Quick Facts
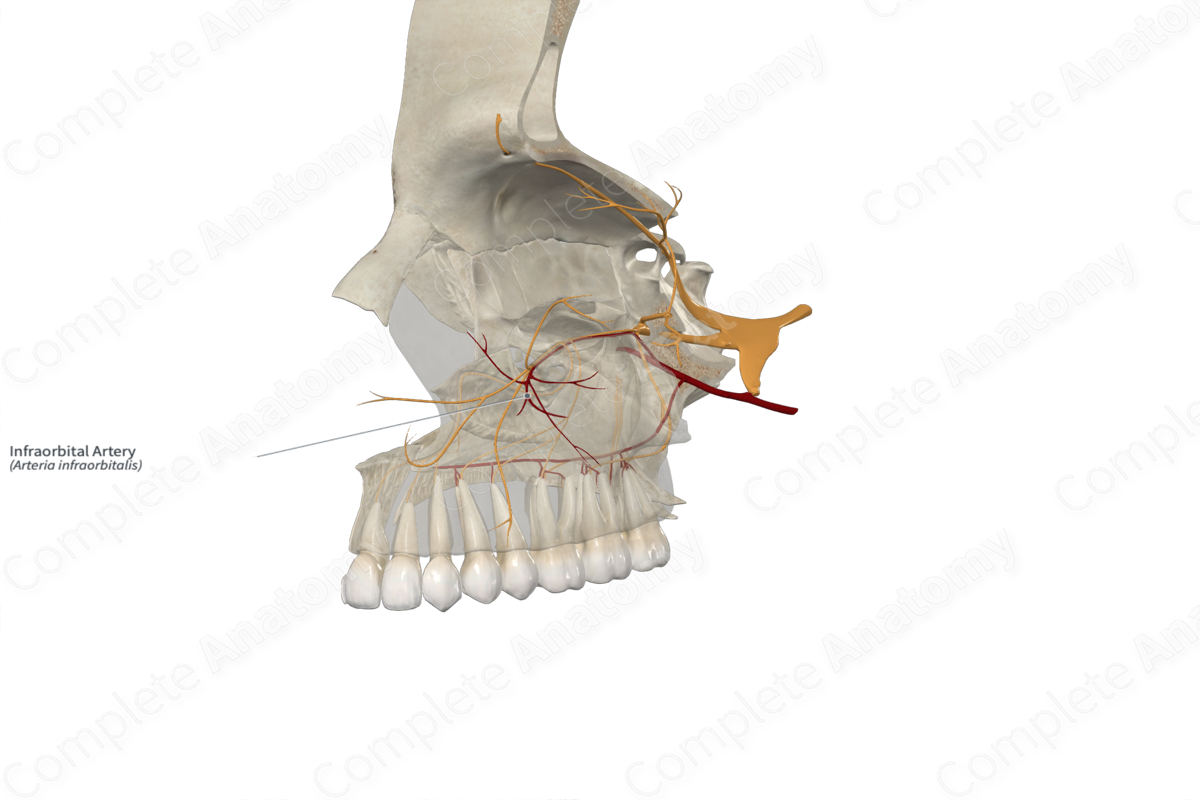
Origin: Maxillary artery.
Course: Exits the orbit via the infraorbital canal and then emerges onto the face through the infraorbital foramen.
Branches: Anterior and middle superior alveolar arteries.
Supplied Structures: Maxilla and its sinus, maxillary dental arcade, inferior eyelid, cheek, and nose.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The infraorbital artery arises from the third part of the maxillary artery as it passes through the pterygopalatine fossa. Sometimes, it may share a common trunk with the posterior superior alveolar artery.
Course
The infraorbital artery ascends to the orbit of the eye, entering it through the inferior orbital fissure. The infraorbital artery exits the orbit via the infraorbital canal of the maxillary bone. It emerges onto the face through the infraorbital foramen.
Branches
Within the infraorbital canal, the infraorbital artery gives rise to the anterior and middle superior alveolar arteries.
Supplied Structures
The infraorbital artery supplies numerous structures. The anterior and middle superior alveolar arteries supply the teeth of the upper jaw and the maxillary sinus, while the terminal ramifications of the infraorbital artery supply the skin of the inferior eyelid, cheek, and nose.




