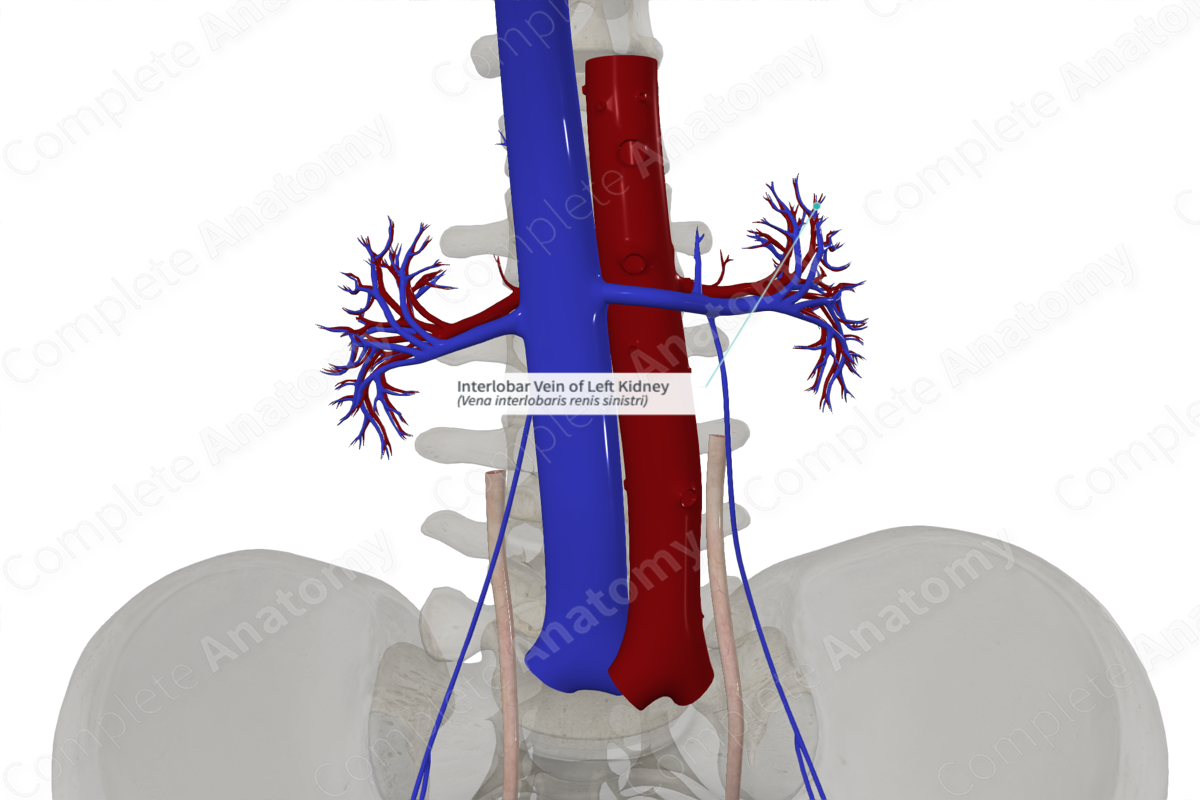
Quick Facts
Origin: Convergence of the renal arcuate veins.
Course: Pass from superficial to deep within the renal columns and drain into the renal veins.
Tributaries: Renal arcuate veins.
Drainage: Renal cortex and medulla.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The renal arcuate veins converge along the corticomedullary junction at the superficial end of each renal column to form the interlobar veins.
Course
From the corticomedullary junction at the superficial end of the renal columns, the interlobar veins travel parallel to the axis of the column from superficial to deep. There is one interlobar vein per column (lobe). Each vein accompanies an interlobar renal artery.
Tributaries
The interlobar veins receive the arcuate veins.
Structures Drained
The interlobar veins drain the renal cortex and medulla.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Vein

A venous sinus is a vein with a thin wall of endothelium that is devoid of smooth muscle to regulate its diameter.



