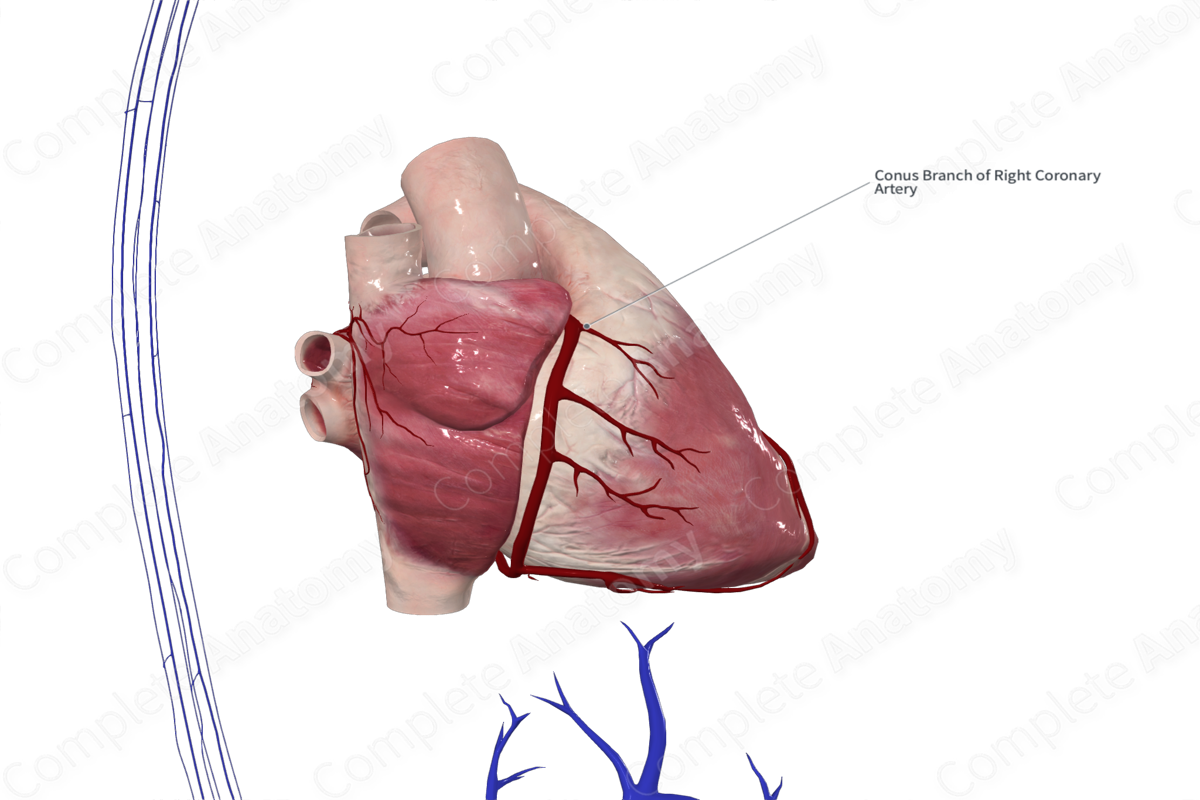
Conal Branch of Right Coronary Artery
Ramus coni arteriosi arteriae coronariae dextrae
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Right coronary artery.
Course: Inferiorly along the conus arteriosus.
Branches: Small unnamed branches.
Supplied Structures: Conus arteriosus.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The conal branch is the first branch of the right coronary artery. It may arise from the anterior aortic sinus in up to one third of individuals where it may occasionally be called the third coronary artery (Standring, 2016).
Course
The conal branch of the right coronary artery is a small artery that courses in an anteroinferior direction over the upper portion of the right ventricle.
Branches
The conal branch of the right coronary artery has many small unnamed branches that may anastomose with the branches of the left interventricular artery. In this case, they form an anastomotic ring (annulus of Vieussens) which encircles the outflow tract of the right ventricle (Standring, 2016).
Supplied Structures
The conal branch of the right coronary artery supplies the region of the conus arteriosus.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Coronary artery disease
- Coronary atherosclerosis
- Coronary bypass graft
- Coronary angioplasty
- Coronary occlusion
- Coronary revascularization
- Coronary artery fistula
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





