Quick Facts
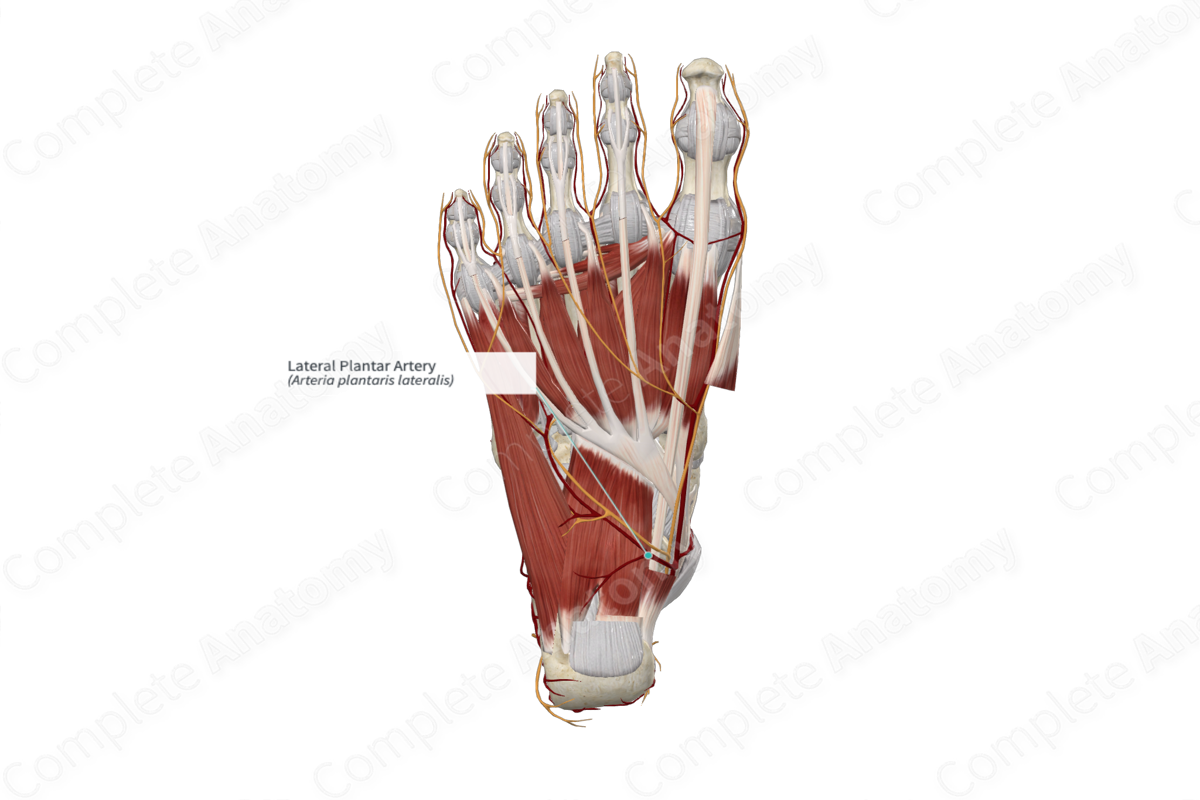
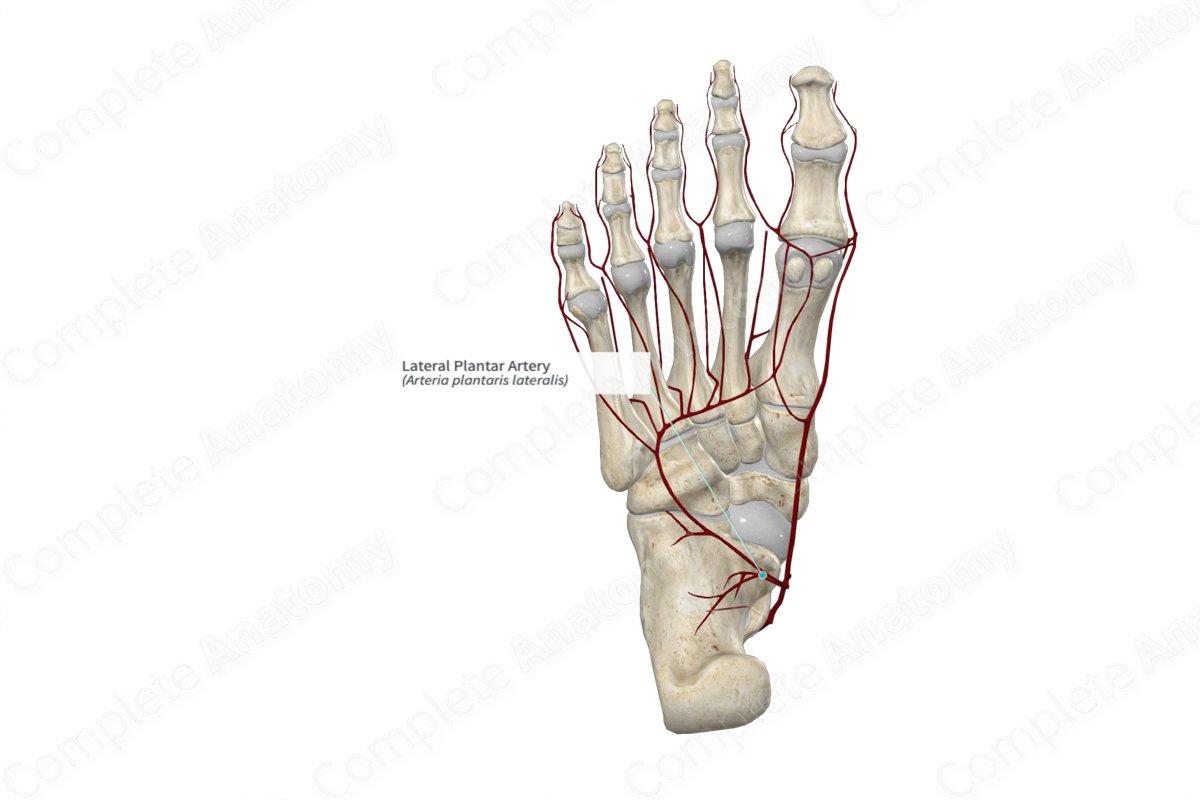
Origin: Terminal branch of posterior tibial artery.
Course: Distally along the lateral aspect of the foot.
Branches: Plantar metatarsal branch.
Supplied Structures: Lateral aspect of plantar surface of the foot.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The medial and lateral plantar arteries are the terminal branches of the posterior tibial artery. The posterior tibial artery bifurcates into the medial and lateral plantar arteries in the region of the sustentaculum tali (Tubbs, Shoja and Loukas, 2016). The lateral plantar artery is the larger of these two vessels.
Course
The lateral plantar artery continues in a lateral direction on the plantar aspect of the quadratus plantae muscle, deep to the flexor digitorum brevis muscle. It then passes over the tendon of the fibularis longus muscle, continues distally along the cuboid, until it reaches the level of the base of the fifth metatarsal. It accompanies the lateral plantar nerve which sits medial to the artery.
At the base of the fifth metatarsal bone, the lateral plantar artery unites with the deep plantar artery from the dorsalis pedis artery to form the plantar arch.
Branches
The lateral plantar artery gives rise to a plantar metatarsal branch that extends along the lateral surface of the fifth metatarsal bone (Netter, 2011).
Supplied Structures
The lateral plantar artery supplies the lateral aspect of the sole of the foot, including muscular, cutaneous, and articular elements. It also contributes to the supply of the plantar aspect of the toes.
References
Netter, F. H. (2011) Atlas of Human Anatomy. Netter Basic Science Series: Saunders/Elsevier.
Tubbs, R. S., Shoja, M. M. and Loukas, M. (2016) Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Wiley.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Artery

Arteries are vessels transporting blood between heart, tissues, and other organs in order to supply them with nutrition and oxygen.