Quick Facts
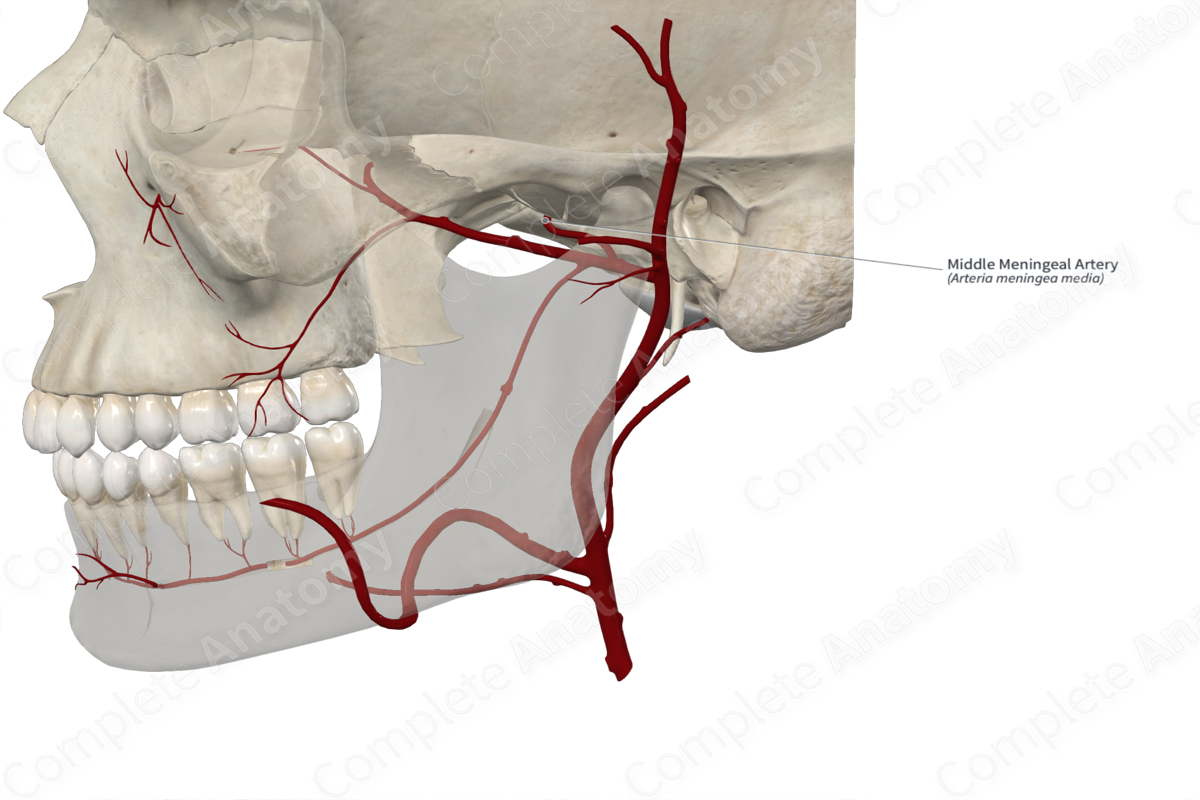
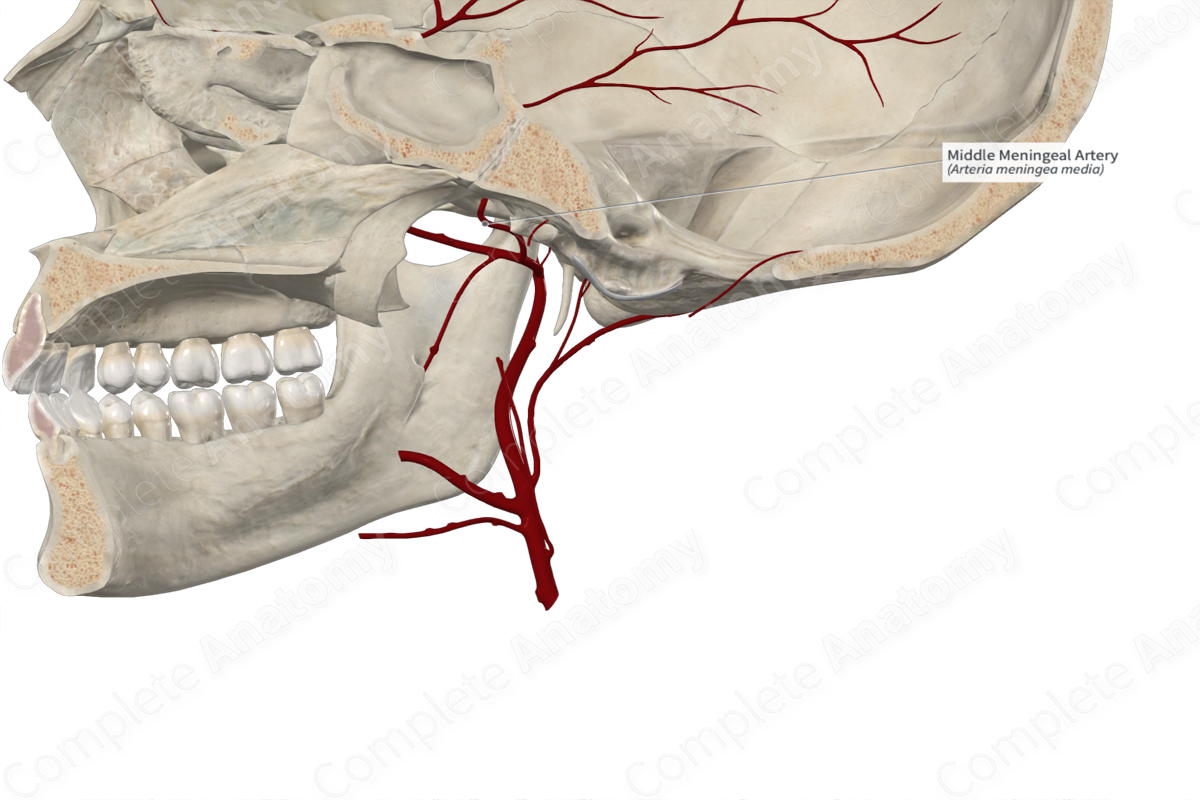
Origin: Maxillary artery.
