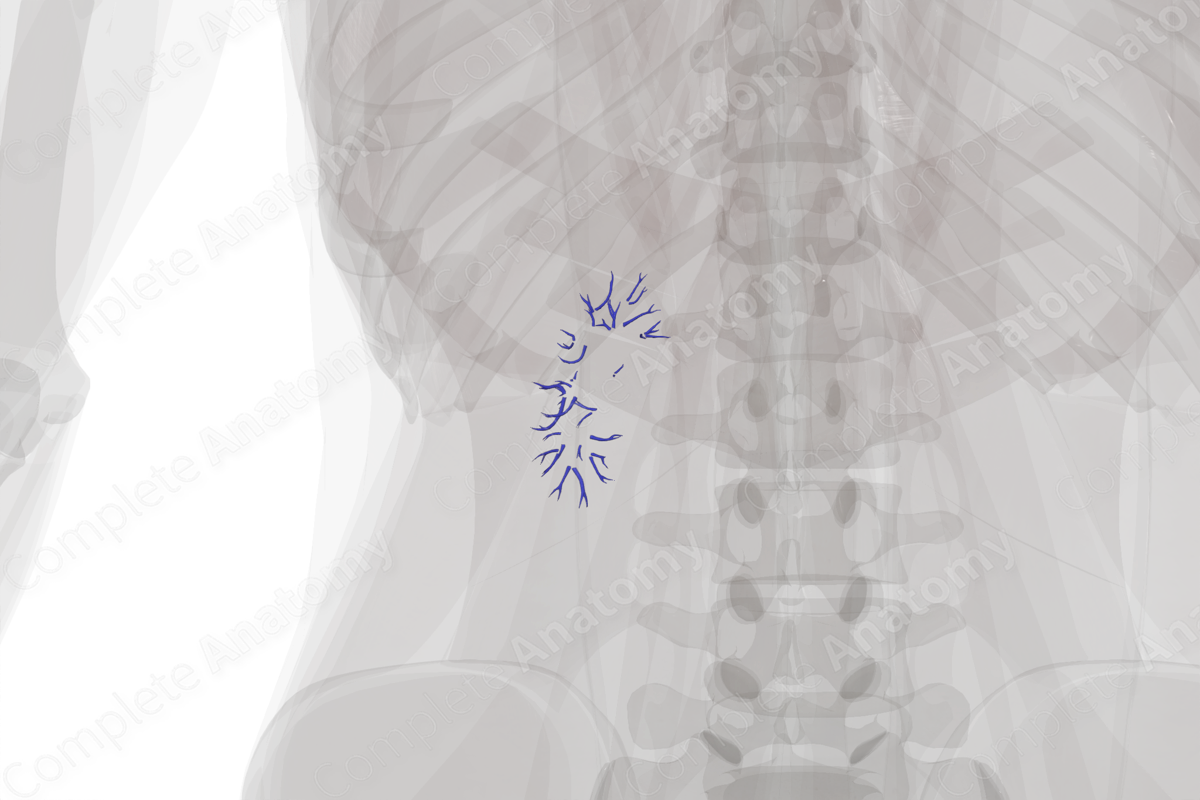
Description
Intrarenal veins are the collective term for the series of veins that drain the kidney parenchyma (cortex and medulla). From distal to proximal this venous system includes the: peritubular capillary plexus, interlobular veins and vasa recta, arcuate veins, and interlobar veins.
The intrarenal veins course from the external kidney surface, cortex, across the renal medulla converging onto the renal sinus and empty into the renal veins. They follow along with the intrarenal arteries with the exception of small tributaries that cross the boundaries between renal segments. Intrarenal arteries respect segmental boundaries. In this way, the intrarenal vascular system is similar to that of the lung and liver (Graves, 1956).
Related parts of the anatomy
References
Graves, F. T. (1956) 'The anatomy of the intrarenal arteries in health and disease', Br J Surg, 43(182), pp. 605-16.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Vein

A venous sinus is a vein with a thin wall of endothelium that is devoid of smooth muscle to regulate its diameter.




