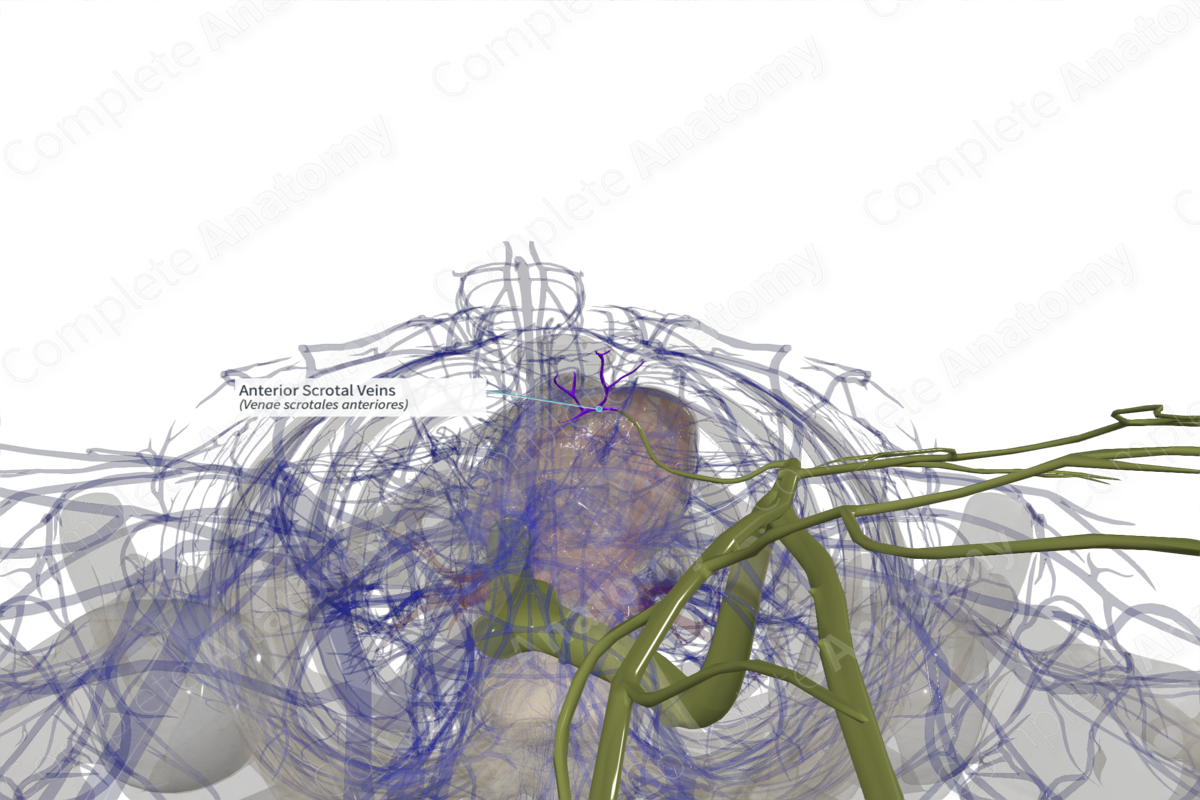
Quick Facts
Origin: Skin and connective tissue of anterior scrotum.
Course: Subcutaneous veins converge superolaterally and drain into the external pudendal vein.
Tributaries: None.
Drainage: Skin of anterior scrotum.
Origin
The anterior scrotal veins are a collection of veins the originate in the skin and connective tissue of anterior scrotum.
Course
These superficial veins course subcutaneously across the anterior surface of the scrotum drain into the external pudendal vein. There are abundant anastomoses between the anterior and posterior scrotal veins superolaterally. This dense superficial network of scrotal veins facilitates temperature regulation of the testes, which is important given the high rate of germ cell production occurring there.
The external pudendal vein drains into the greater saphenous vein and eventually into the femoral vein.
Tributaries
There are no named tributaries.
Structures Drained
The anterior scrotal veins drain the skin of the anterior scrotum.




