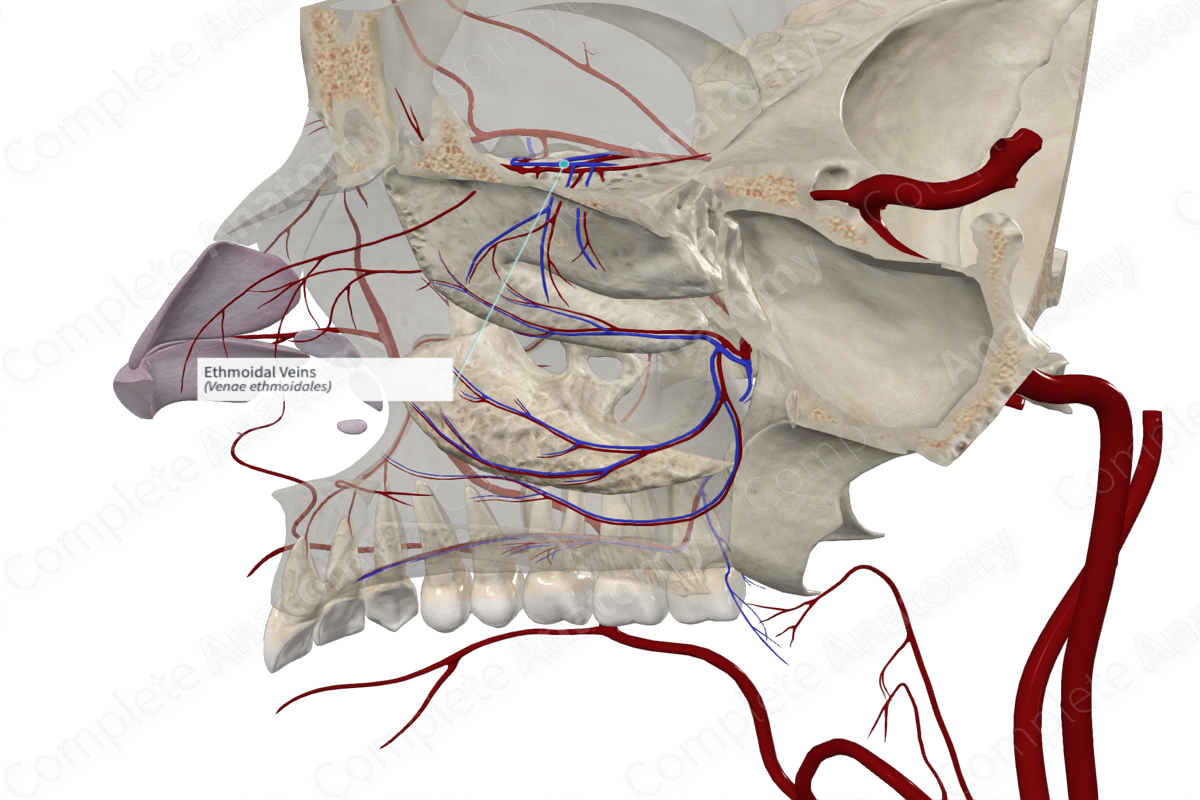
Quick Facts
Origin: Nasal cavity.
Course: Serve as the vena comitans of the ethmoidal arteries and accompany them along their course.
Tributaries: None.
Drainage: Roof and upper medial and lateral walls of the nasal cavity, ethmoidal air sinuses, dorsum of the nose, and dura mater (in the anterior cranial fossa).
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The ethmoidal veins originate in the mucosa of the nasal cavity.
Course
The ethmoidal veins serve as the vena comitans of the anterior and posterior ethmoidal arteries. They accompany the corresponding arteries to enter ethmoidal canals in the medial wall of the orbit to reach the superior ophthalmic vein.
Tributaries
There are no named tributaries.
Structures Drained
The ethmoidal veins drain venous blood from the roof and upper medial and lateral walls of the nasal cavity, ethmoidal air sinuses, dorsum of the nose, and the dura mater (in the anterior cranial fossa).
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Vein

A venous sinus is a vein with a thin wall of endothelium that is devoid of smooth muscle to regulate its diameter.



