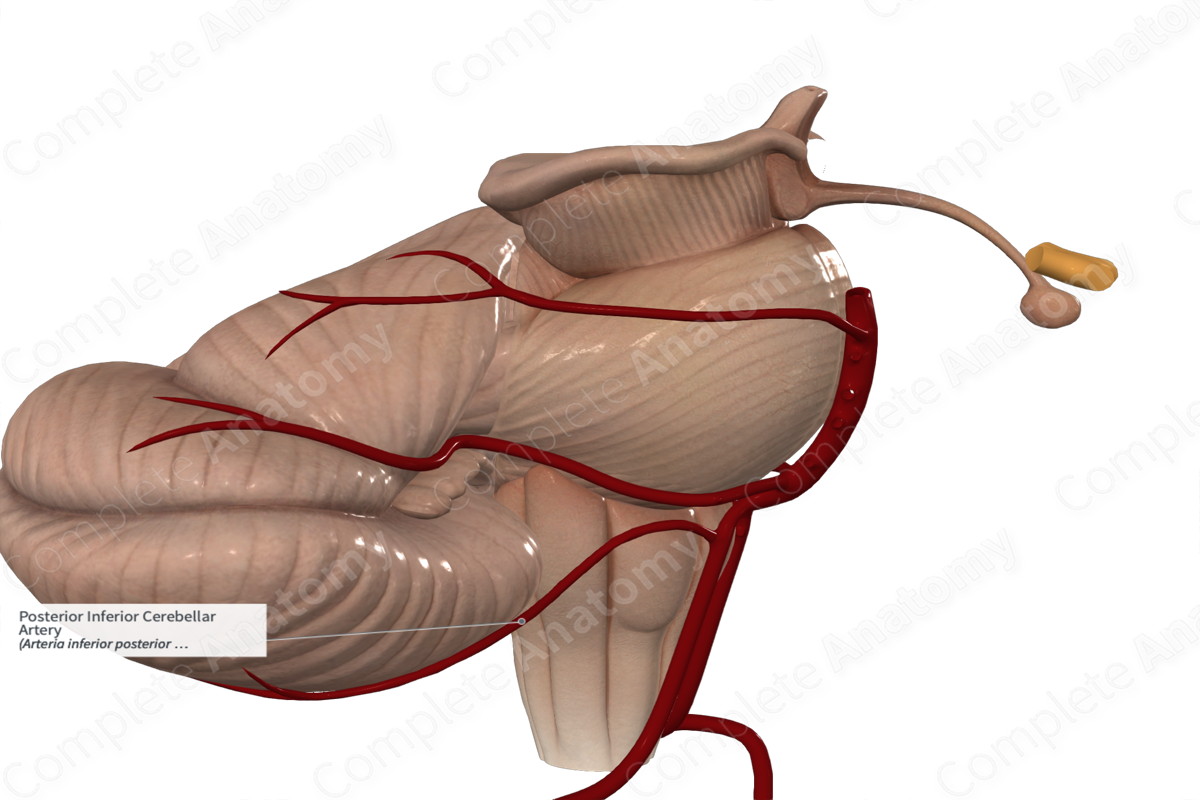
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery
Arteria inferior posterior cerebelli
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Vertebral artery.
Course: Travels superiorly to pons then follows the inferolateral border of fourth ventricle and turns laterally to reach the cerebellum.
Branches: Posterior spinal artery, cerebellar cortical, inferior vermian, and cerebellar tonsillar branches, choroidal branches to fourth ventricle.
Supplied Structures: Medulla oblongata, cerebellum, choroid plexus of fourth ventricle.
Origin
The posterior inferior cerebellar artery is the largest branch of the intracranial part of the vertebral artery, just inferior to the basilar artery. It arises within the cisterna magna.
Course
From its origin, located at the inferior part of the olive, the posterior inferior cerebellar artery takes a tortuous path on the lateral medullary surface. It travels superiorly to reach the lower part of the pons. It travels inferiorly along the inferolateral border of the fourth ventricle and takes a lateral turn, over the cerebellar peduncle to reach the cerebellar vallecula.
Branches
Along its path, the posterior inferior cerebellar artery gives off the posterior spinal artery, cerebellar tonsillar branches, and a choroidal branch to the fourth ventricle. It also forms an anastomosis with the anterior inferior and anterior superior cerebellar arteries.
Supplied Structures
The posterior inferior cerebellar artery supplies the medulla oblongata, dorsal to the olivary nucleus and lateral to the hypoglossal nucleus. The artery also supplies the inferior surface of the cerebellum and sends a branch to supply the choroid plexus of the fourth ventricle.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Wallenberg syndrome (lateral medullary syndrome)
- Occlusion: loss of pain and thermal sense on ipsilateral face
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Posterior Inferior Cerebellar Artery

The posterior inferior cerebellar artery arises from the vertebral artery and supplies the posterior and caudal cerebellum.




