Quick Facts
Origin: Subclavian artery.
Course: Ascends medial to the scalenus anterior muscle.
Branches: Suprascapular, transverse cervical, and inferior thyroid arteries.
Supplied Structures: Structures of the neck and scapular region.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
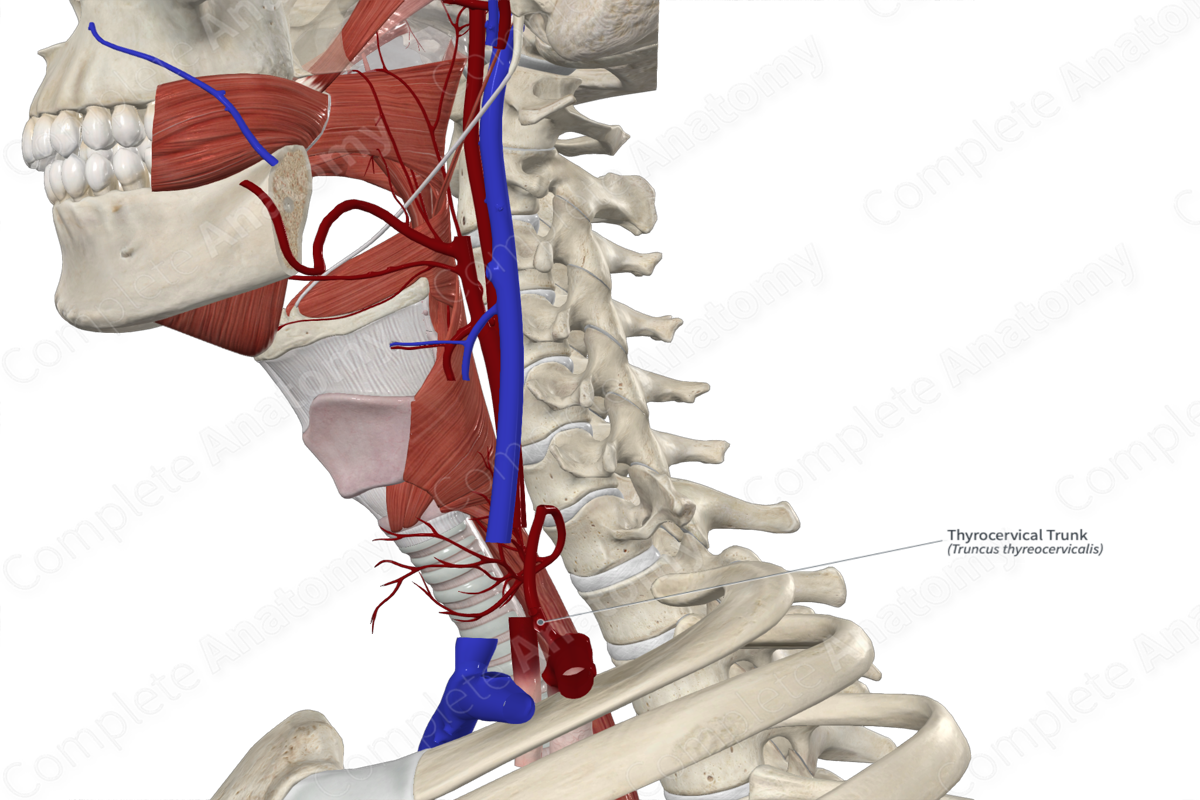
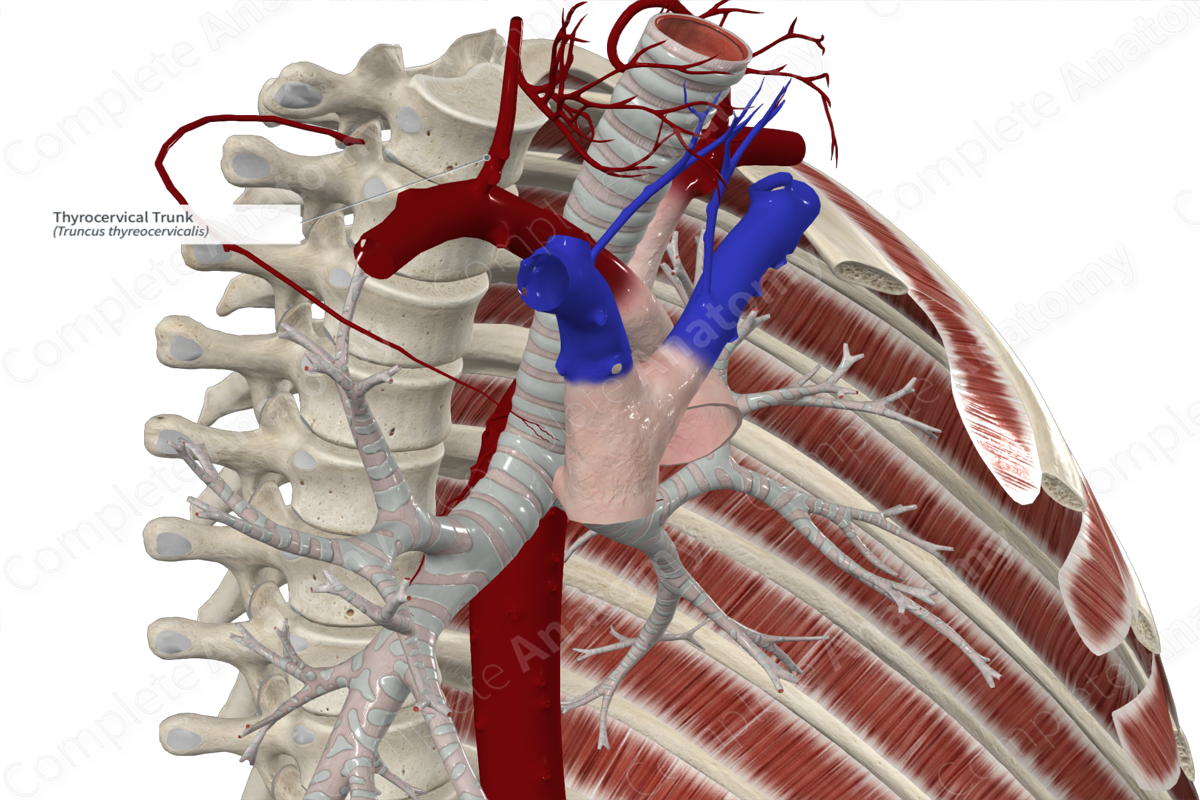
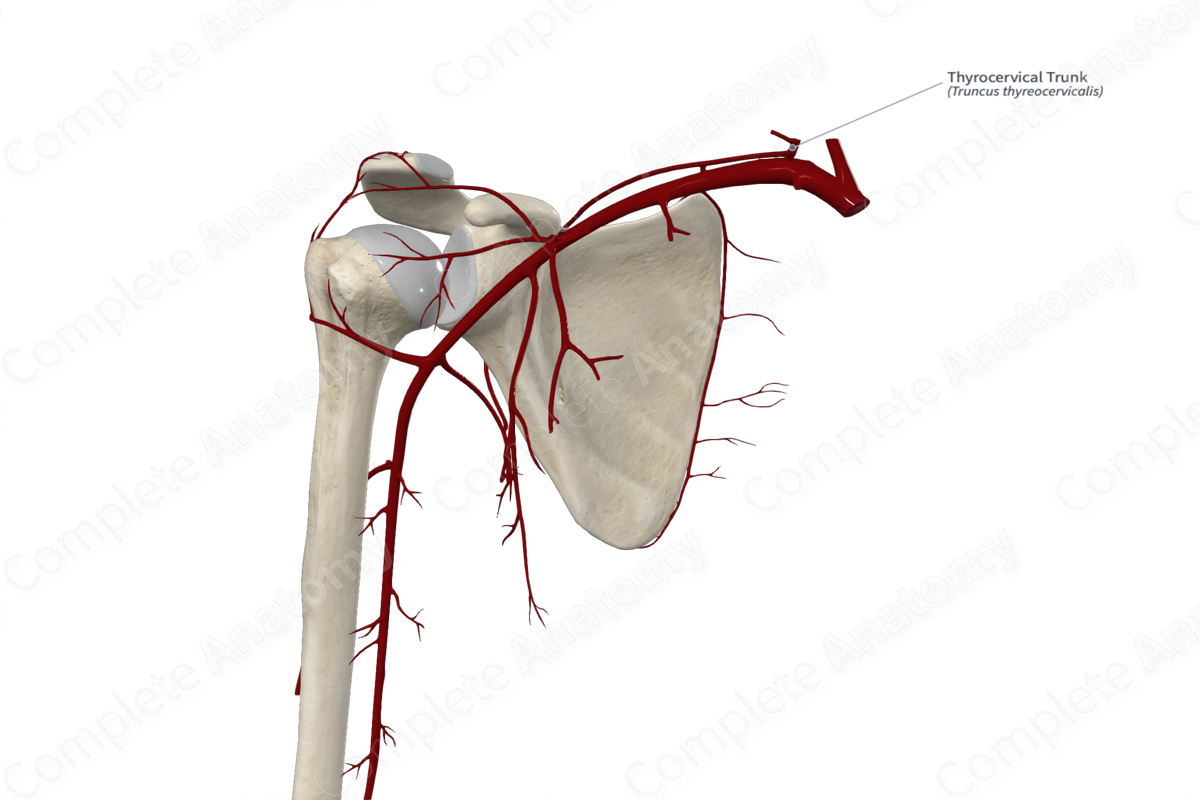
The thyrocervical trunk arises from the anterior surface of the first part of the subclavian artery.
