Morphology/Structure
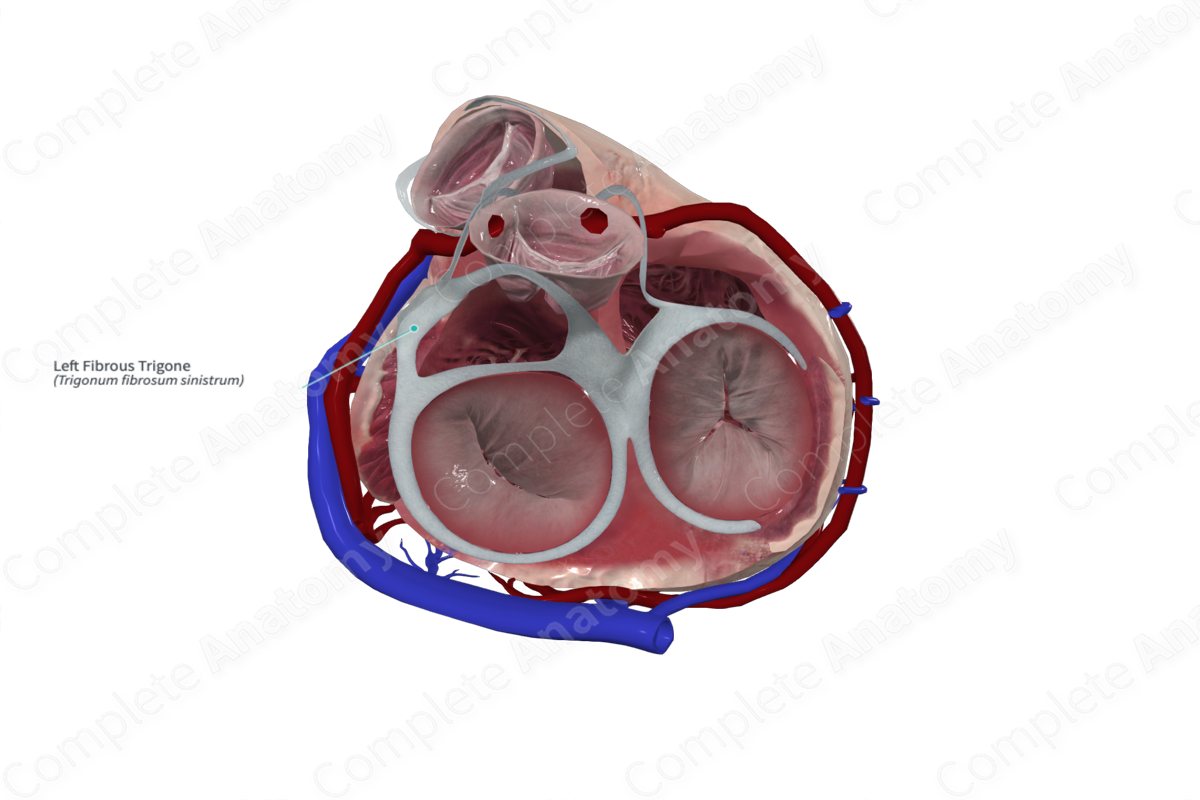
The right and left fibrous trigones are the strongest portions of the fibrous skeleton and consist of dense connective tissue which sits around the right atrioventricular orifices.
Key Features/Anatomical Relations
The left fibrous trigone connects the left fibrous ring to the aortic ring.
Function
The left fibrous trigone provides structural support to the left atrioventricular and aortic valves. It also aids in the structural support of the membranous septum and serves as a direct attachment for the myocardium. The collagen of the fibrous ring helps to separate electrical activities between the chambers by insulating the propagation of electrical impulses during a heartbeat.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Bladder Trigone

The bladder trigone is a triangular area at the base of the bladder bounded by the internal urethral meatus and the two ureteric orifices.



