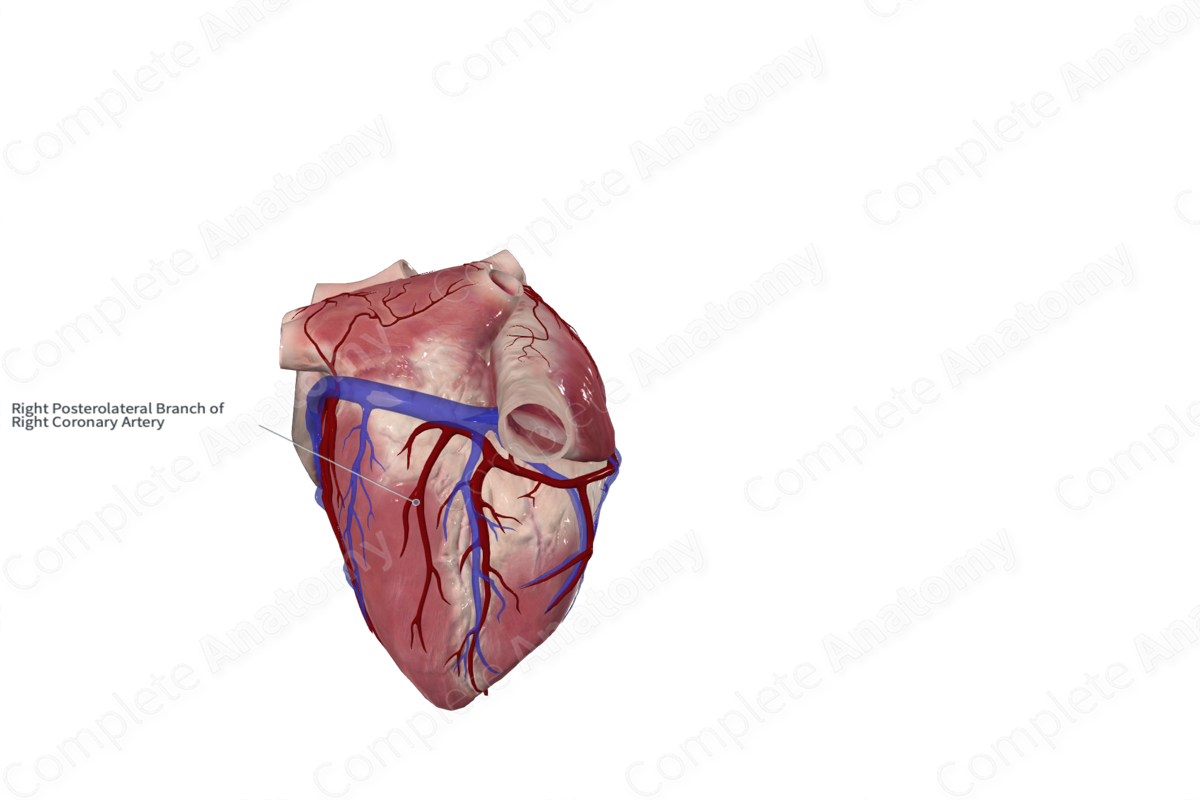
Right Inferolateral Branch of Right Coronary Artery
Ramus inferolateralis dexter arteriae coronariae dextrae
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Right coronary artery
Course: Inferiorly on diaphragmatic surface of left ventricle
Branches: Several small unnamed branches
Supplied Structures: Contributes to the supply of the left ventricle
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The right inferolateral branch arises from the right coronary artery after it has reached the left ventricle on the diaphragmatic surface of the left ventricle. This branch is a common variation of the branching pattern of the right coronary artery on the diaphragmatic surface. Other variations do not have this branch and the final branch of the right coronary artery is the posterior interventricular artery (Tubbs et al., 2016).
Course
The right inferolateral branch runs inferiorly towards the apex of the heart along the diaphragmatic surface of the left ventricle.
Branches
The right inferolateral branch gives off several small unnamed branches.
Supplied Structures
The right inferolateral branch contributes to the supply of the left ventricle.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Coronary artery disease
- Coronary atherosclerosis
- Coronary bypass graft
- Coronary angioplasty
- Coronary occlusion
- Coronary revascularization
- Coronary artery fistula
References
Tubbs, R. S., Shoja, M. M. and Loukas, M. (2016) Bergman's Comprehensive Encyclopedia of Human Anatomic Variation. Wiley.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





