Quick Facts
Origin: Third posterior intercostal artery.
Course: Along the right tracheobronchial tree.
Branches: Esophageal branch.
Supplied Structures: Trachea, right bronchus, lung parenchyma, lymph nodes, visceral pleura.
Origin
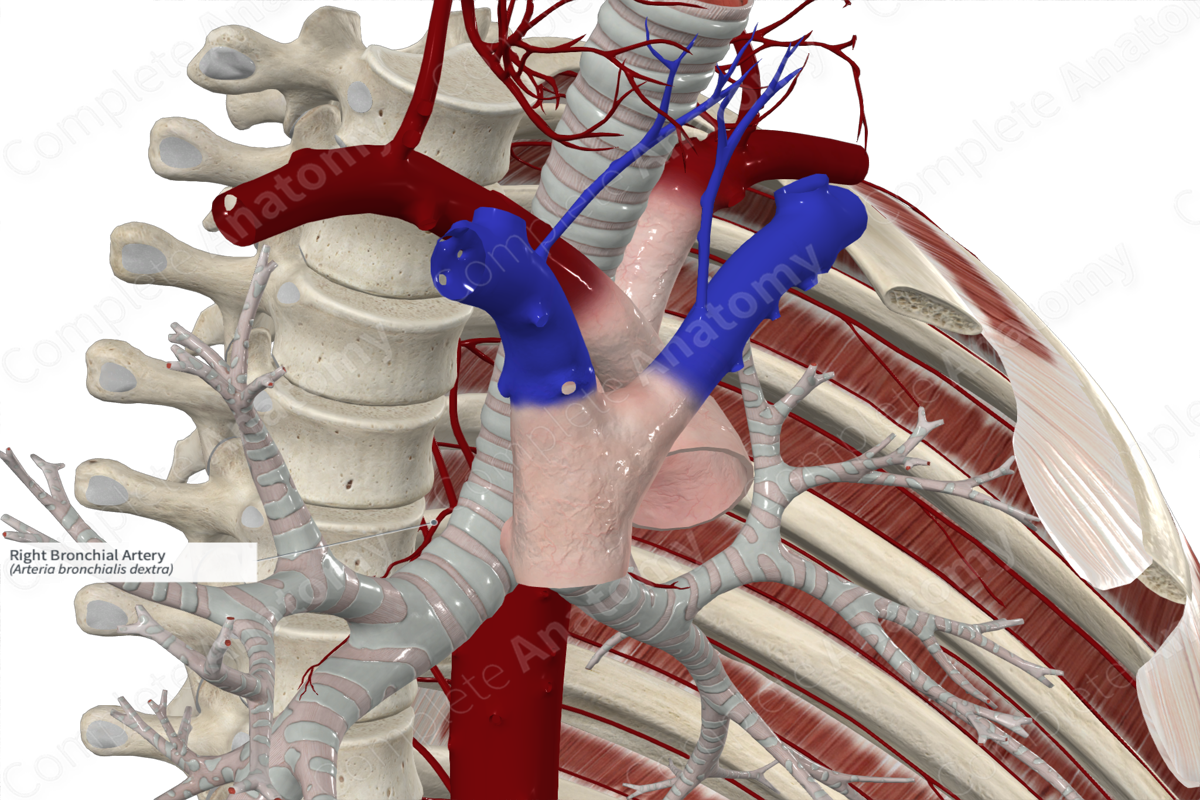
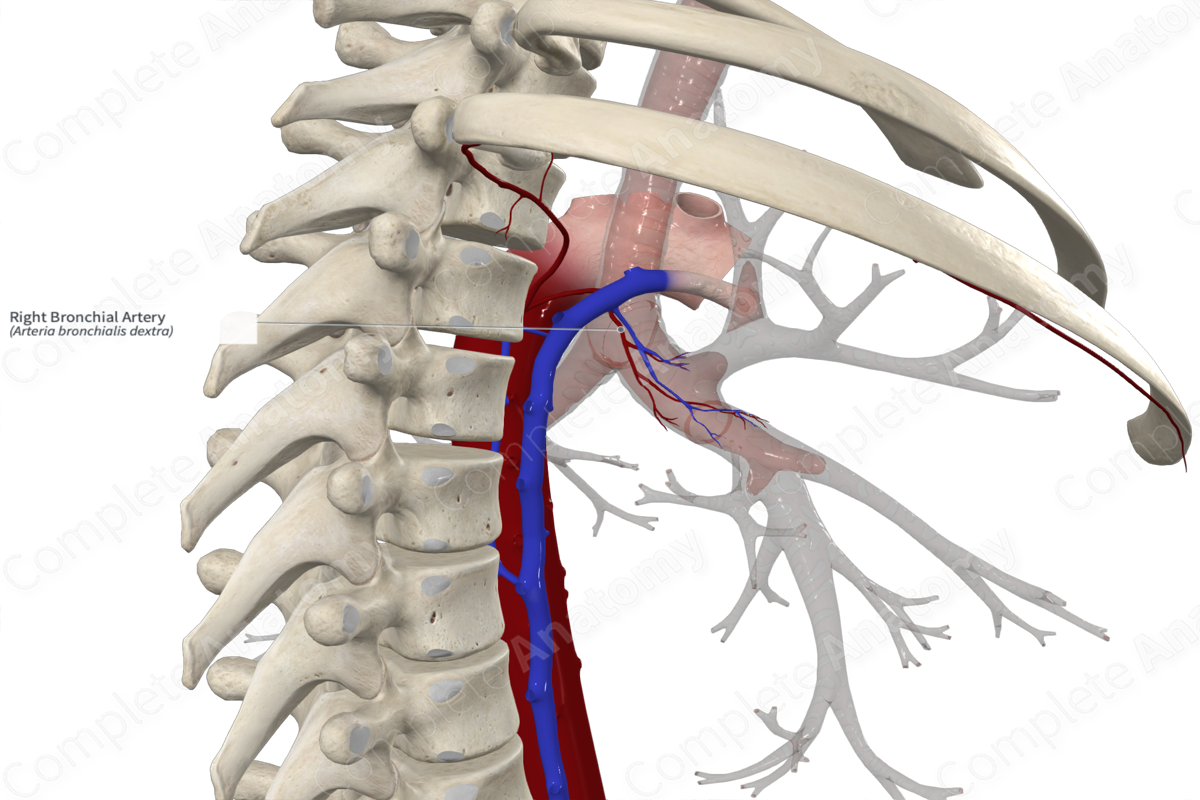
The right bronchial artery most commonly arises from the proximal end of the third right posterior intercostal artery (Standring, 2016).
Course
From its origin, the right bronchial artery travels to the posterior surface of the right main bronchus, travels along its surface, then follows the same branching pattern as the right bronchial tree. The right bronchial artery terminates around the level of the respiratory bronchioles.
It is important to note that bronchial vessels are a part of the systemic circulation, not the pulmonary circulation. They are not involved in the gas exchange that takes place at the alveoli between the blood and inspired air, although some distal bronchial vessels do anastomose with pulmonary vessels.
Branches
It may give off an esophageal branch.
Supplied Structures
The right bronchial artery provides an arterial supply to the structures of the right bronchial tree, as well as the distal trachea, adjoining lymph nodes, and visceral pleura.
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edition edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Right Bronchial Artery

The right bronchial artery arises from the descending aorta, one of the right intercostal branches, or subclavian or internal thoracic arteries.