Description
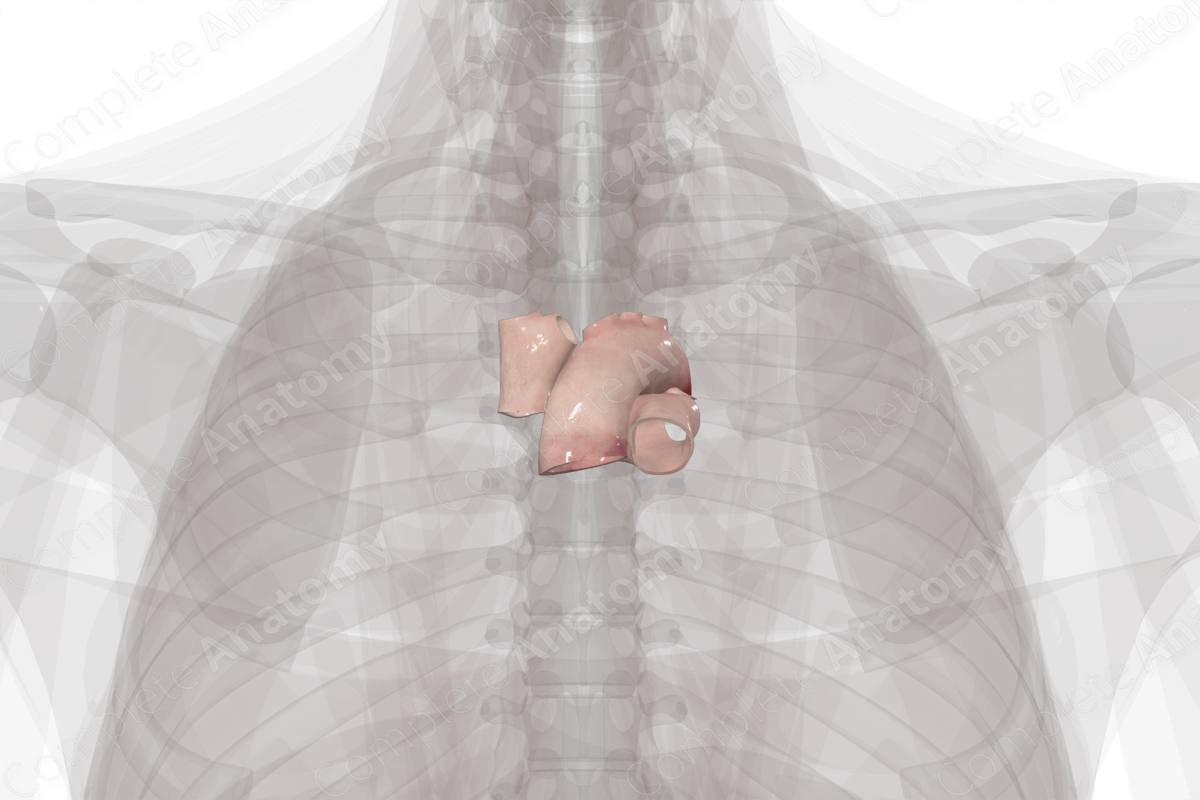
The great vessels include the major arteries and veins that link the systemic and pulmonary circulation. The aorta, pulmonary trunk, pulmonary veins, superior vena cava, and the inferior vena cava are considered the most important of the major vessels due to their size, function, and direct connection to the heart.
Systemic circulation supplies all tissues with oxygen, nutrients, and hormones, while also removing waste products, such as carbon dioxide. The pulmonary system is responsible for the oxygenation of blood.
The right atrium receives all the deoxygenated blood from the systemic circulation, primarily via the superior and inferior vena cava. From here the blood enters the right ventricle, which directs blood to the pulmonary system via the pulmonary trunk. Oxygenated blood is returned via the pulmonary veins which drain into the left atrium. The blood then travels to the left ventricle and is pumped back into the systemic circulation via the aorta.
Related parts of the anatomy




