Carotid Sinus Key Features & Anatomical Relations
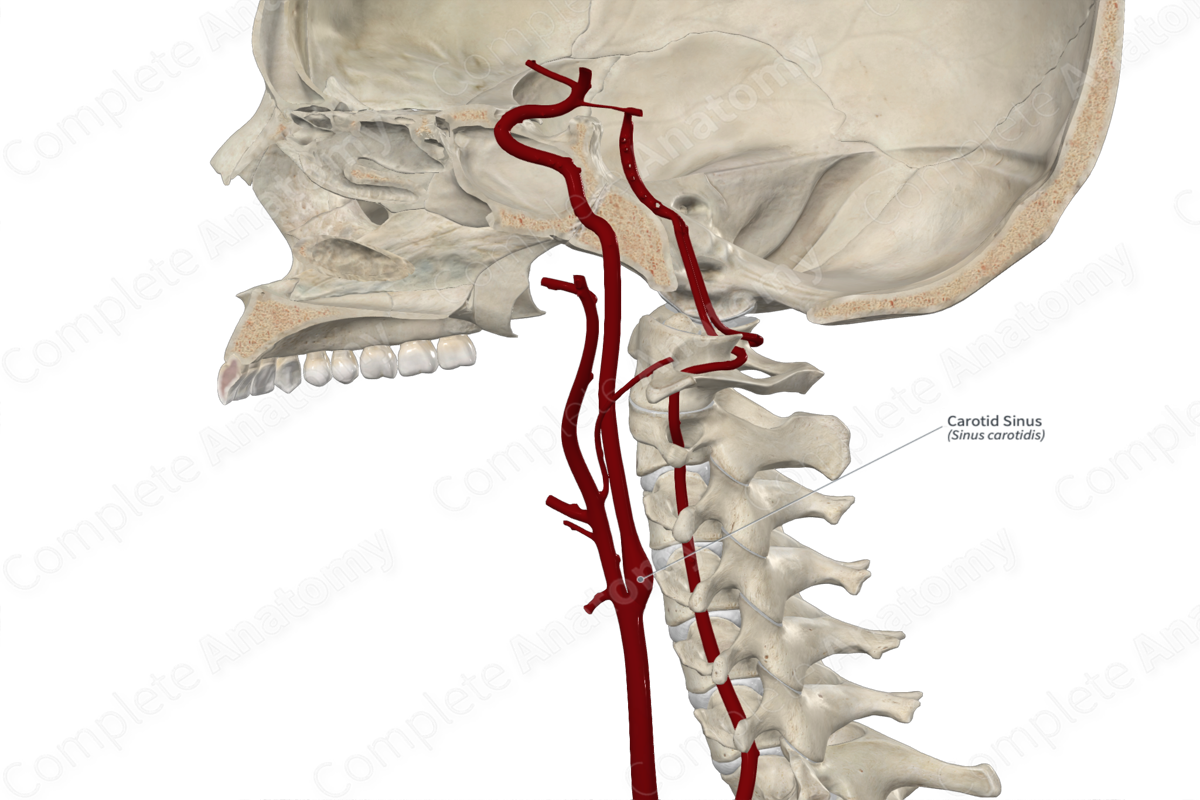
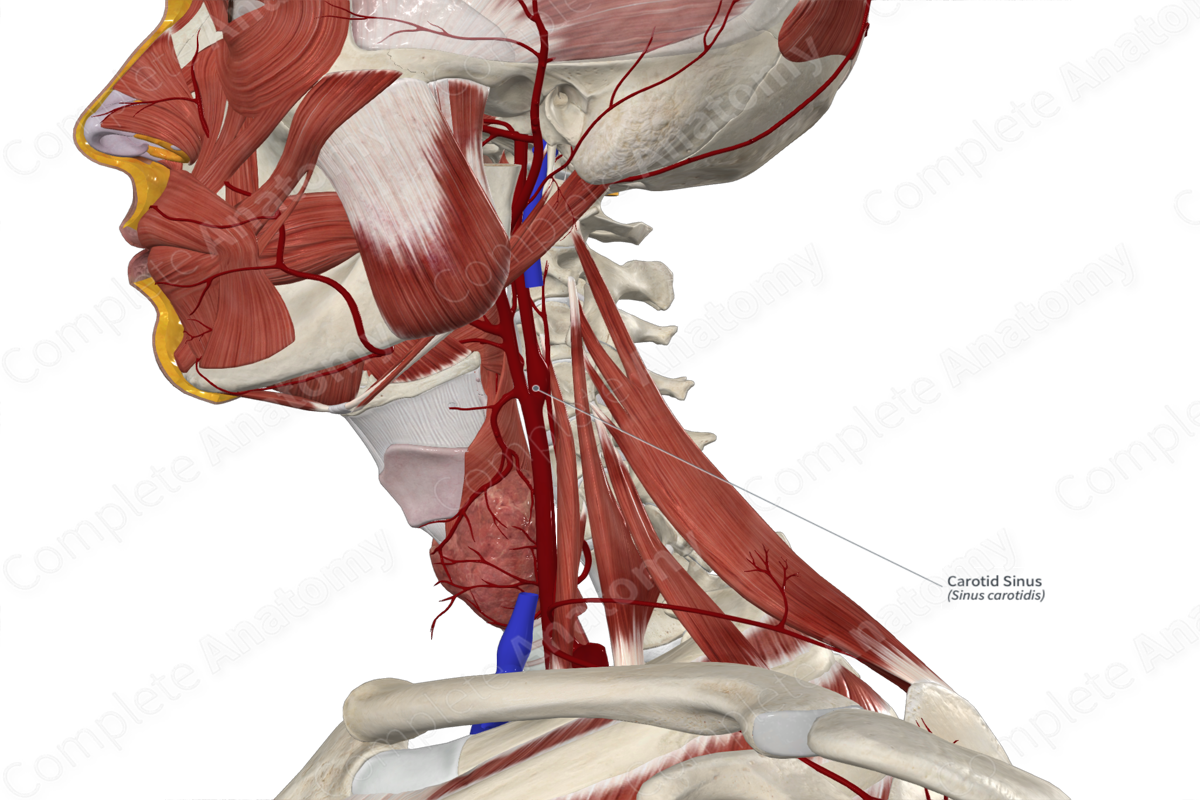
The carotid sinus is a dilated area at the bifurcation of the common carotid artery and the proximal end of the internal carotid artery.
Related parts of the anatomy
Carotid Sinus Structure
