Quick Facts
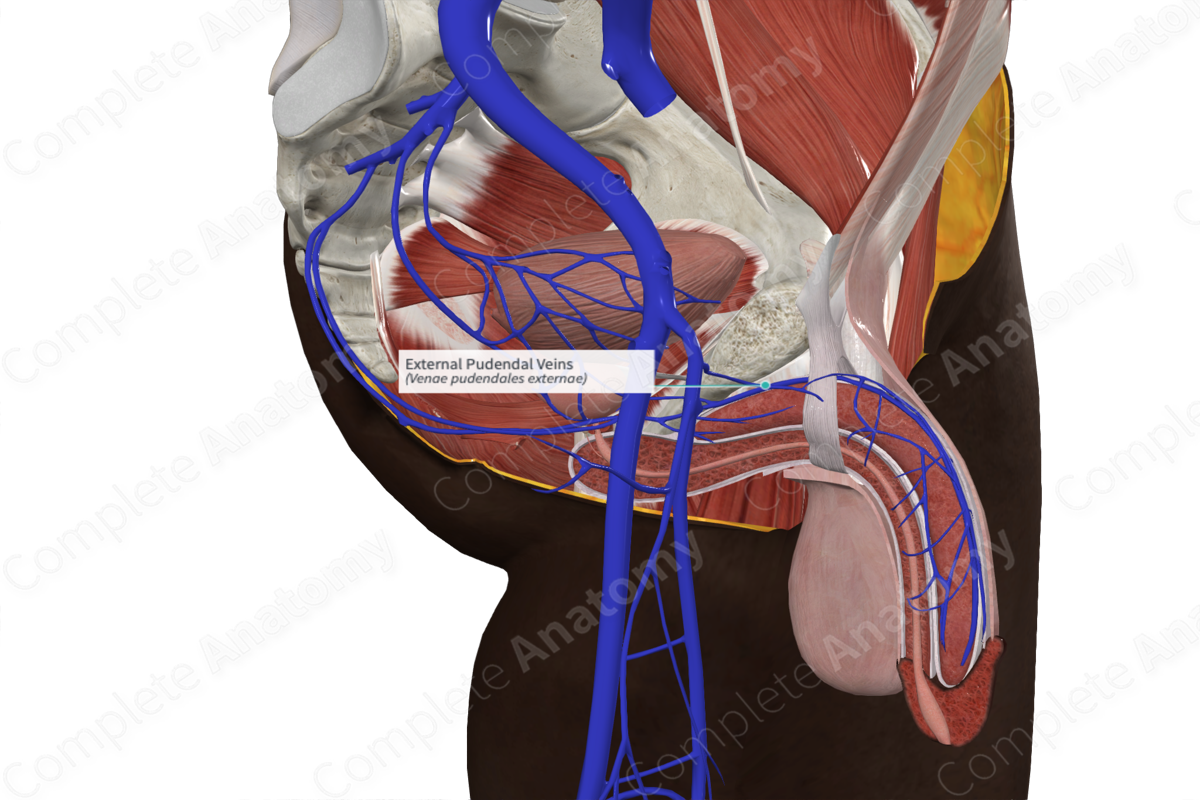
Origin: External genitalia and skin of lower abdomen.
Course: Passes superomedially to join the greater saphenous vein.
Tributaries: Anterior scrotal and superficial dorsal vein of penis (male); anterior labial and superficial dorsal vein of clitoris (female)
Drainage: External genitalia and skin of lower abdomen.
Origin
The external pudendal vein forms from veins in the skin of the external genitalia of males (anterior scrotum and prepuce and shaft of the penis) and females (anterior labia majora). It receives some contribution from the skin of the inferior anterior abdominal wall.
Course
The external pudendal vein has a short course that passes superomedially from the anterior scrotum/labia and penis/clitoris. In most cases, it joins the greater saphenous vein just before it passes through the saphenous opening to join the femoral vein. Occasionally, it can pass through the opening before directly draining into the femoral vein.
Tributaries
The external pudendal vein receives the anterior scrotal and superficial dorsal vein of penis (male), or the anterior labial and superficial dorsal vein of clitoris (female).
Structures Drained
The external pudendal vein drains the skin of anterior scrotum/labia and penis/clitoris, including the prepuce.



