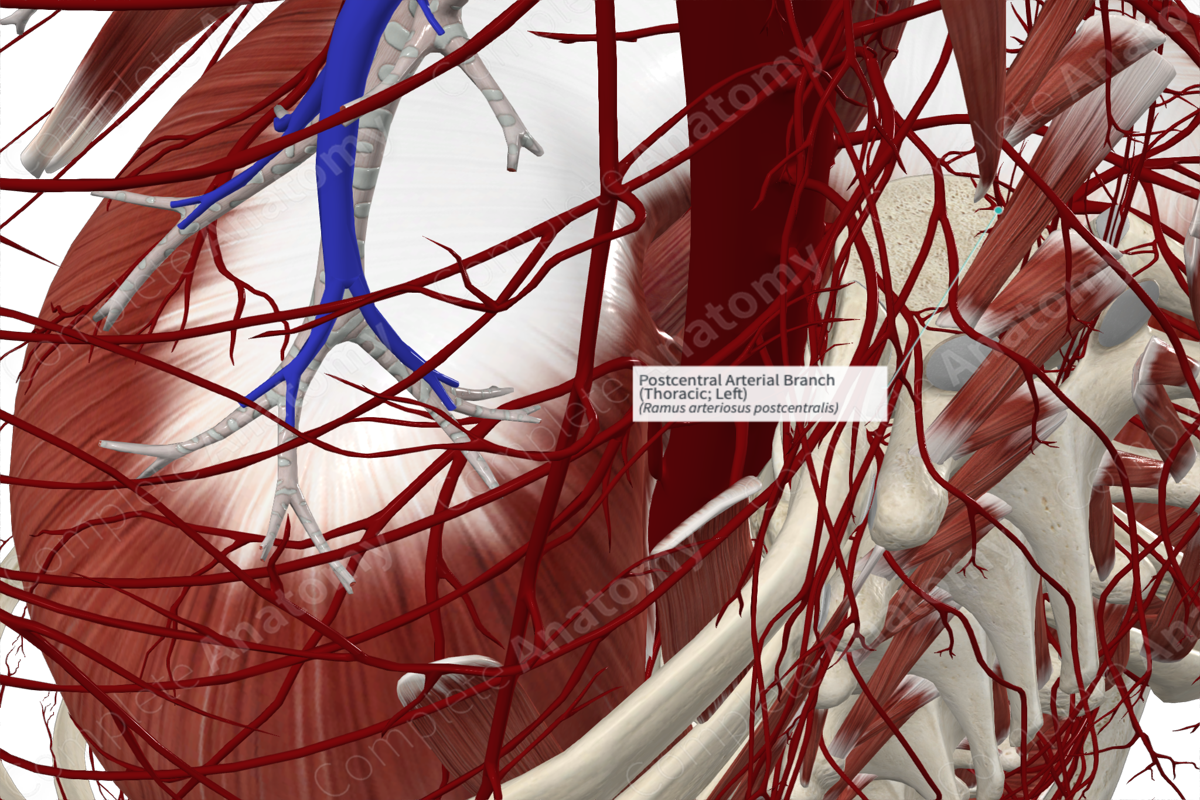
Postcentral Arterial Branch (Thoracic; Left)
Ramus arteriosus postcentralis
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Spinal branches.
Course: Pass medially within the vertebral canal.
Branches: Ascending and descending branches.
Supplied Structures: Vertebral body, periphery of intervertebral discs, and adjacent dura and epidural tissue.
Origin
The postcentral arterial branch is one of three branches of the spinal arteries, the others are the radicular and prelaminar arteries (Standring, 2020).
Course
The postcentral arterial branch passes over the dorsolateral surface of the intervertebral disc, beneath the posterior longitudinal ligament within the vertebral canal.
Branches
The postcentral arterial branch divides into ascending and descending branches which extend to two adjacent vertebral bodies. It forms an anastomosis with its fellow arteries from above and below.
Supplied Structures
The extensive anastomotic network of the postcentral branches supplies the vertebral bodies, the periphery of the intervertebral discs, as well as the adjacent dura and epidural tissue (Standring, 2020). The small radicular arteries supply the anterior and posterior roots of the spinal cord (including the spinal, or dorsal root, ganglion).
References
Standring, S. (2020) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 42nd edn.: Elsevier Health Sciences.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Artery

Arteries are vessels transporting blood between heart, tissues, and other organs in order to supply them with nutrition and oxygen.
