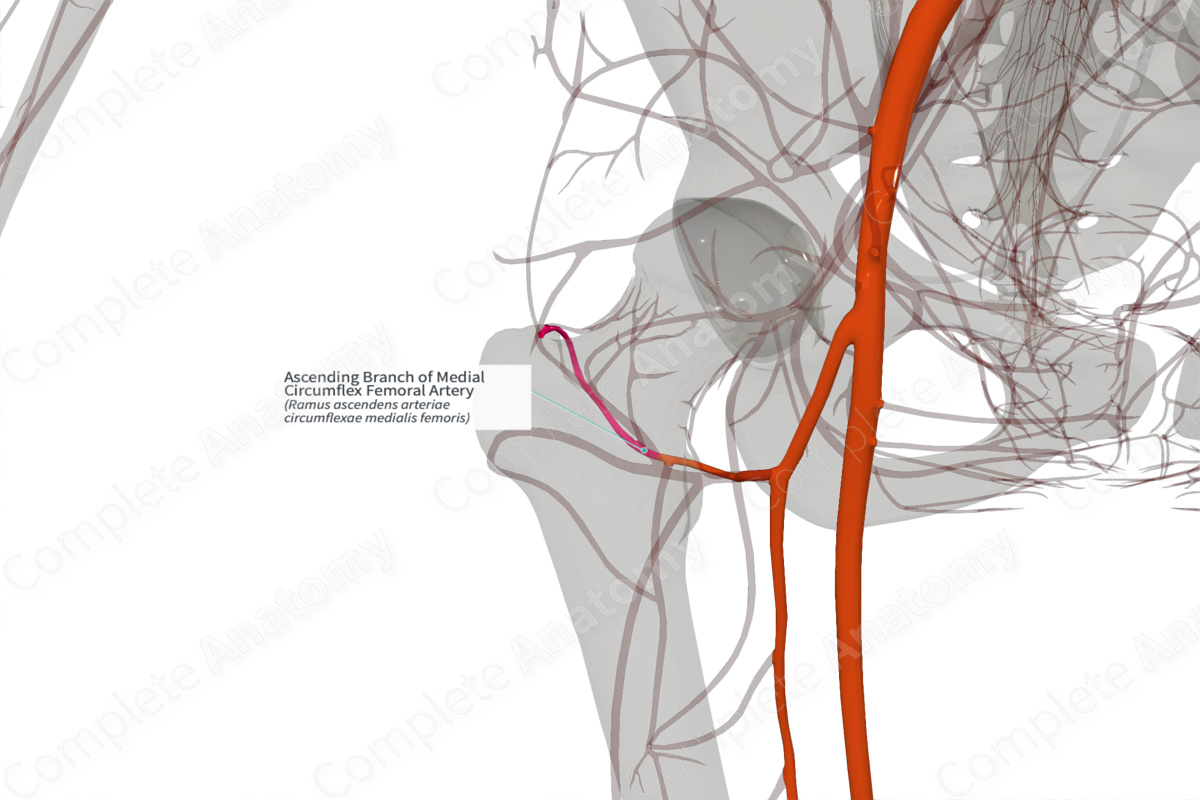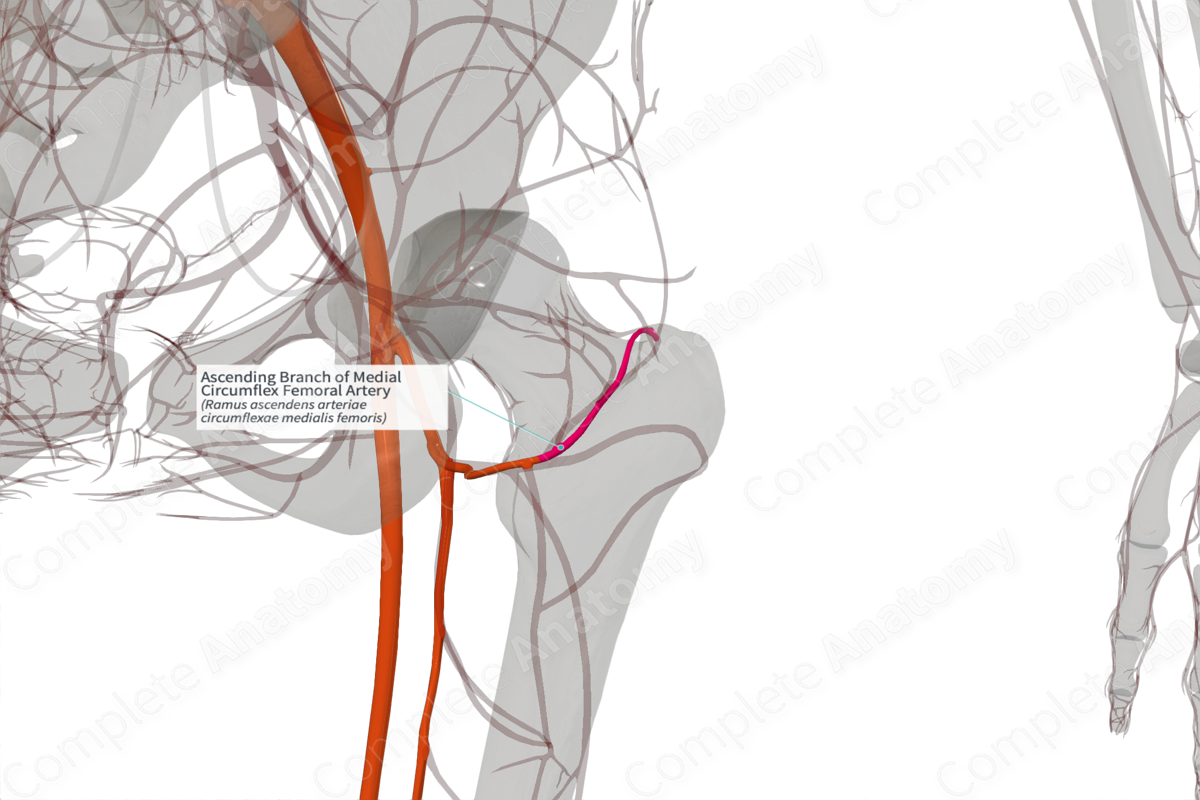
Ascending Branch of Medial Circumflex Femoral Artery (Left)
Ramus ascendens arteriae circumflexae medialis femoris
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Medial circumflex femoral artery.
Course: Along the trochanteric fossa.
Branches: Retinacular arteries.
Supplied Structures: Proximal femur, hip joint, gluteal, and thigh muscles.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The ascending branch originates from the medial circumflex femoral artery.
Course
The ascending branch of the medial circumflex femoral artery travels superiorly on the obturator externus tendon, in front of the quadratus femoris muscle and extends into the trochanteric fossa.
Branches
The ascending branch of the medial circumflex femoral artery gives retinacular branches that supply the head of the femur. It anastomoses with the ascending branch of the lateral circumflex femoral artery and with branches of the gluteal arteries.
Supplied Structures
The ascending branch of the medial circumflex femoral artery contributes to the supply of the proximal femur and hip joint, as well as muscles of the thigh and gluteal region.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Femoral Artery

Femoral artery pseudoaneurysm represents a pulsatile mass that is contained by incomplete elements of the arterial wall and surrounding subcutaneous/fibrous tissue and may result from disruption of a previous femoral suture line, femoral artery access for a catheter-based procedure, or injury resulting from puncture due to self-administered drug abuse.