Quick Facts
Origin: Common carotid artery.
Course: Ascends on either side of the neck to enter the parotid gland.
Branches: Superior thyroid, ascending pharyngeal, lingual, facial, occipital, posterior auricular, superficial temporal, and maxillary arteries.
Supplied Structures: Face, scalp, tongue, teeth, palatine tonsils, frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses, auditory tube, external and middle ear, pharynx, larynx, muscles in the neck, and thyroid gland.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
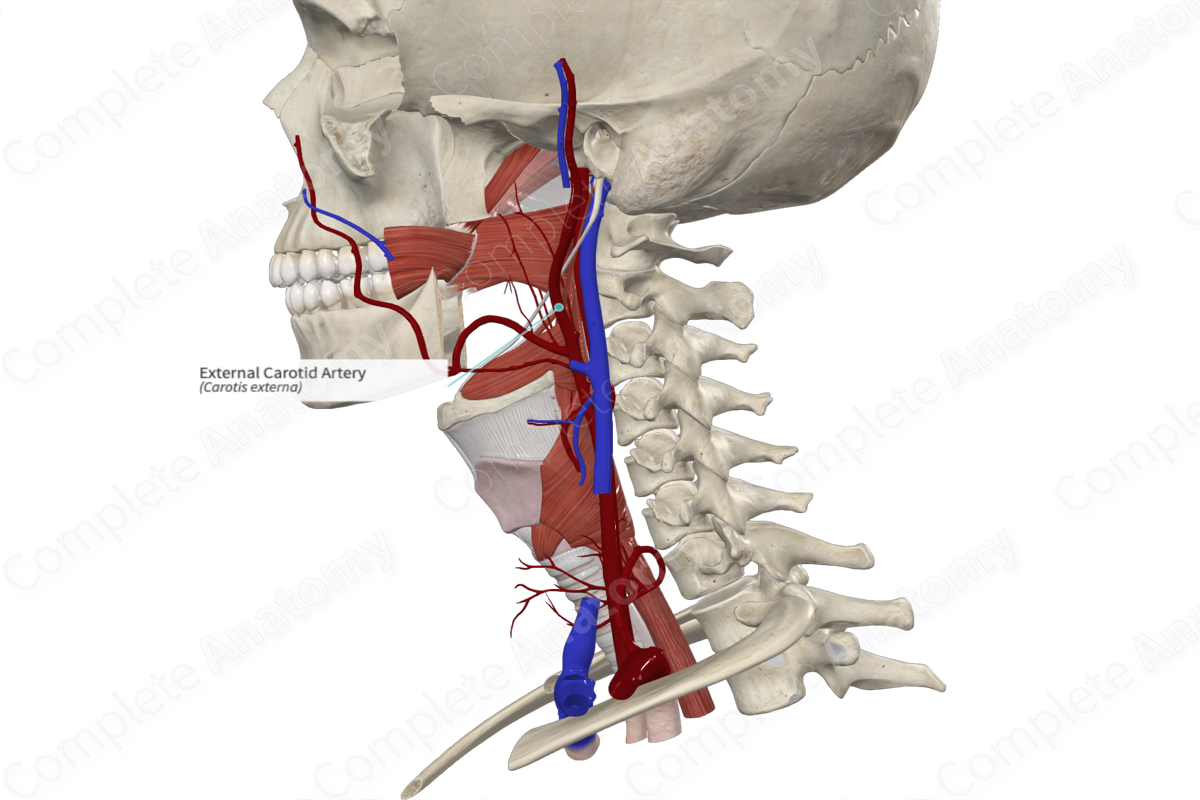
The external carotid artery arises when the common carotid artery bifurcates into the interior and external carotid arteries, usually at the level of C4 (or the upper border of the thyroid cartilage). The external carotid artery is easily distinguishable from the internal carotid artery, since the latter has no branches in the neck.
