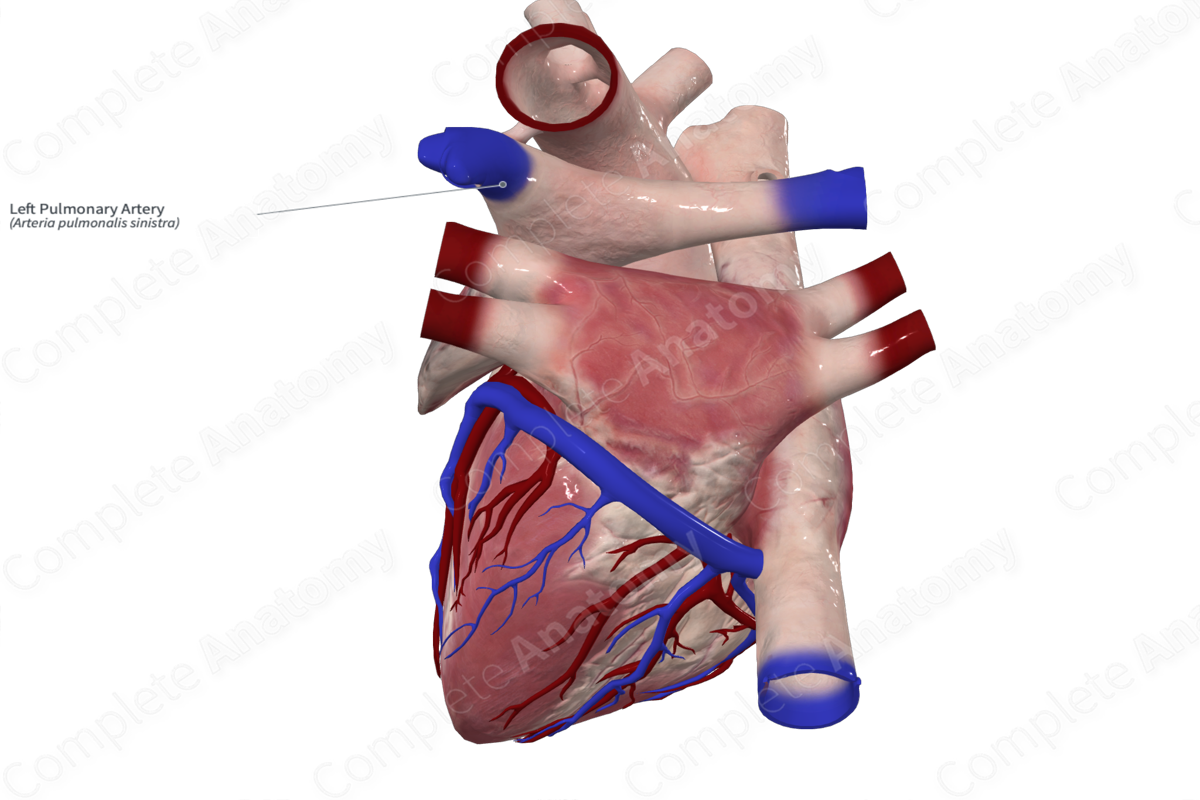
Quick Facts
Origin: Pulmonary trunk.
Course: Extends laterally to the left, towards the hilum of the left lung.
Branches: Superior and inferior lobar arteries.
Supplied Structures: The bronchopulmonary segments of the left lung.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
As the pulmonary trunk extends posteriorly to the left of the ascending aorta, it bifurcates into right and left pulmonary arteries in the concavity of the aortic arch. The left pulmonary artery is shorter than its right counterpart.
Course
The left pulmonary artery travels a short distance anterior to the descending thoracic aorta towards the hilum of the lung. The ligamentum arteriosum, a remnant of the ductus arteriosus during fetal development, attaches the proximal end of the left pulmonary artery to the inferior surface of the overlying aortic arch.
The left pulmonary artery accompanies the left main bronchus to reach the hilum of the left lung. Here, it bifurcates into superior and inferior lobar arteries. The distal branches of the left pulmonary artery accompany the segmental bronchi, usually in a posterolateral position.
Branches
The branches of the left pulmonary artery can be extremely variable (Standring, 2016). The superior lobar artery gives rise to a large anterior segmental artery, a lingular artery, and a variable number of segmental arteries supplying the apicoposterior bronchopulmonary segments. Sometimes a common trunk, the apicoposterior segmental artery, gives rise to apical and posterior segmental arteries (Lee et al., 1991).
The inferior lobar artery gives off a superior segmental artery and a variable number of arteries supplying the basal bronchopulmonary segments of the inferior lobe of the left lung (Lee et al., 1991).
Supplied Structures
The left pulmonary artery provides the alveolar structures in each bronchopulmonary segment of the left lung with deoxygenated blood. It is the bronchial arteries from the systemic circulation that provide oxygenated blood to the tissue of the lungs.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Pulmonary embolism
References
Lee, K. S., Bae, W. K., Lee, B. H., Kim, I. Y. and Choi, E. W. (1991) “Bronchovascular anatomy of the upper lobes: evaluation with thin-section CT”, Radiology, 181(3), pp. 765-72.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