Course
The thyrocervical trunk is a short thick vessel that ascends just medial to the scalenus anterior muscle and divides almost immediately from its origin.
Branches
The suprascapular artery arises from the thyrocervical trunk and passes inferolaterally across the scalenus anterior muscle to reach the superior scapular border.
The transverse cervical artery arises just superior to the suprascapular artery and takes a lateral course across the occipital triangle of the neck.
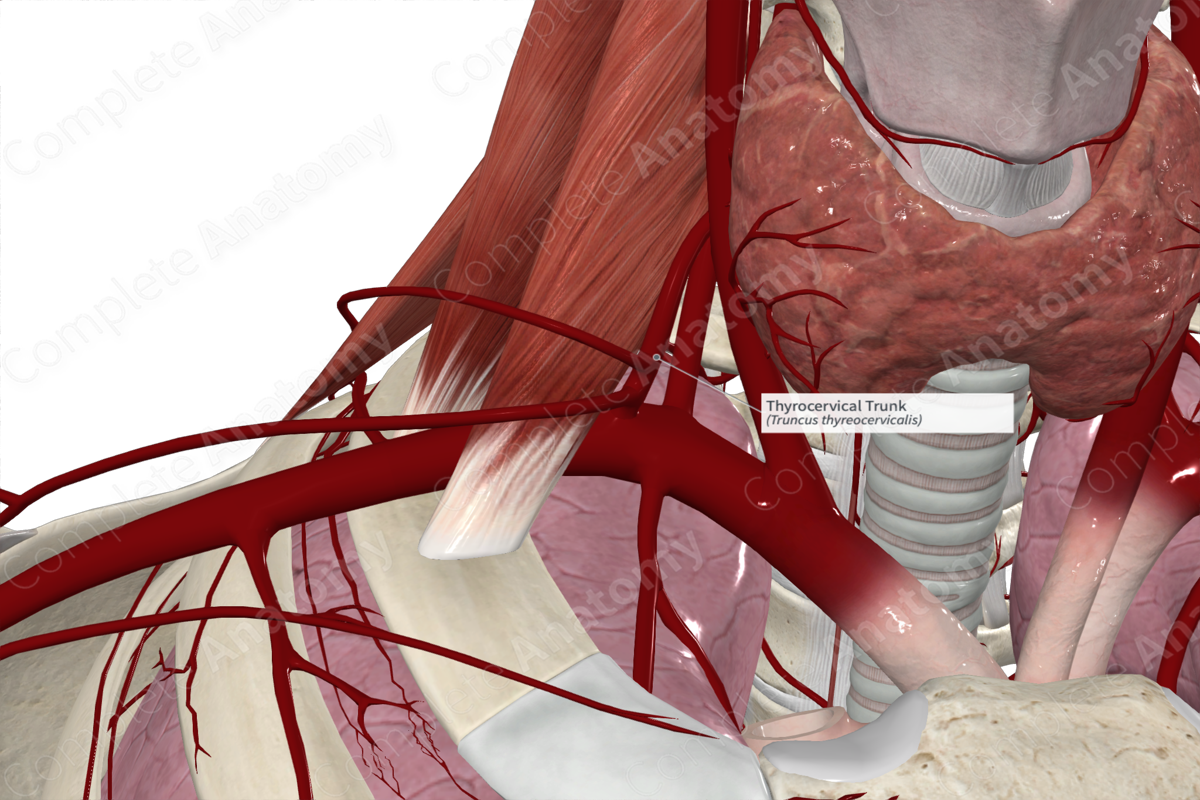
The inferior thyroid artery is the largest terminal branch of the thyrocervical trunk. It ascends anterior to the scalenus anterior muscle. Sometimes, the ascending cervical artery may arise directly from the thyrocervical trunk, but it usually arises from the inferior thyroid artery.