Course
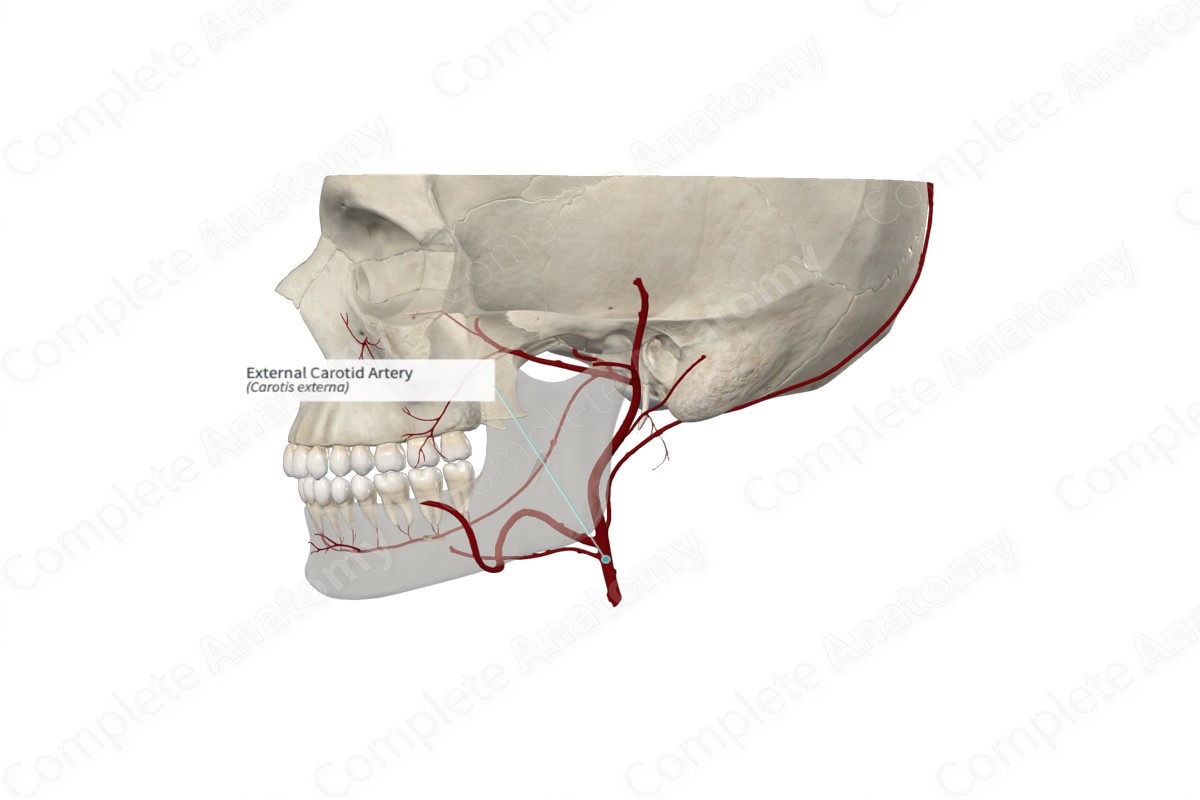
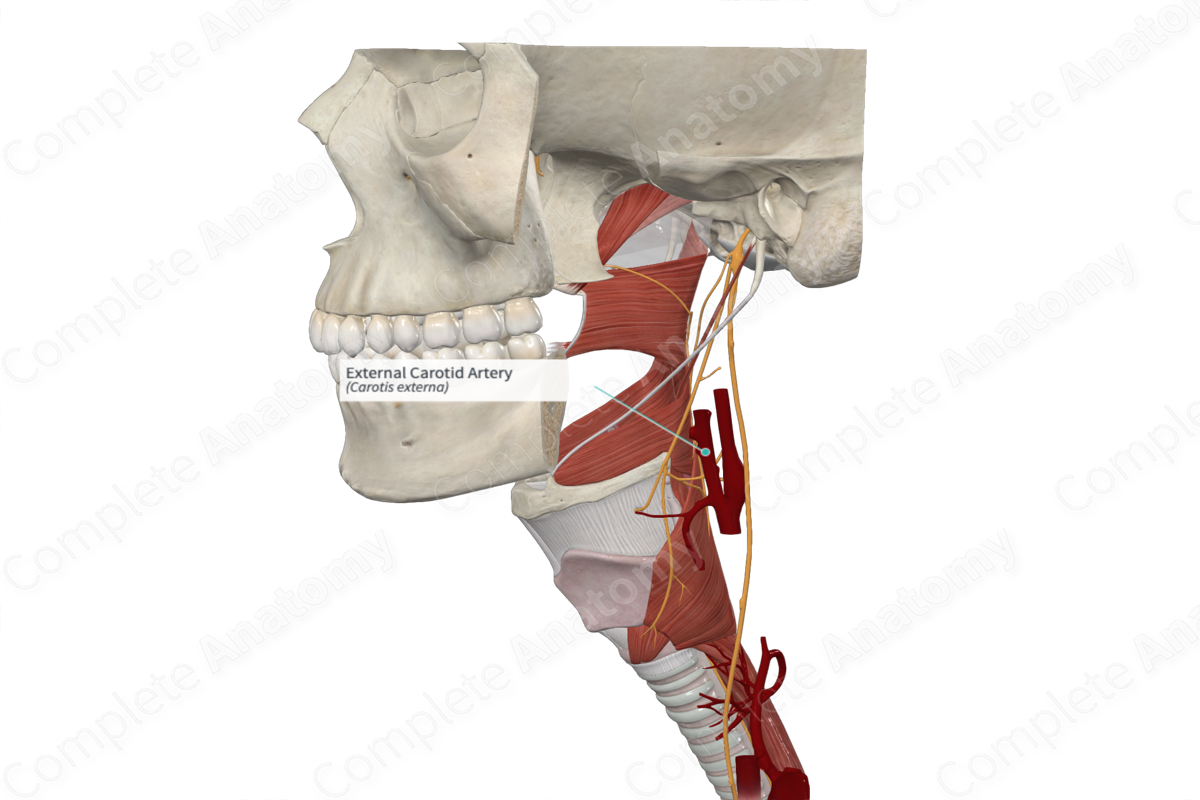
The external carotid artery originates in the carotid triangle of the neck and lies anteromedially to the internal carotid artery. Initially, it is slightly curved, as it bends anteriorly then posteriorly and slightly laterally. As it ascends, it passes more laterally to the internal carotid artery and gives off numerous branches to become diminished in size. It enters the parotid gland behind the neck of the mandible where it gives off its terminal branches.
