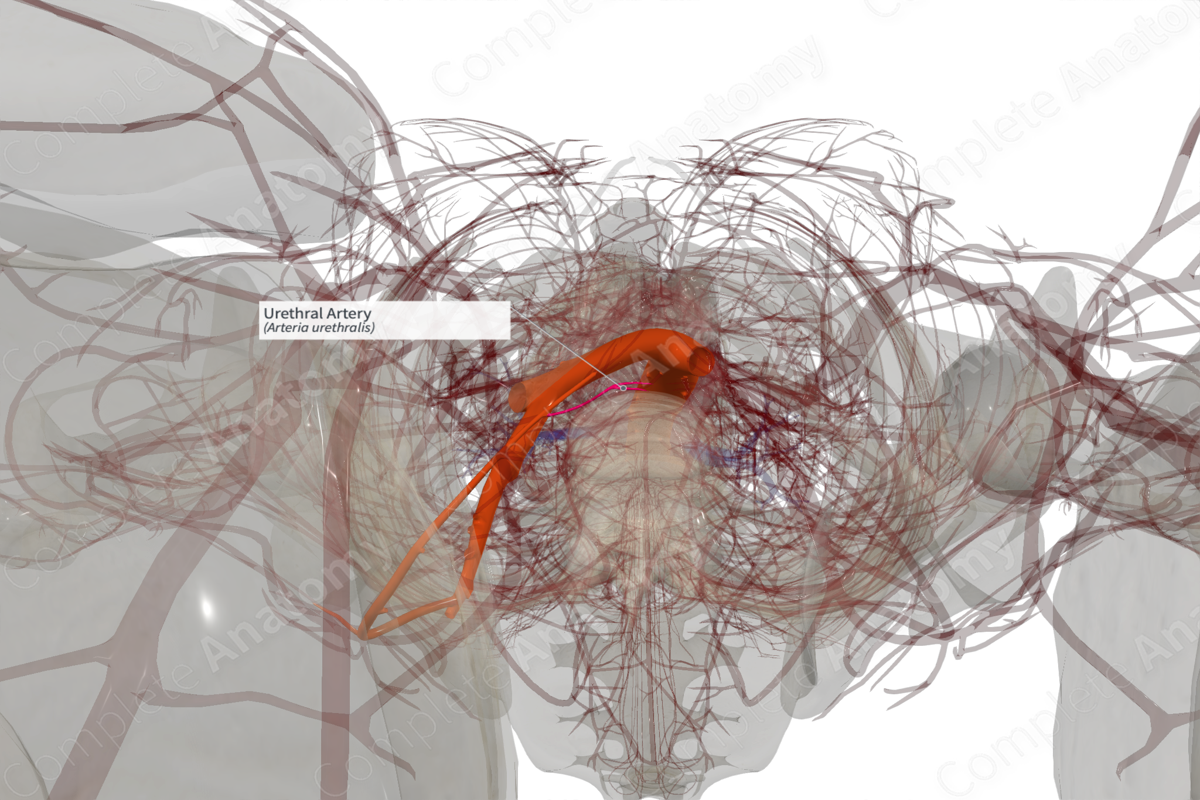
Quick Facts
Origin: Internal pudendal artery.
Course: Passes through the perineal membrane, through corpus spongiosum to reach the glans penis (male).
Branches: No branches.
Supplied Structures: Urethra (males and females), corpus spongiosum, and glans penis (males).
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The urethral artery originates in the superficial perineal pouch, just inferior to the perineal membrane.
Course
In males, the urethral artery passes medially to travel through the corpus spongiosum to reach the glans penis. It travels through the perineal membrane, through corpus spongiosum and into the glans penis.
As the urethra is much shorter in females, the urethral artery is much small in caliber and is not always present. In these cases, the urethra is supplied by the vaginal and inferior vesical arteries.
Branches
The urethral artery does not give off any branches.
Supplied Structures
In males, the urethral artery supplies the urethra, corpus spongiosum, and glans penis. In females, the urethral artery may be present and supplies the urethra.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Artery

Arteries are vessels transporting blood between heart, tissues, and other organs in order to supply them with nutrition and oxygen.
