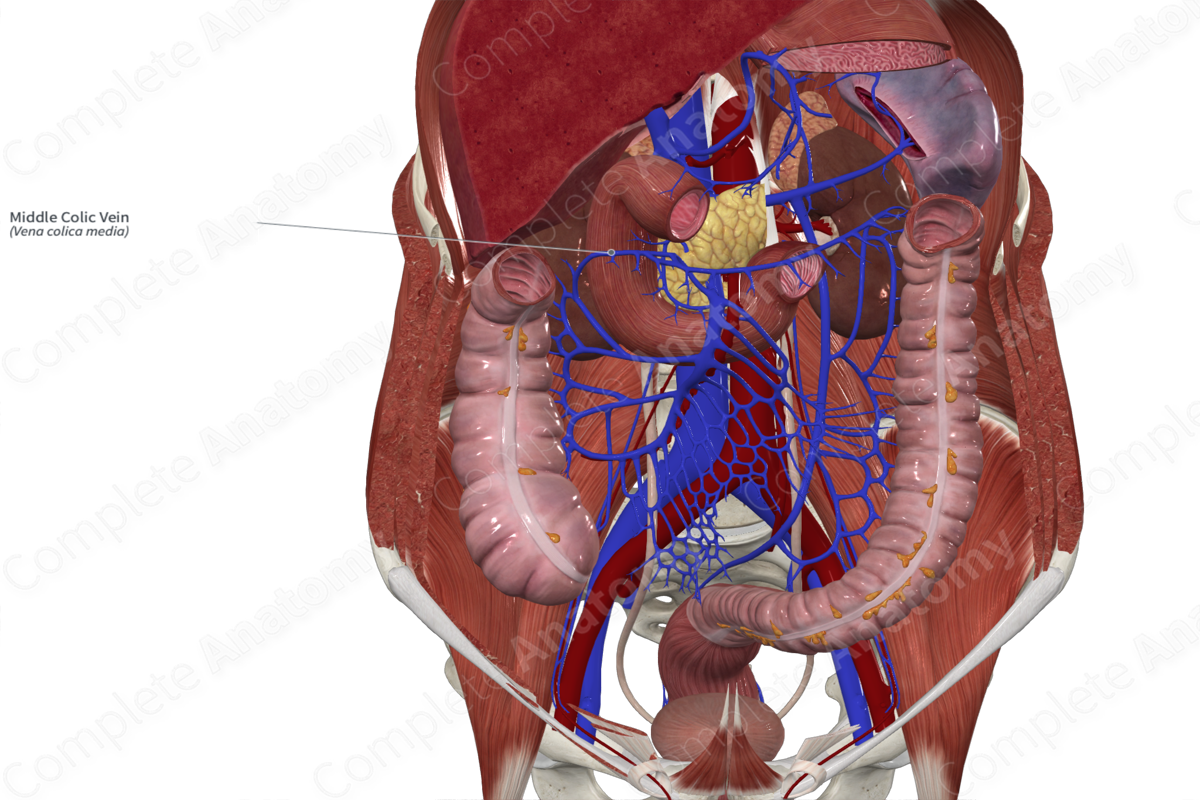
Quick Facts
Origin: Arises along the transverse colon.
Course: Travels inferiorly and posteriorly from the transverse colon to drain into the superior mesenteric vein.
Tributaries: Small, unnamed tributaries.
Drainage: Proximal two thirds of the transverse colon.