Supplied Structures
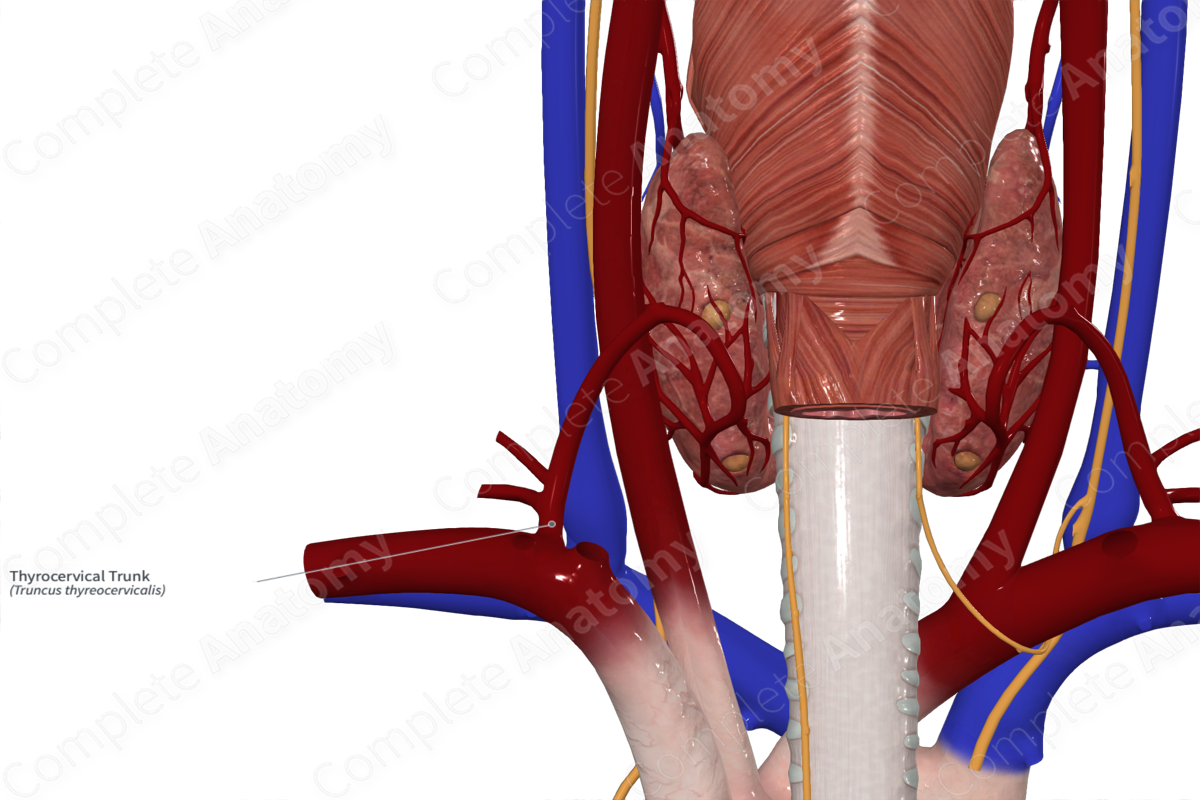
Branches from the thyrocervical trunk supply various structures of the neck and scapular region.
- The suprascapular artery supplies the supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles and part of the sternocleidomastoid and the subclavius muscles.
- The transverse cervical artery supplies trapezius and sternocleidomastoid muscles.
- The inferior thyroid artery supplies the inferior poles of the thyroid gland, parathyroid gland, larynx, pharynx, infrahyoid muscles, longus colli, scalenus anterior, and the inferior pharyngeal constrictor muscles.