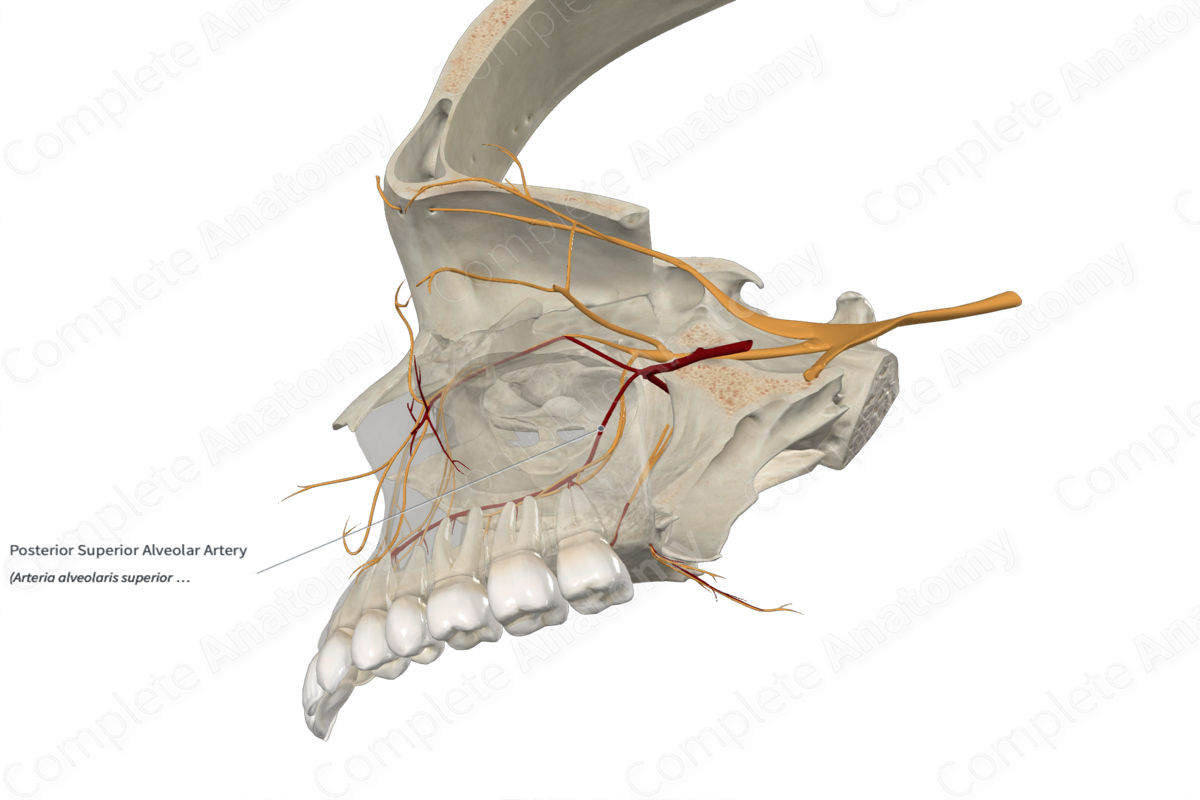
Posterior Superior Alveolar Artery
Arteria alveolaris superior posterior
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Maxillary artery.
Course: Descends slightly before entering the posterior superior alveolar foramina on the maxillary tuberosity.
Branches: Dental and peridental branches.
Supplied Structures: Molars and premolars of maxillary dental arcade, maxillary sinus.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The posterior superior alveolar artery arises from the maxillary artery as it passes through the pterygopalatine fossa (third part of the maxillary artery).
Course
The posterior superior alveolar artery descends slightly before entering the posterior superior alveolar foramina on the maxillary tuberosity.
Branches
After passing through the posterior superior alveolar foramina, the posterior superior alveolar artery gives rise to dental and peridental branches, which penetrate the maxillary bone. Additionally, the posterior superior alveolar artery forms an anastomosis with the anterior superior alveolar artery (Fehrenbach & Herring, 2015).
Supplied Structures
The branches of the posterior superior alveolar artery supply the maxillary sinus and the molars and premolars of the upper jaw.
References
Fehrenbach, M. J. & Herring, S. W. (2015) Illustrated Anatomy of the Head and Neck—E-Book. Elsevier Health Sciences.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Artery

Arteries are vessels transporting blood between heart, tissues, and other organs in order to supply them with nutrition and oxygen.