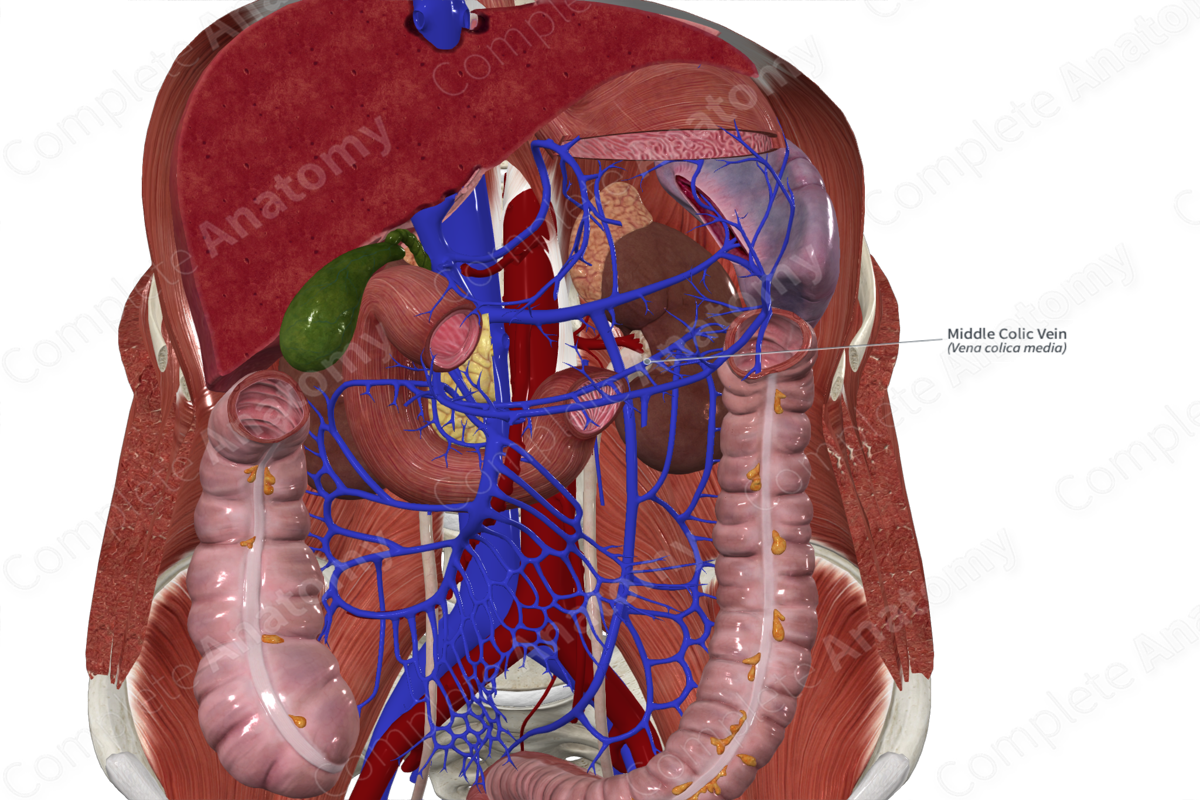
Origin
The middle colic vein originates along the surface of the transverse colon within the transverse mesocolon.
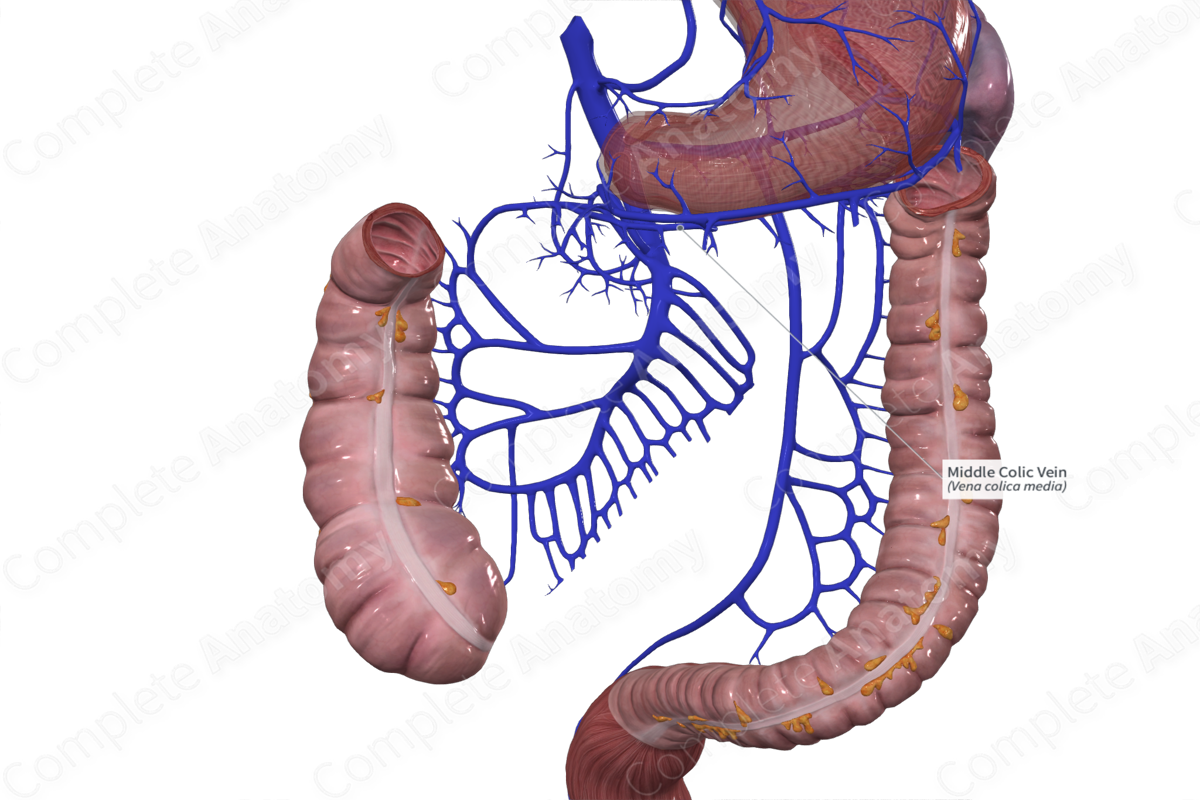
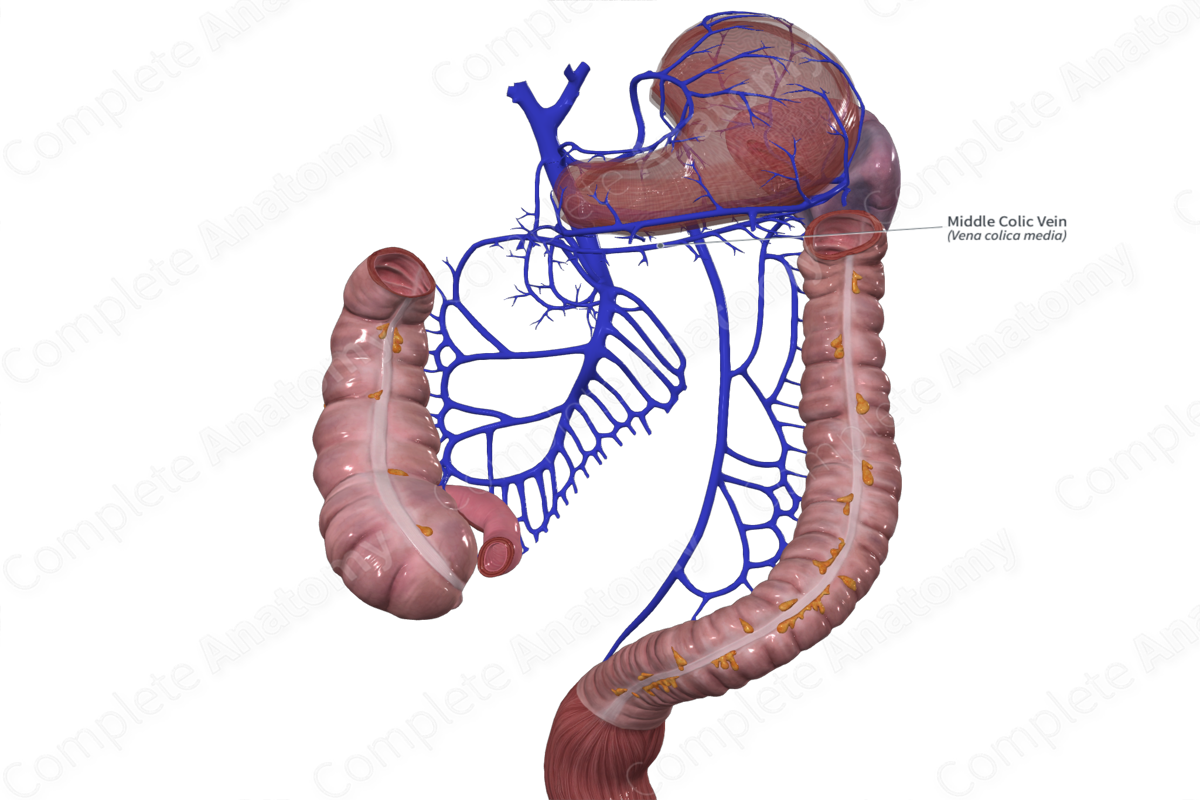
Course
The middle colic vein travels inferiorly from the surface of the transverse colon through the transverse mesocolon. Typically, the middle colic vein drains directly into the superior mesenteric vein (~63%) or the gastrocolic trunk of Henle, the common trunk formed by the confluence of the right gastroomental and right colic veins (~29%) (Standring, 2016; Maki et al., 2016).
