Quick Facts
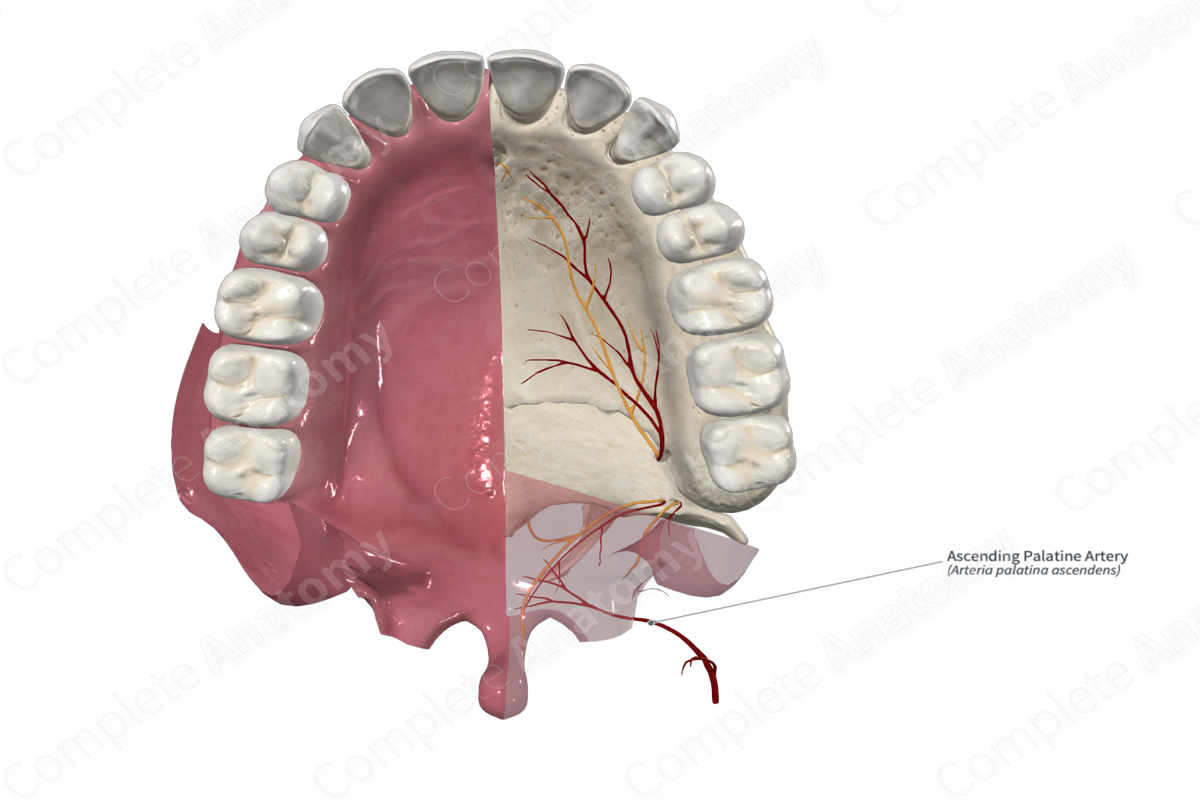
Origin: Facial artery.
Course: Ascends between the styloglossus and stylopharyngeus muscles, then between the superior pharyngeal constrictor and medial pterygoid muscles.
Branches: None.
Supplied Structures: Soft palate.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The ascending palatine artery arises from the facial artery, close to its origin from the external carotid artery.
Course
As its name suggests, the ascending palatine artery ascends between the styloglossus and stylopharyngeus muscles. As it reaches the pharynx, it continues to ascend between the superior pharyngeal constrictor and medial pterygoid muscles. Just below the levator veli palatine muscle, the ascending palatine artery gives off two terminal unnamed branches. One branch arches over the superior margin of the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle to reach the soft palate, while another terminal branch pierces the superior pharyngeal constrictor muscle to reach the palatine tonsils and auditory tube.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The ascending palatine artery supplies the soft palate, tonsils, and auditory tube (Eustachian or pharyngotympanic tube).



