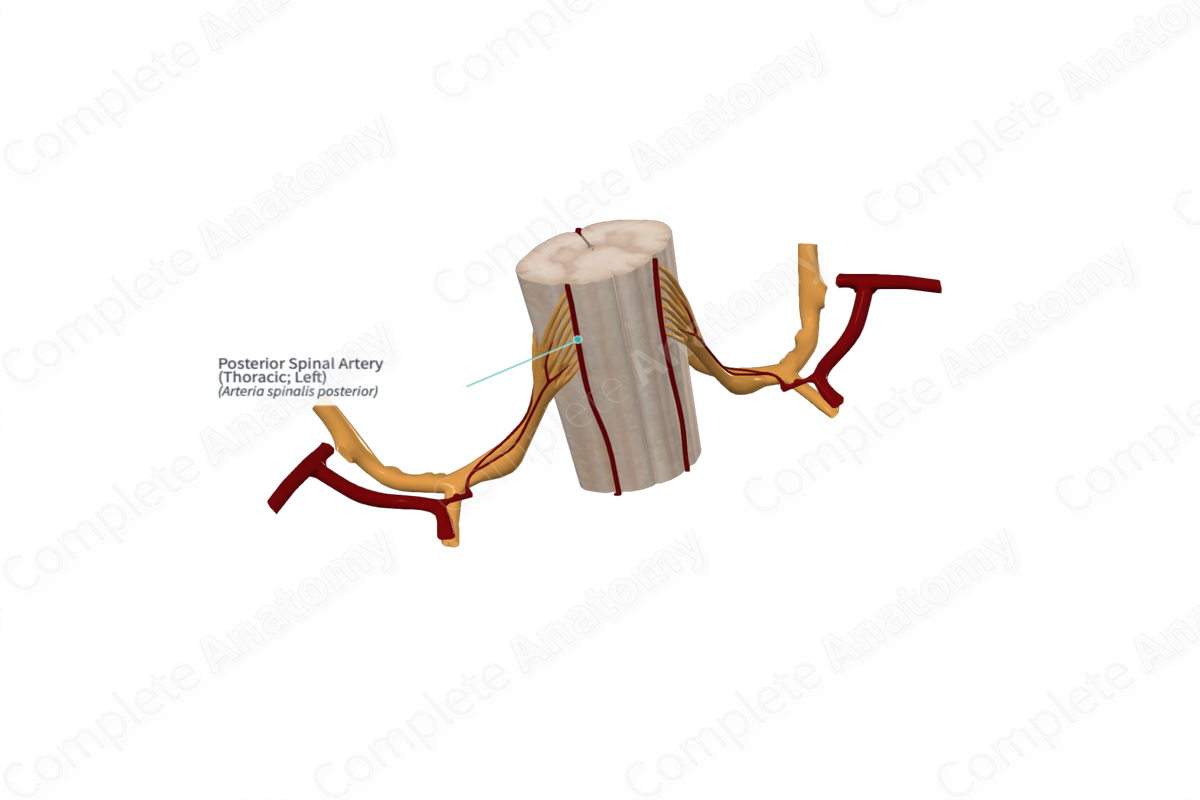
Quick Facts
Origin: Vertebral artery.
Course: Descends in the posterolateral sulci of the spinal cord.
Branches: Pial plexus.
Supplied Structures: Posterior spinal cord.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The posterior spinal arteries (two in number) arise either directly from the vertebral artery or from the posterior inferior cerebellar artery (a branch of the vertebral artery).
Course
The posterior spinal arteries descend in posterolateral sulci of the spinal cord.
Branches
The posterior spinal arteries contribute to the pial plexus. Additionally, they receive contributions from 10 to 23 posterior segmental medullary (radiculomedullary) arteries (Jones et al., 2013).
Supplied Structures
The posterior spinal arteries supply the remaining dorsal gray and white columns and peripheral parts of the lateral and ventral white columns (Standring, 2020).
List of Clinical Correlates
- Spinal cord ischemia
References
Jones, H. R., Burns, T., Aminoff, M. J. and Pomeroy, S. (2013) The Netter Collection of Medical Illustrations: Nervous System, Volume 7, Part 1 - Brain e-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Standring, S. (2020) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 42nd edn.: Elsevier Health Sciences.



