Quick Facts
Origin: Union of the right ascending lumbar and subcostal veins.
Course: Ascends in the posterior mediastinum to join the superior vena cava.
Tributaries: Fourth to eleventh right posterior intercostal veins, right subcostal vein, right ascending lumbar vein, esophageal and right bronchial veins, and hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins.
Drainage: Thoracic and abdominal walls, esophagus, bronchi, and trachea.
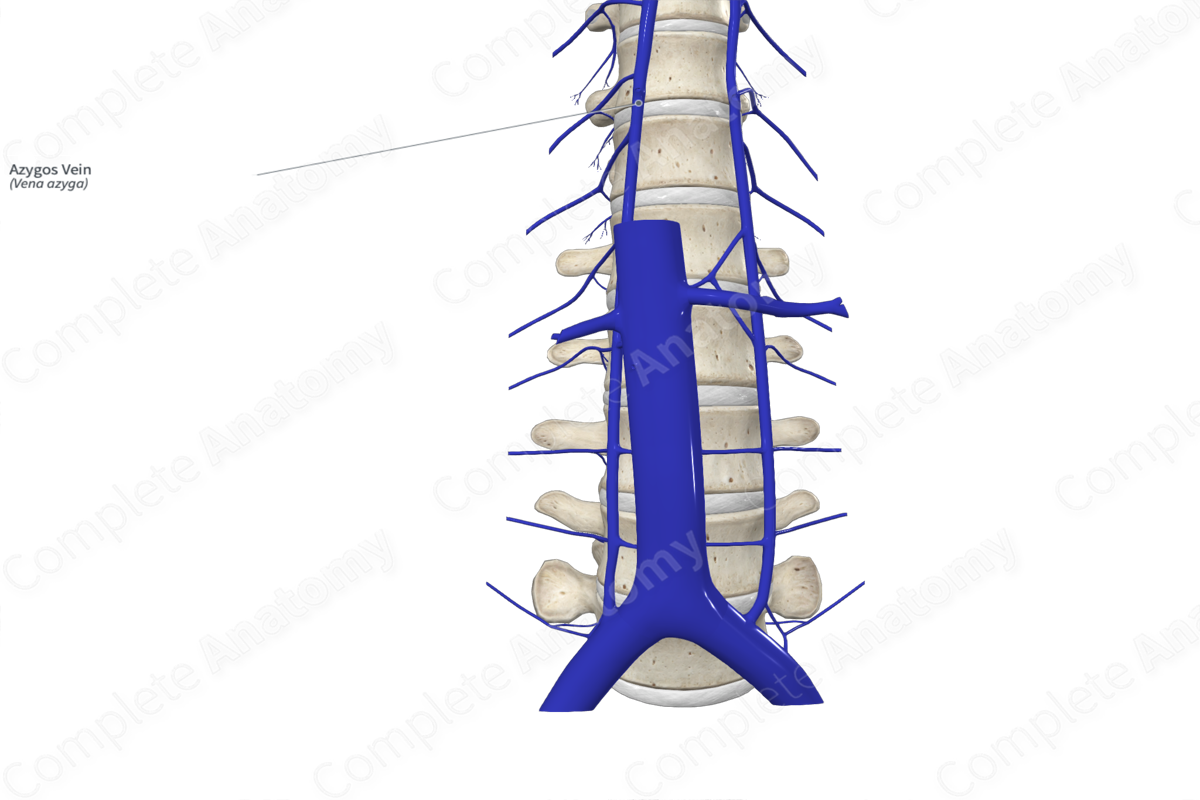
Origin
The azygos vein is an unpaired vein formed by the union of the right subcostal and ascending lumbar veins, posterior to the right crus of the respiratory diaphragm at the level of the twelfth thoracic vertebra.
Course
The azygos vein ascends in the posterior mediastinum, sitting on the right side of the lower eight vertebral bodies. At the level of the fourth thoracic vertebra, the azygos vein arches forwards over the right pulmonary hilum to open into the superior vena cava.
The azygos vein lies anterior to the anterior longitudinal ligament and the posterior intercostal arteries, while the right lung, right greater splanchnic nerve, and right sympathetic chain all lie laterally to the right. The thoracic duct, esophagus, descending thoracic aorta, and right vagus nerve all sit to the left of the azygos vein.
The origin, course, tributaries and termination of the azygos system is highly variable. Sometimes, the left side (the hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins) is absent or underdeveloped, meaning that the azygos vein is responsible for drainage of the left posterior intercostal veins. If the accessory hemiazygos drains into the left brachiocephalic vein, the azygos vein assumes a median position in the posterior mediastinum.
Tributaries
The major tributaries of the azygos vein include the fourth to eleventh right posterior intercostal veins, the right subcostal vein, right ascending lumbar vein, esophageal and right bronchial veins, and the hemiazygos and accessory hemiazygos veins.
Structures Drained
Numerous structures are drained indirectly by the azygos vein via its tributaries, including the thoracic and abdominal wall, esophagus, bronchi, and trachea.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