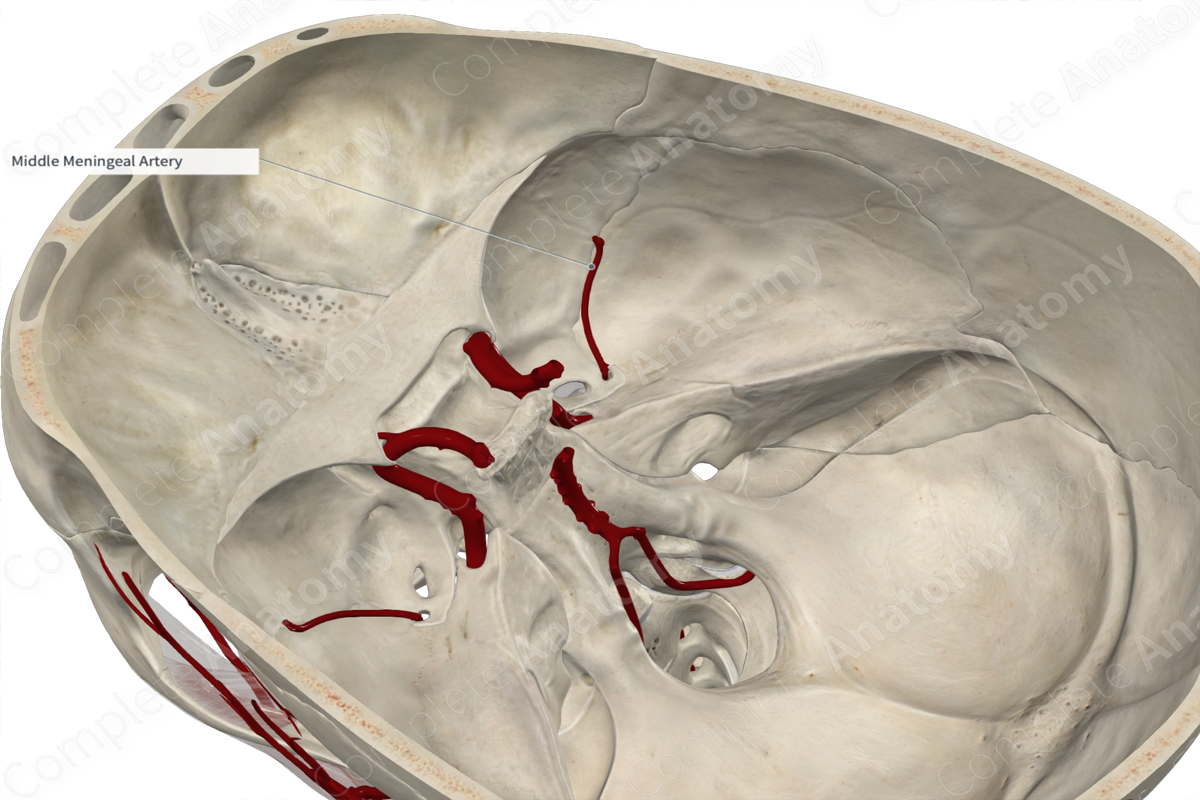
Course: Ascends in infratemporal fossa and enters the middle cranial fossa via the foramen spinosum.