Tributaries
The middle colic vein is often continuous with branches of the right and left colic veins.
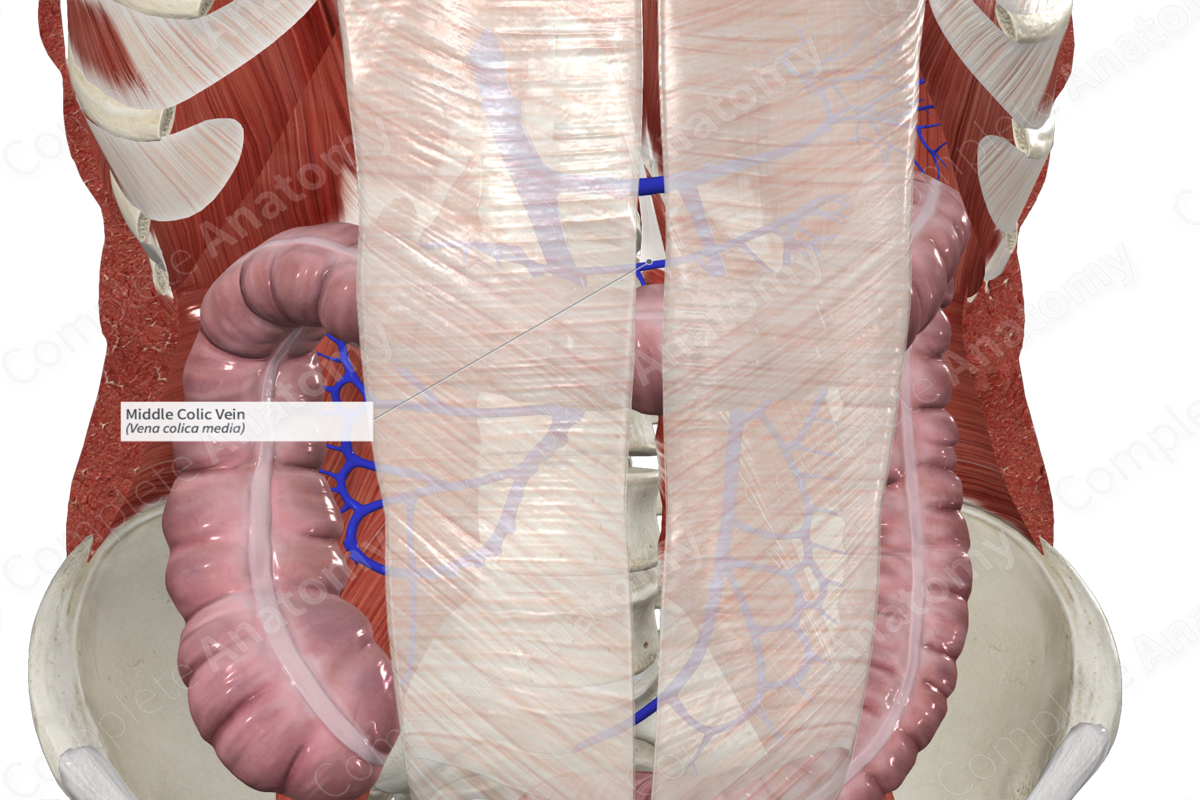
Structures Drained
The middle colic vein supplies the proximal two thirds of the transverse colon.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Transverse colectomy
References
Maki, Y., Mizutani, M., Morimoto, M., Kawai, T., Nakagawa, M., Ozawa, Y., Takeuchi, M., Maki, H., Kurosaka, K. and Shibamoto, Y. (2016) 'The variations of the middle colic vein tributaries: depiction by three-dimensional CT angiography', Br J Radiol, 89(1063), pp. 20150841.
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products