Quick Facts
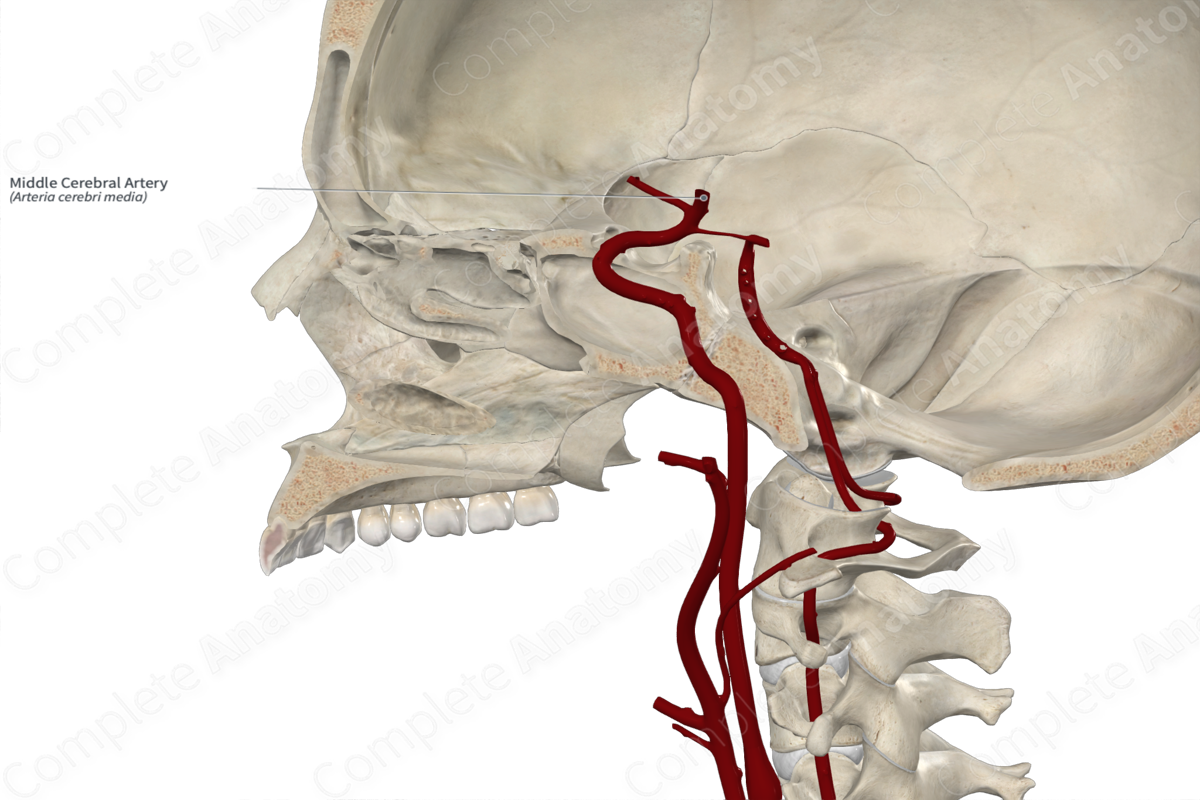
The middle cerebral artery (aka Sylvian artery) is the larger of the two terminal branches of the internal carotid artery, the other being the anterior cerebral artery. It is the direct continuation of the internal carotid artery.
From its origin, the middle cerebral artery travels laterally to the lateral sulcus (aka Sylvian fissure). This part of the middle cerebral artery is known as the sphenoid part, and it gives off the polar temporal artery, as well as proximal and distal lateral striate branches.
Upon reaching the lateral sulcus the middle cerebral artery ends by dividing into its superior and inferior terminal branches. Both of these branches travel posterosuperiorly along the lateral sulcus, giving off branches along their way.
Overall, the middle cerebral artery and its branches provide an arterial supply to the temporal, frontal and parietal lobes, especially on their lateral surfaces.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Middle Cerebral Artery

The dense middle cerebral artery (MCA) sign refers to the hyperattenuating appearance of the M1 segment of the MCA secondary to thrombosis of the vessel.