Quick Facts
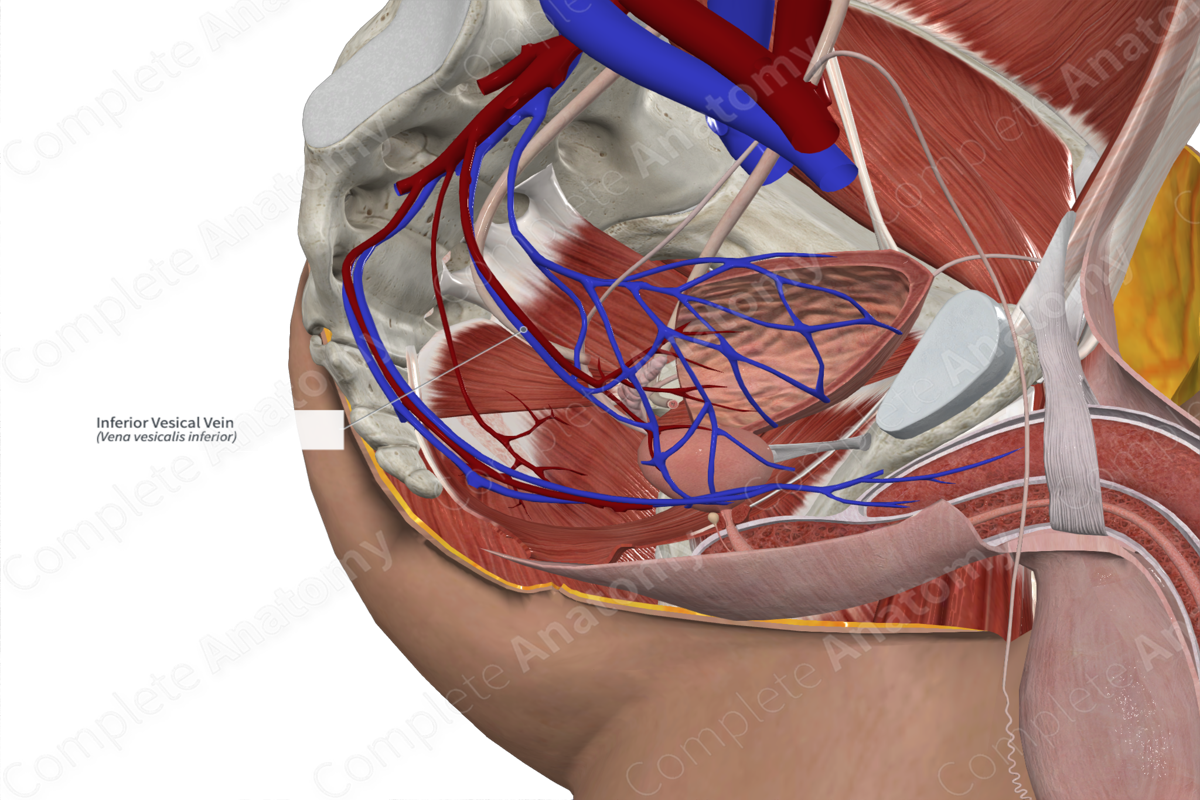
Origin: Union of vessels from the vesical venous plexus.
Course: Ascends in the pelvis to drain into the internal iliac vein.
Tributaries: Ramifications of the vesical venous plexus enter the inferior surface of the bladder.
Drainage: Bladder and distal ureter; prostate, seminal vesicles, and ductus deferens (males).
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The inferior vesical vein is formed by the union of vessels from the vesical venous plexus. Some of these ramifications enter the surface of the bladder in order to drain it.
Course
The inferior vesical vein ascends in the pelvis, with the inferior vesical artery, to drain into the internal iliac vein.
Tributaries
The inferior vesical vein branches into ramifications that enter the surface of the bladder as the vesical venous plexus. In males, small branches will also drain the prostate and seminal vesical (glands).
Structures Drained
Due to the ramifications of the inferior vesical vein into the vesical venous plexus, it drains multiple structures in the pelvic area. The inferior vesical vein drains mainly the inferior surface of the bladder. The superior surface is drained by the superior vesical vein. In males, the plexus ramifies and may drain part of the prostate, seminal vesical and ductus deferens (Moore et al., 2013).
References
Moore, K. L., Dalley, A. F. and Agur, A. M. R. (2013) Clinically Oriented Anatomy. Clinically Oriented Anatomy 7th edn.: Wolters Kluwer Health/Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Vein

A venous sinus is a vein with a thin wall of endothelium that is devoid of smooth muscle to regulate its diameter.