Branches
The external carotid artery gives to eight branches distributed to the head and neck. Six of these branches arise from either the anterior, posterior, or medial surface of the external carotid artery.
- The superior thyroid, lingual, and facial arteries arise from the anterior surface of the external carotid artery.
- The occipital and posterior auricular arteries arise from posterior surface of the external carotid artery.
- The ascending pharyngeal artery arises from the medial surface of the external carotid artery.
The remaining two branches of the external carotid artery arise as terminal branches within the substance of the parotid gland, the maxillary and superficial temporal arteries.
Supplied Structures
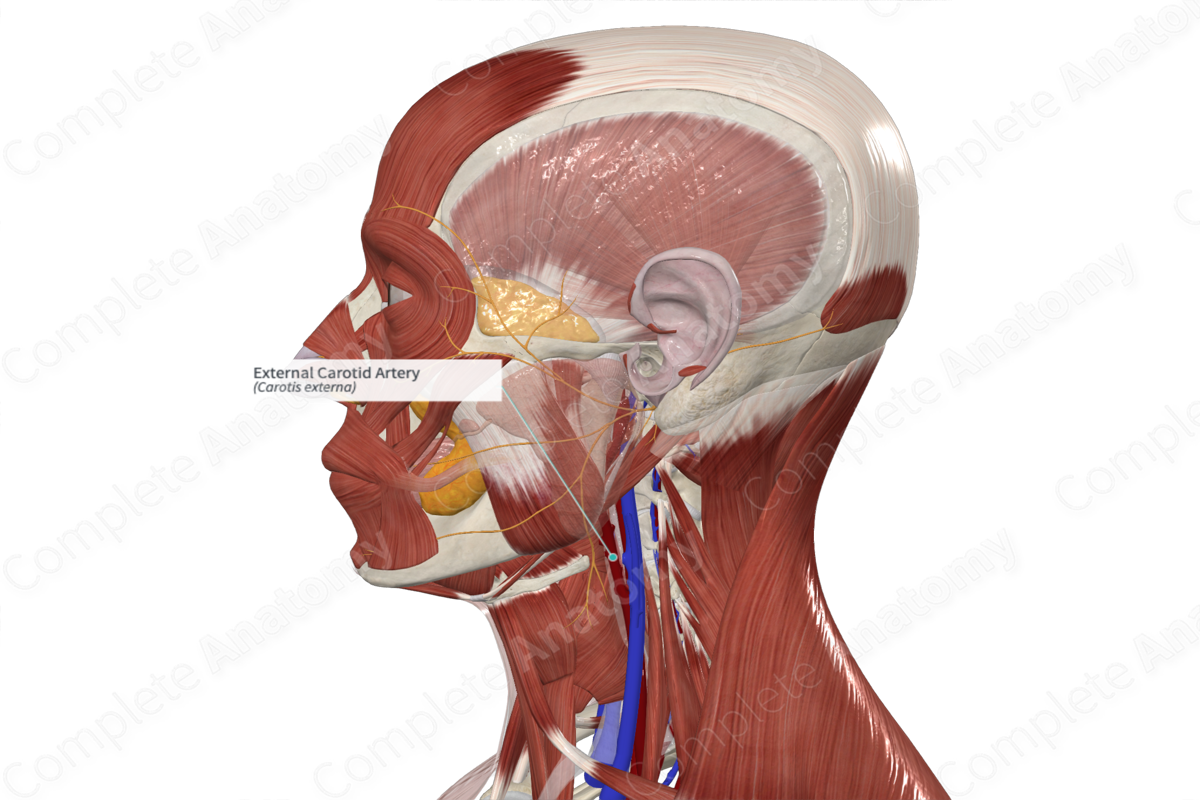
The external carotid artery is widely distributed to structures of the head and neck. These include the face, scalp, tongue, teeth, palatine tonsil, frontal, ethmoidal, sphenoidal, and maxillary sinuses, auditory tube, external and middle ear, pharynx, larynx, muscles in the neck, and thyroid gland.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products