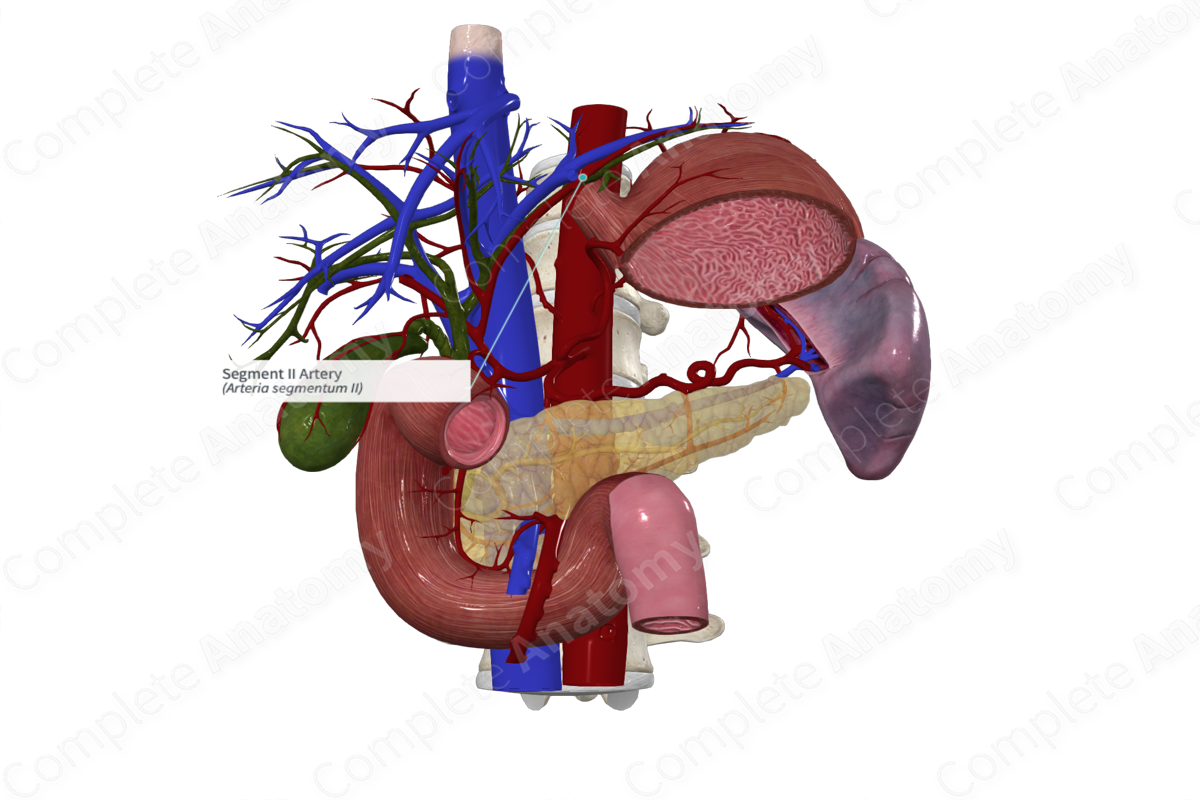
Quick Facts
Origin: Lateral segmental artery of liver.
Course: Passes straight to the left corner of the liver.
Branches: None.
Supplied Structures: Liver segment II.
Origin
The segment II artery arises from the lateral segmental artery of liver.
Course
The segment II artery passes straight to the left corner of the liver, superior to the segmental III artery.
The pattern of segmental artery origins and courses is extremely variable. Most of the research is based on contrast proper hepatic artery arteriography (Furuta et al., 2009; Favelier et al., 2015). The account given is the most common but was found in only 27% of cases in a cadaveric study of 100 livers (Garg et al., 2019).
Branches
There are no named branches.
Supplied Structures
The segment II artery supplies segment II of the liver.
References
Favelier, S., Germain, T., Genson, P. Y., Cercueil, J. P., Denys, A., Krausé, D. and Guiu, B. (2015) 'Anatomy of liver arteries for interventional radiology', Diagn Interv Imaging, 96(6), pp. 537-46.
Furuta, T., Maeda, E., Akai, H., Hanaoka, S., Yoshioka, N., Akahane, M., Watadani, T. and Ohtomo, K. (2009) 'Hepatic Segments and Vasculature: Projecting CT Anatomy onto Angiograms', Radiographics, 29(7), pp. e37.
Garg, S., Sahni, D., Kumar, H., Yadav, T. D., Aggarwal, A. and Gupta, T. (2019) 'The segmental branching of the hepatic arteries in the liver: a cadaveric study', Anat Sci Int, 94(2), pp. 216-223.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Artery

Arteries are vessels transporting blood between heart, tissues, and other organs in order to supply them with nutrition and oxygen.
