Description
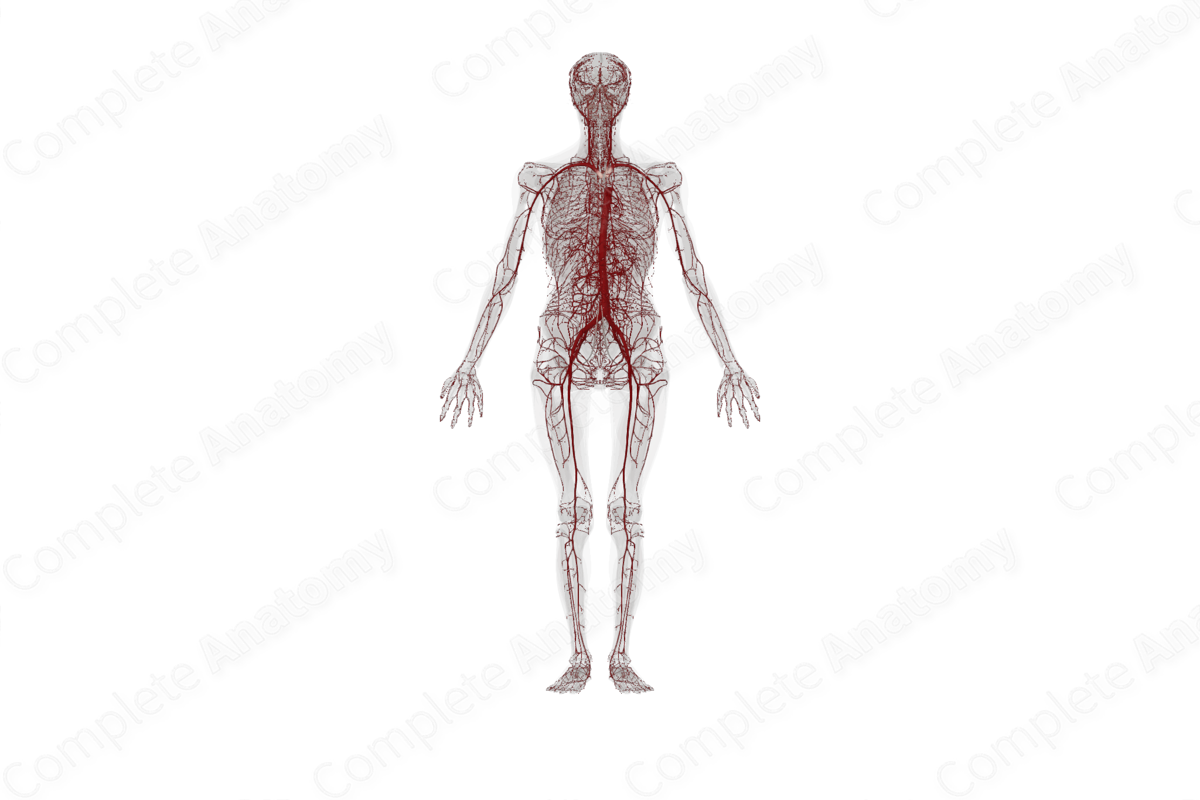
Systemic arteries are one of the three types of blood vessels found within the systemic circulation, the other two being systemic veins and systemic capillaries. They are described as the blood vessels that carry blood away from the heart to all the tissues of the body, except the lungs. Systemic arteries are all distal branches of the aorta, and carry oxygenated blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the capillaries of all tissues of the body, except the lungs.
Systemic capillaries are located within the tissues of the body; they are the sites where the exchange of nutrients and waste products occurs between the blood and these tissues.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Artery

Arteries are vessels transporting blood between heart, tissues, and other organs in order to supply them with nutrition and oxygen.




