Quick Facts
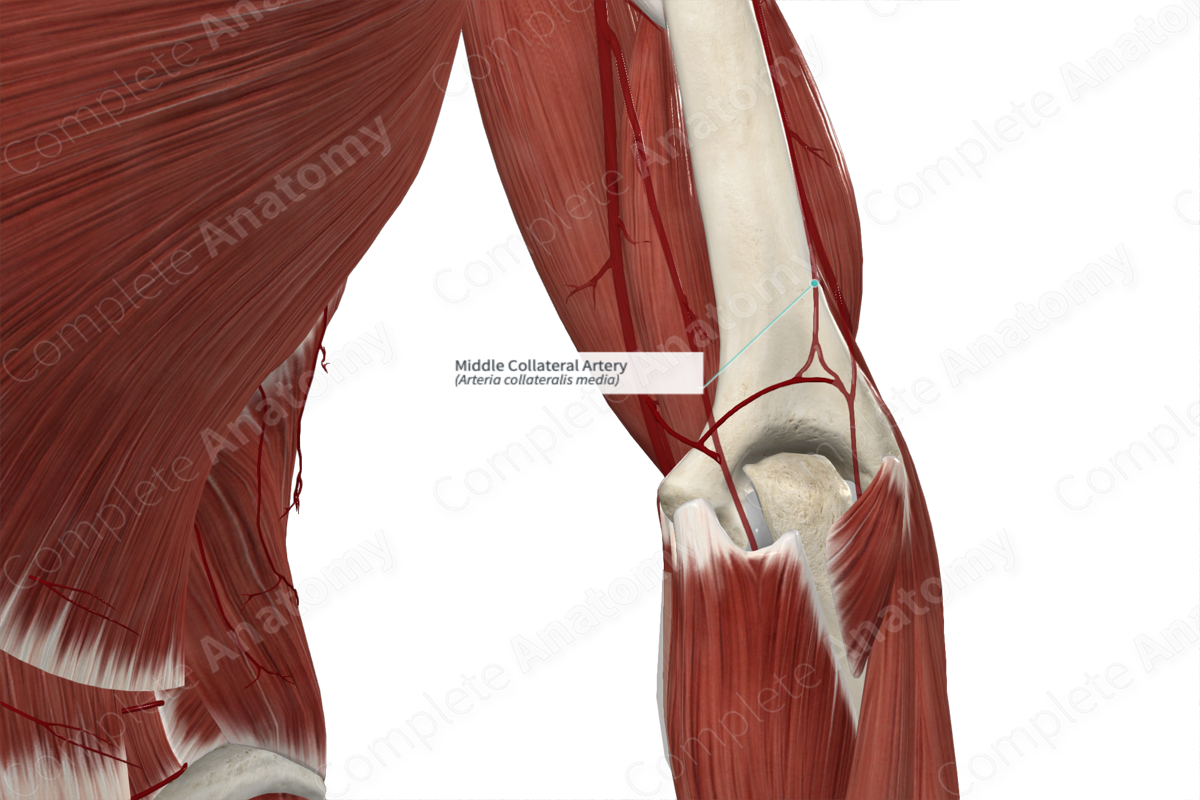
Origin: Deep brachial artery.
Course: Distally, posterior to the shaft of the humerus.
Branches: No named branches.
Supplied Structures: Anconeus, elbow joint, and cutaneous supply to the lateral aspect of the arm.
Origin
The terminal branches of the deep brachial artery are the larger middle collateral artery and the smaller radial collateral artery.
Course
The middle collateral artery courses distally, superficial to the lateral head of the triceps brachii muscle. It is initially accompanied by the radial nerve. It lies deep to the brachialis muscle, then the brachioradialis muscle. Posterior to the lateral epicondyle of the humerus, it anastomoses with the interosseous recurrent artery.
Branches
Distally, the middle collateral artery gives a muscular branch to the anconeus and forms an anastomosis with the interosseous recurrent artery.
Supplied Structures
The middle collateral artery supplies the anconeus and contributes to the anastomotic network that supplies the elbow joint. It gives cutaneous supply to the lateral aspect of the arm.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products