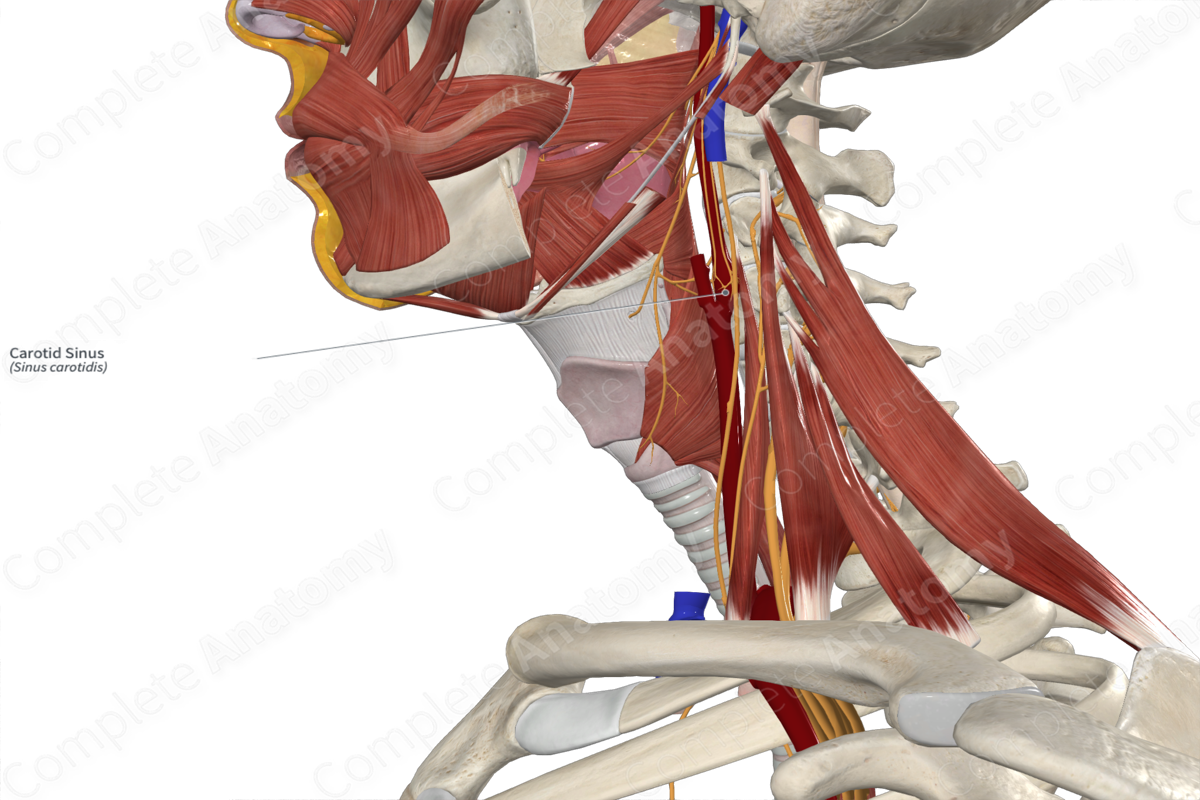
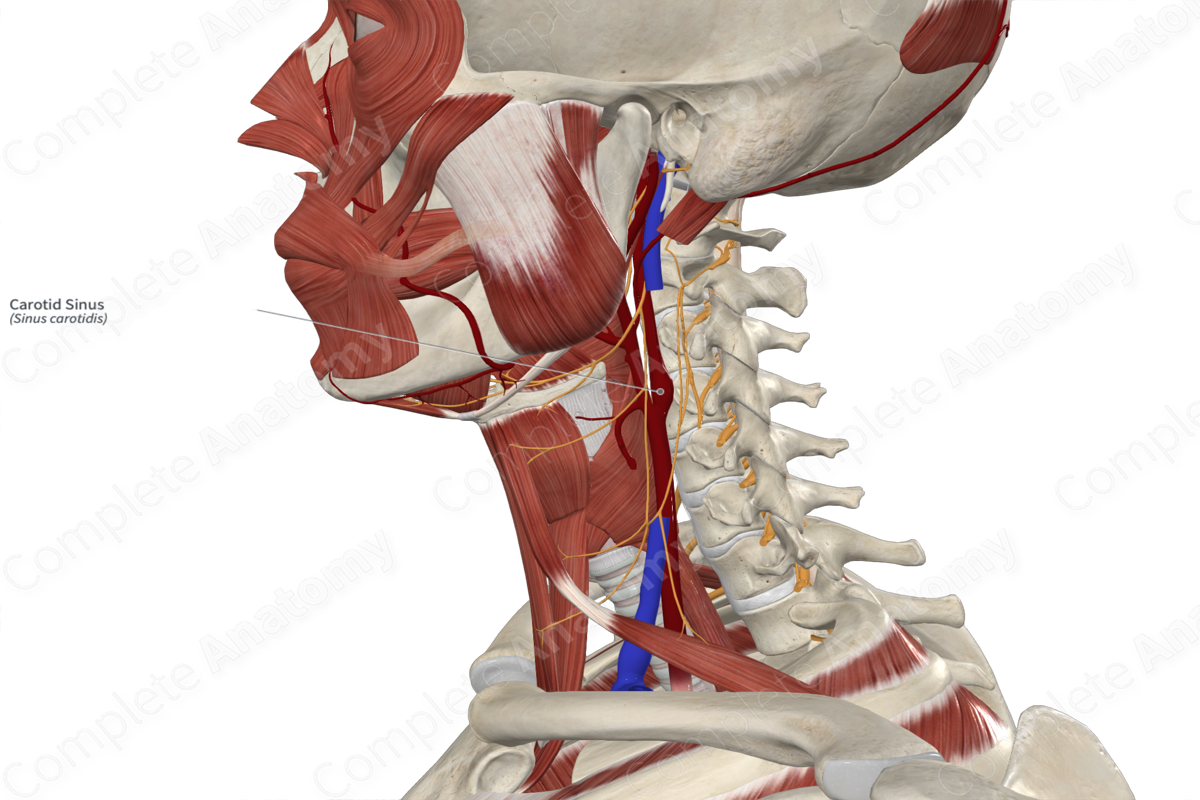
Visceral afferent fibers convey information from the carotid sinus via the glossopharyngeal nerve (CNIX).
Carotid Sinus Function
The carotid sinus is a baroreceptor (pressorecptor), which monitors changes in arterial blood pressure.
Carotid Sinus List of Clinical Correlates
- Carotid sinus syndrome
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Carotid Sinus

The carotid sinus is a thin-walled dilatation located at the proximal end of the internal carotid artery just above the bifurcation of the common carotid artery into the internal and external carotid artery.