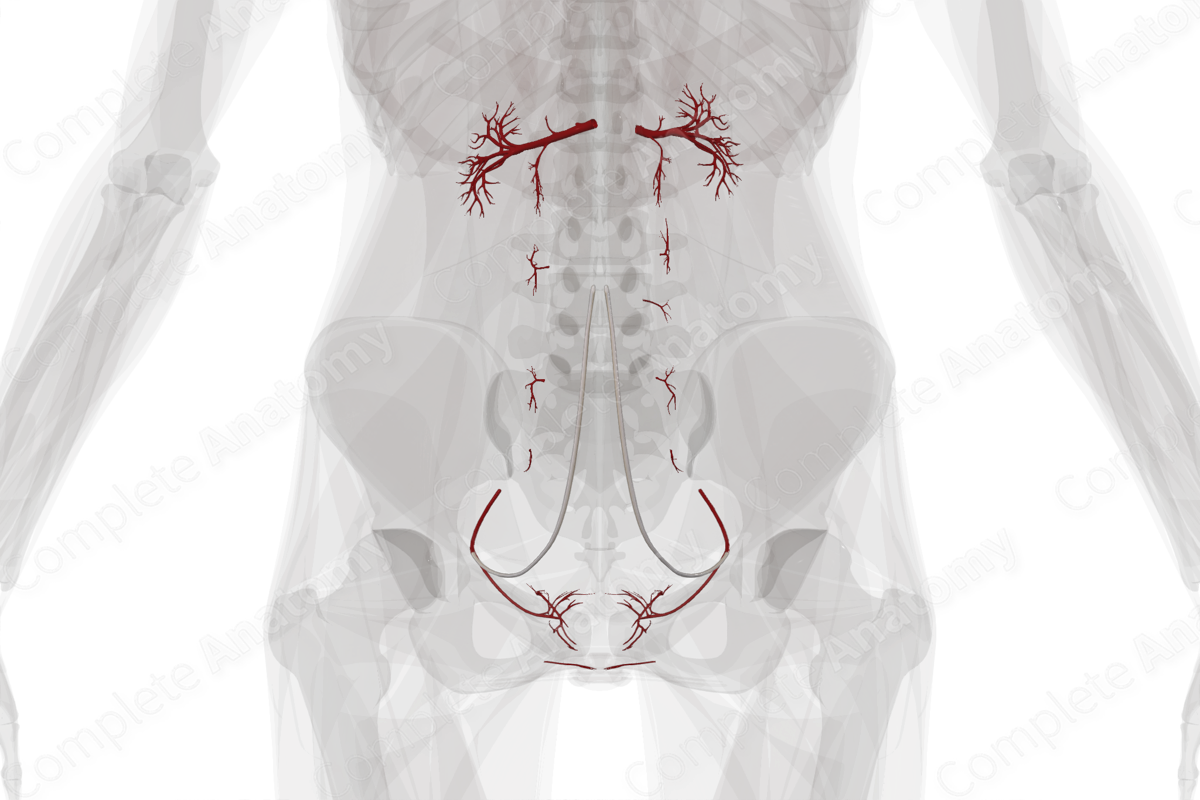
Description
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, urinary bladder and urethra. The kidneys are supplied directly from the abdominal aorta via the renal arteries. The ureters receive their blood supply through a series of small ureteric branches arising from the abdominal aorta and renal, gonadal, and common iliac arteries. The bladder receives blood via the superior and inferior (male) vesical arteries.
The urethra which is the most sexually dimorphic component of the urinary system has slightly different supply between both sexes. In the female, the arterial supply to the urethra is derived from the internal pudendal and the vaginal arteries. In the male, it is supplied by the inferior vesicle, middle rectal and internal pudendal arteries.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Urinary System

The urinary system is a multicomponent organ system with the primary function of producing, transporting, storing, and eliminating urine to maintain homeostasis by regulating the water and ionic balance of the blood [1].




