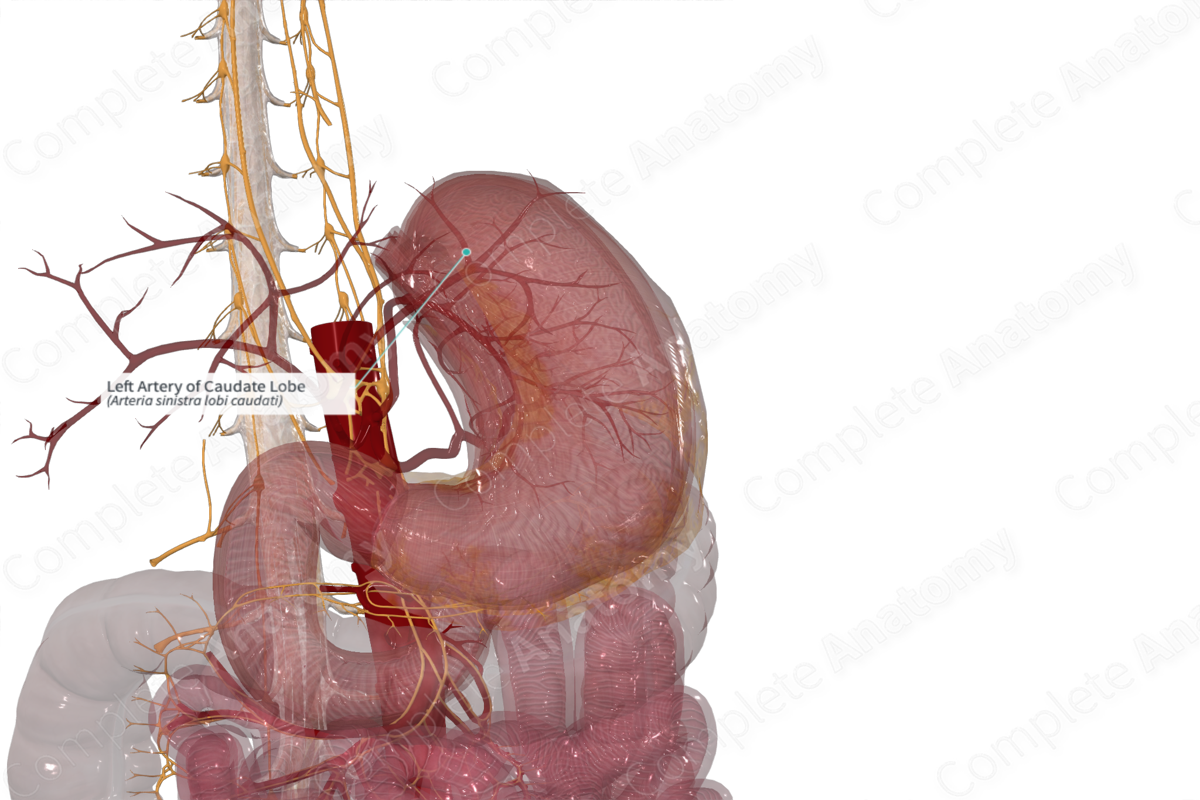
Quick Facts
Origin: Left hepatic artery (typically).
Course: Passes posteriorly
Branches: Small, unnamed branches
Supplied Structures: Medial portion of the caudate lobe of the liver.
Origin
The left artery of the caudate lobe typically arises from the left hepatic artery (Furuta et al., 2009; Miyayama et al., 1990).
Course
The left artery of the caudate lobe courses posteriorly.
Branches
The left artery of the caudate lobe gives off multiple small unnamed branches.
Supplied Structures
The left artery of the caudate lobe mainly supplies the medial portion of the caudate lobe (Furuta et al., 2009).
Typically, the caudate lobe receives two arteries, one each from the right and left hepatic arteries (53% of cases). In 35% of individuals, this territory is supplied by the right hepatic artery branch only, or in 12% by the left hepatic artery branch (Furuta et al., 2009).
References
Furuta, T., Maeda, E., Akai, H., Hanaoka, S., Yoshioka, N., Akahane, M., Watadani, T. and Ohtomo, K. (2009) 'Hepatic Segments and Vasculature: Projecting CT Anatomy onto Angiograms', Radiographics, 29(7), pp. e37.
Miyayama, S., Matsui, O., Kameyama, T., Hirose, J., Konishi, H., Chyotoh, S., Kadoya, M. and Takashima, T. (1990) '[Angiographic anatomy of arterial branches to the caudate lobe of the liver with special reference to its effect on transarterial embolization of hepatocellular carcinoma]', Rinsho Hoshasen, 35(3), pp. 353-9.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products


