Quick Facts
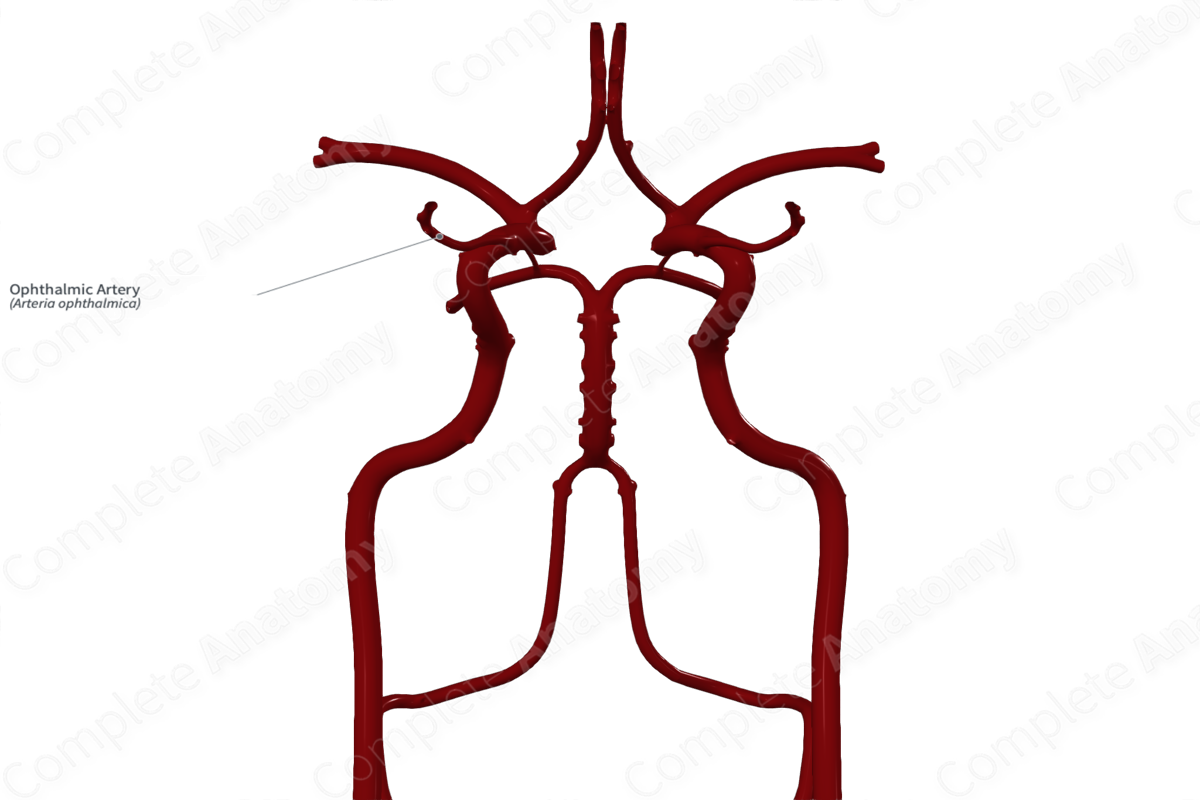
Origin: Internal carotid artery.
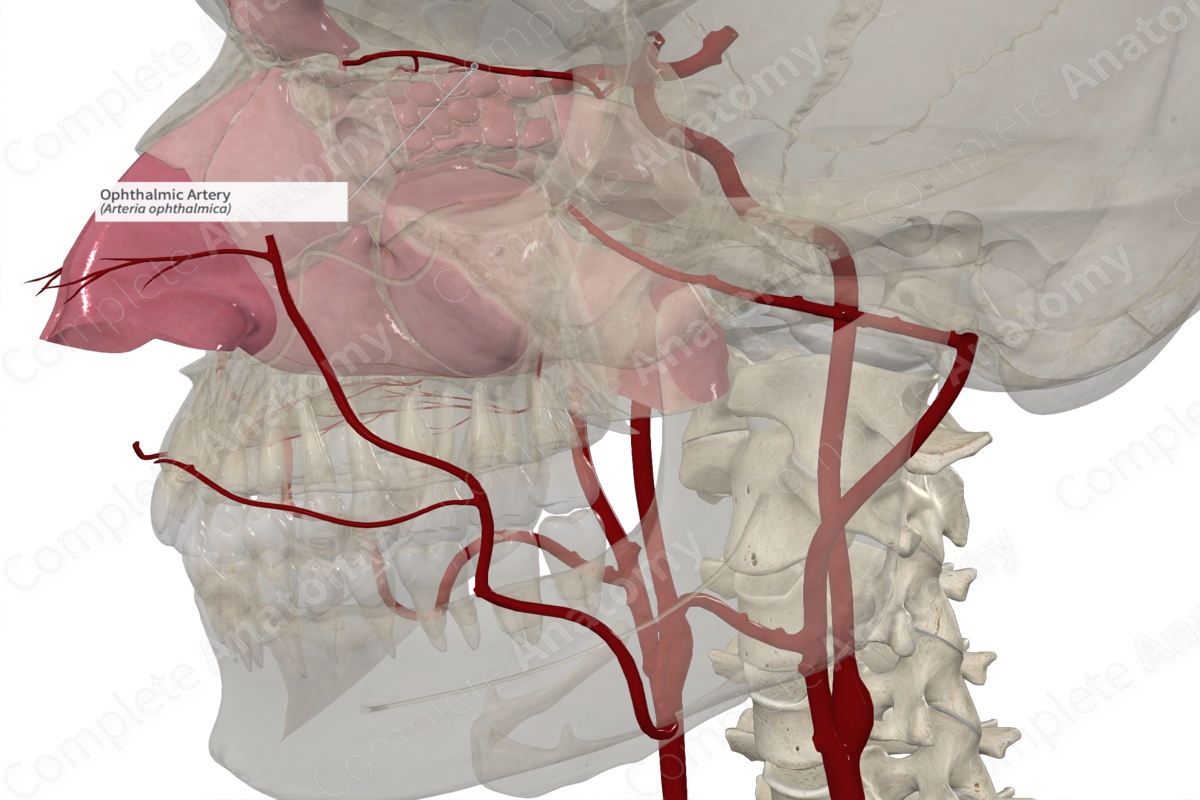
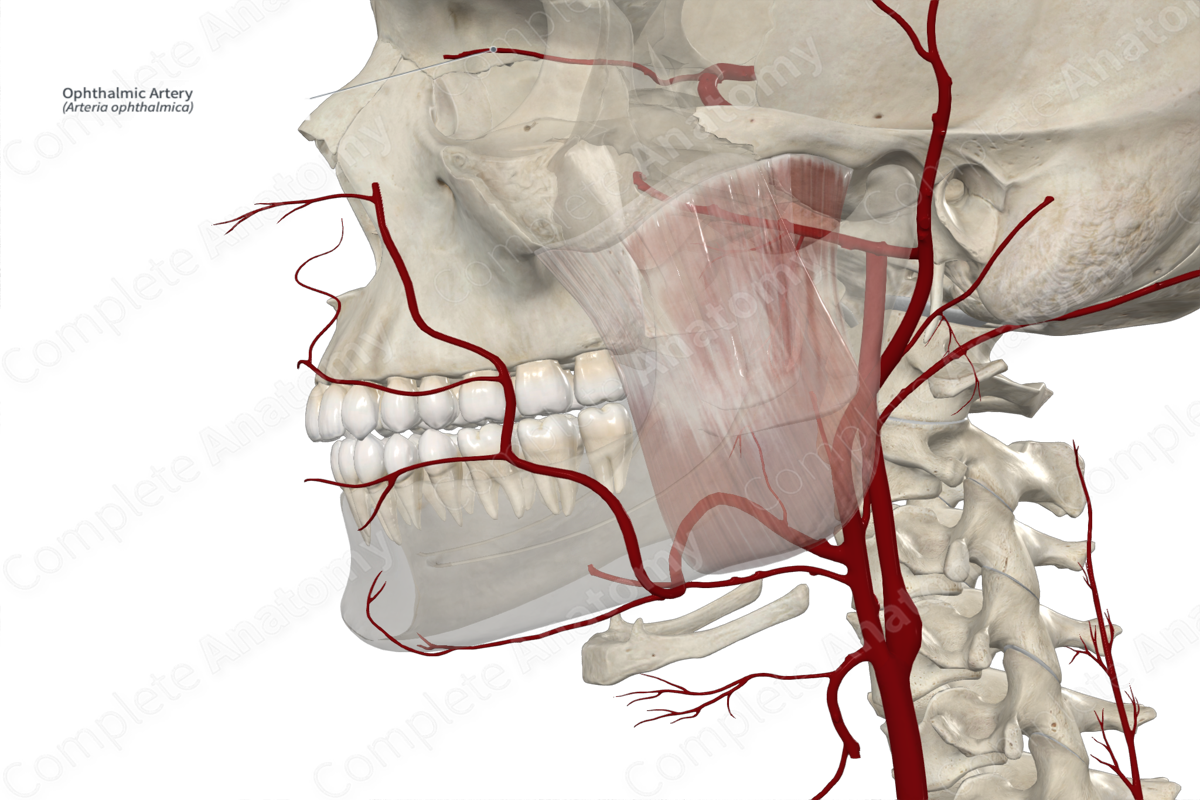
Course: Enters the orbit and travels along the medial wall between the superior oblique and medial rectus muscles.
Branches: Lacrimal, supraorbital, ciliary, muscular, posterior ethmoidal, anterior ethmoidal, palpebral, supratrochlear, and external nasal arteries, central artery of retina, recurrent meningeal branch.
Supplied Structures: Eyeball, orbit, facial structures.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The ophthalmic artery arises from the cerebral part of the internal carotid artery, just as it exits the cavernous sinus.
Course
The ophthalmic artery enters the orbit, inferolateral to the optic nerve, via the optic canal and lies within the common tendinous ring. It continuous anteriorly briefly, before passing medially and crosses over the optic nerve. The ophthalmic artery continues along the medial wall of the orbit, passing between the superior oblique and medial rectus muscles.
Branches
The branches of the ophthalmic artery include the central retinal artery, lacrimal artery, muscular branches, long and short ciliary arteries, supraorbital arteries, posterior and anterior ethmoidal arteries, medial palpebral arteries, and the terminal supratrochlear and external (dorsal) nasal arteries.
Supplied Structures
The ophthalmic artery supplies many structures including the eyeball, structures of the orbit, and adjacent facial structures.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Ophthalmic Artery

The PrVOA is a branch of the cranial division of the internal carotid artery (ICA) (future anterior and middle cerebral arteries), whereas the PrDOA originates from the intracranial portion of the ICA, near its termination, distally to the final point of emergence of the adult OA.