Quick Facts
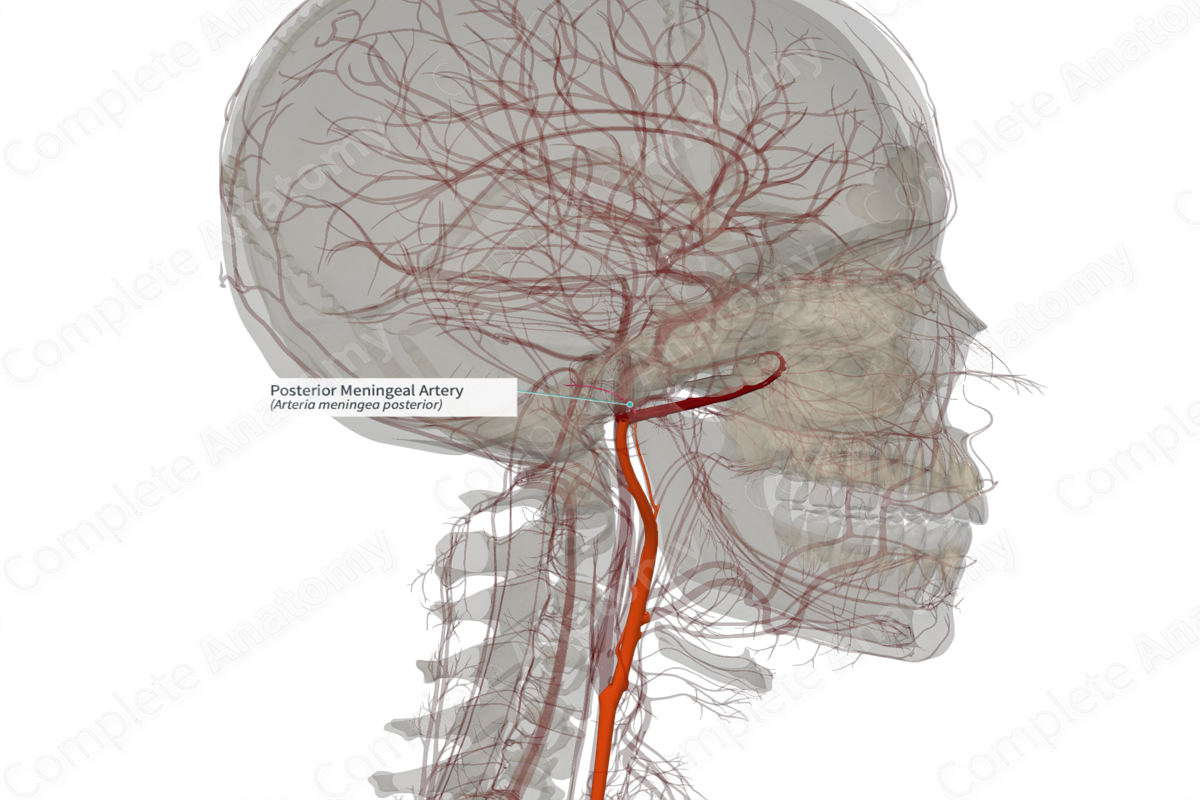
Origin: Neuromeningeal trunk.
Course: Traverses the jugular foramen of skull.
Branches: None.
Supplied Structures: Bones and dura mater of posterior cranial fossa.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The posterior meningeal artery arises from the neuromeningeal trunk, and is considered the terminal branch of the ascending pharyngeal artery (Standring, 2016).
Course
The posterior meningeal artery traverses the jugular foramen to enter the posterior cranial fossa and can reach the cerebellar fossa.
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The posterior meningeal artery supplies the dura mater and bone of the posterior cranial fossa (Hacein-Bey et al, 2002).
References
Hacein-Bey, L., Daniels, D. L., Ulmer, J. L., Mark, L. P., Smith, M. M., Strottmann, J. M., Brown, D., Meyer, G. A. & Wackym, P. A. (2002) The Ascending Pharyngeal Artery: Branches, Anastomoses, and Clinical Significance. American Journal of Neuroradiology, 23(7), 1246. Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products


