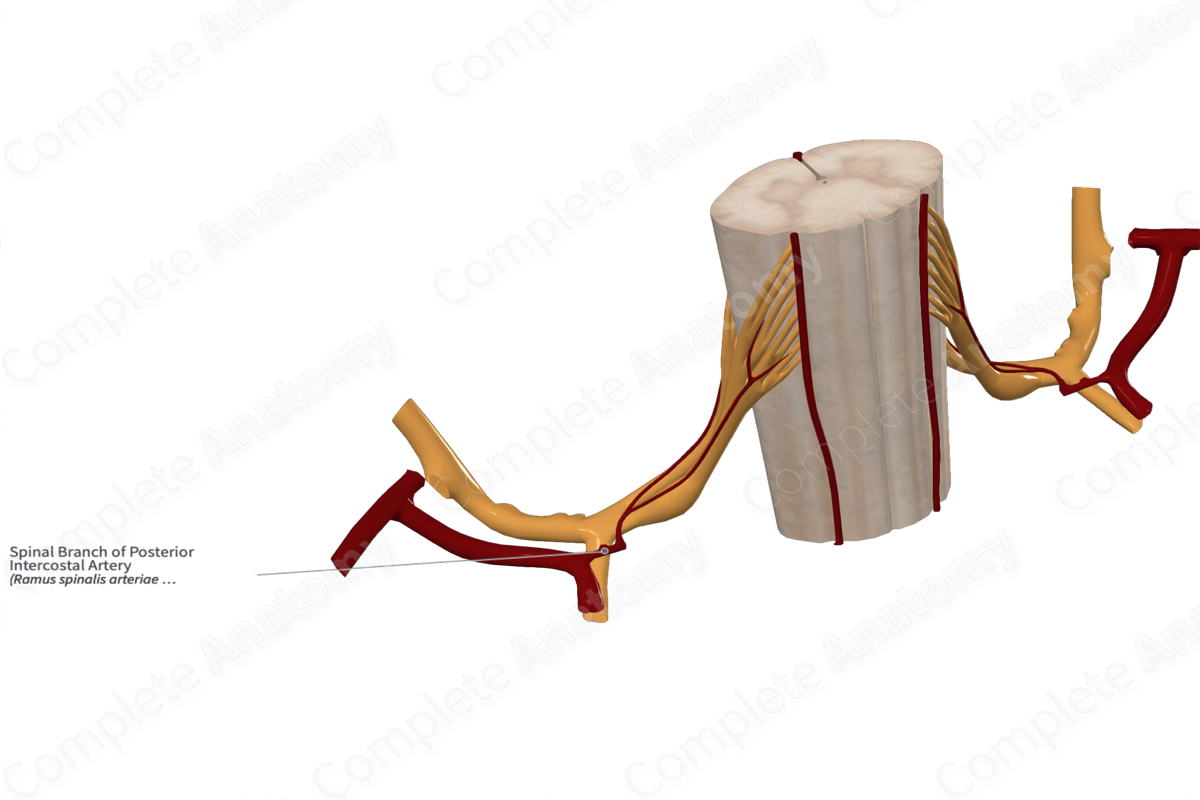
Spinal Branch of Posterior Intercostal Artery
Ramus spinalis arteriae intercostalis posterioris
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Dorsal branch of posterior intercostal arteries.
Course: Enters the intervertebral foramen.
Branches: Prelaminar, radicular, and postcentral branches.
Supplied Structures: Vertebrae, spinal cord, and spinal meninges.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
Each dorsal branch of the posterior intercostal arteries gives rise to a spinal branch before dividing into medial and lateral cutaneous branches.
Course
The spinal branch enters the intervertebral foramen, accompanying a thoracic spinal nerve.
Branches
The spinal branch of the posterior intercostal artery gives rise to prelaminar, radicular, and postcentral branches.
Supplied Structures
The spinal branches of the posterior intercostal arteries supply the thoracic vertebrae, the periphery of the intervertebral discs, as well as the adjacent dura and epidural tissue. The small radicular arteries supply the anterior and posterior roots of the spinal cord (including the spinal, or dorsal root, ganglion). When the radicular arteries are enlarged (segmental medullary arteries), they contribute to the anterior and posterior spinal arteries, which supply the spinal cord (Standring, 2020).
References
Standring, S. (2020) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. 42nd edn.: Elsevier Health Sciences.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Artery

Arteries are vessels transporting blood between heart, tissues, and other organs in order to supply them with nutrition and oxygen.