Branches: Superior tympanic artery; Accessory meningeal, petrosal, frontal, and parietal branches; Lacrimal anastomotic branch.
Supplied Structures: Dura mater and cranium.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The middle meningeal artery arises from the first part of the maxillary artery as it passes through the infratemporal fossa. Sometimes, it may arise from a common trunk with the inferior alveolar artery.
Course
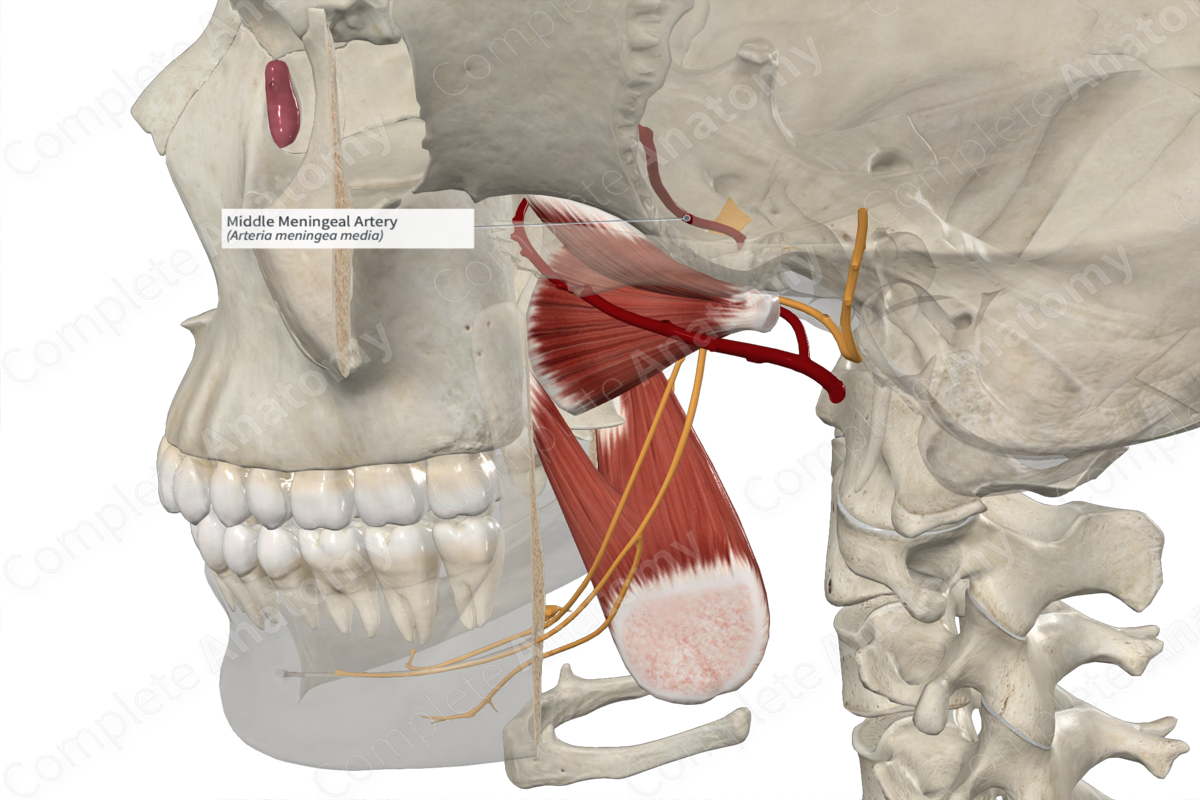
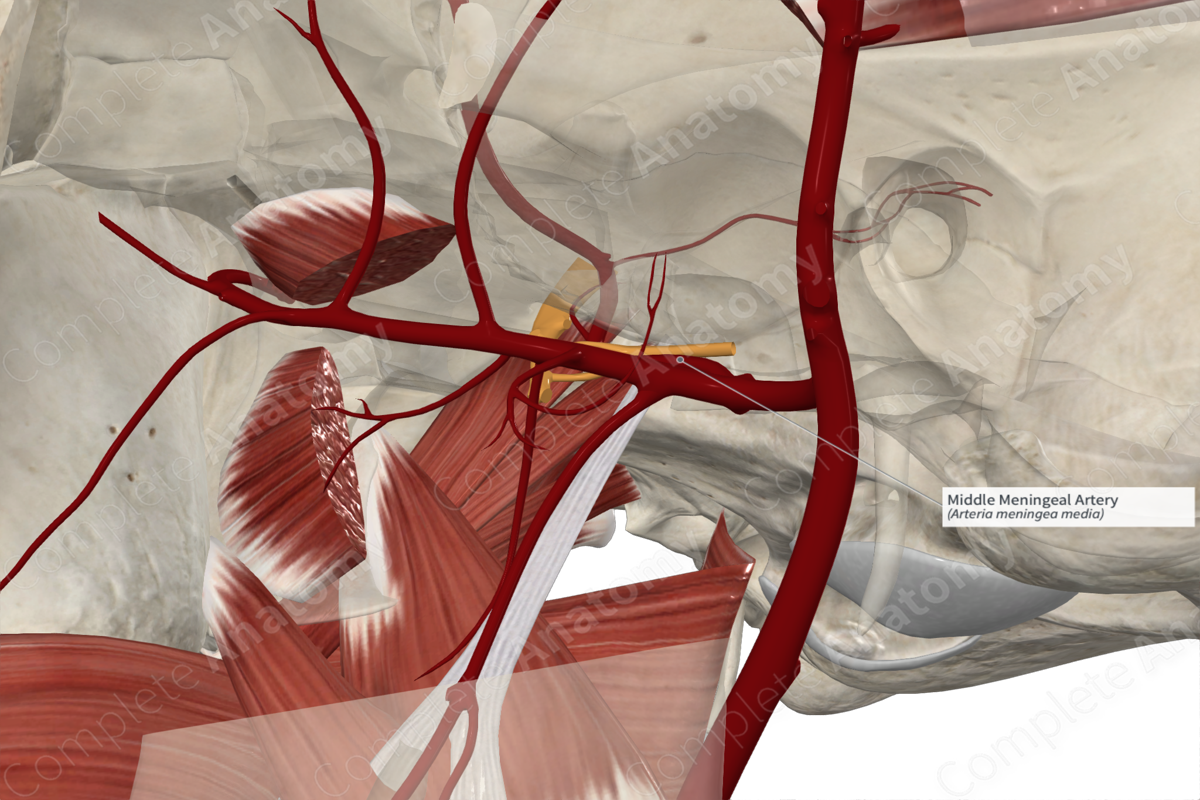
The middle meningeal artery ascends within the infratemporal fossa between the sphenomandibular ligament and the lateral pterygoid muscle. It passes between the roots of the auriculotemporal nerve emerging from the mandibular nerve. The middle meningeal artery passes lateral to the tensor veli palatini muscle and enters the foramen spinosum to reach the middle cranial fossa. It traverses anteriorly within a groove (the groove for the middle meningeal artery), then terminates by dividing into frontal and parietal branches. The branches of the middle meningeal artery upwards, passing over the pterion and towards the vertex of the skull.
Branches
The middle meningeal artery gives rise to several branches including the accessory meningeal, petrosal, frontal, and parietal branches. Additionally, it gives rise to the superior tympanic artery and forms an anastomosis with a branch of the lacrimal artery.
Supplied Structures
The middle meningeal artery supplies the dura mater of the brain and the cranial bones.
List of Clinical Correlates
br>
Extradural hemorrhage
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products