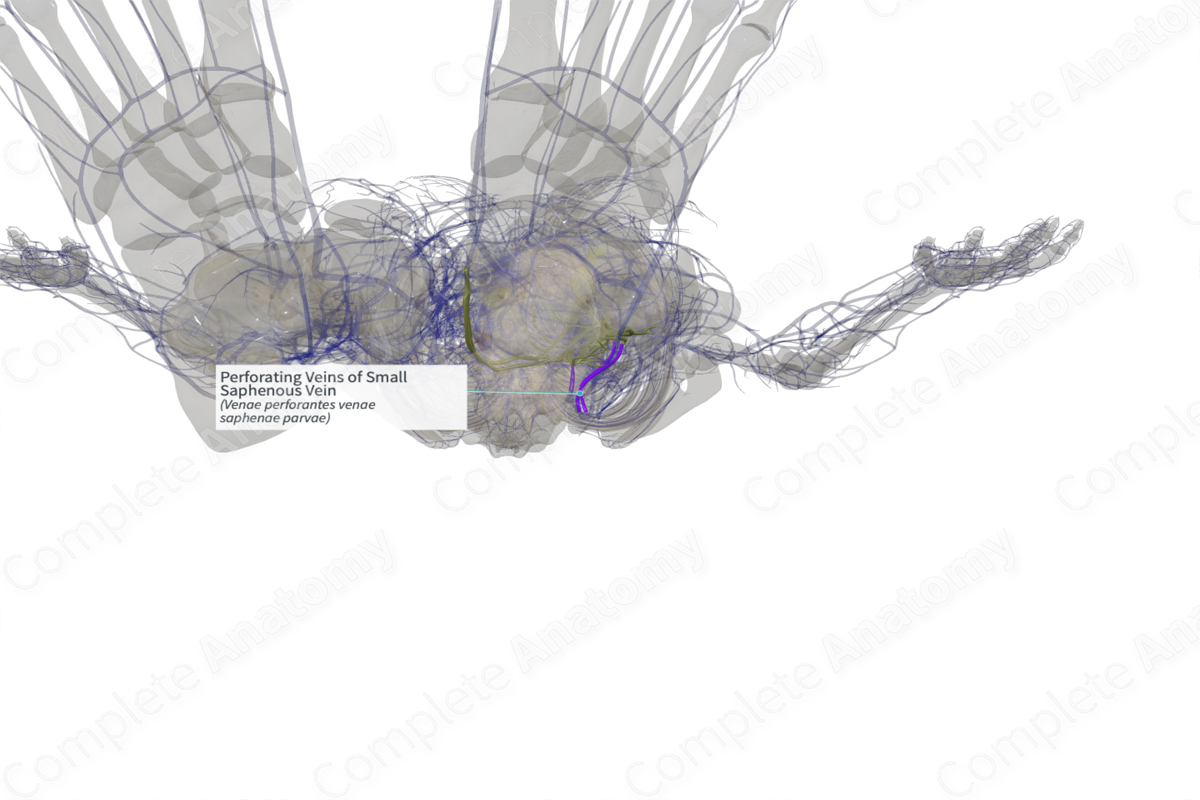
Perforating Veins of Small Saphenous Vein (Right)
Venae perforantes venae saphenae parvae
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Small saphenous vein.
Course: Several veins found along the course of the small saphenous vein.
Tributaries: None.
Drainage: Unite with the fibular vein.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The small saphenous vein has four constant perforating veins found over the length of the vein. They connect the small saphenous vein to the fibular vein. The most proximal two perforating veins, May’s perforating veins, connect the small saphenous veins with the muscular veins draining the gastrocnemius and soleus muscles and terminate in the fibular (or peroneal) veins. The para-Achillean perforating vein, or Bassi’s perforating vein, is located next to the calcaneal tendon. Finally, a direct perforating vein found below the lateral malleolus connects the small saphenous vein to the fibular vein (Caggiati et al, 2014).
Structures Drained
The perforating veins of the small saphenous vein connect the superficial venous system of the lower limb with the deep venous system. The perforating veins shunt blood in one direction, from superficial veins to the high-pressured deep veins. The perforating veins contain valves to prevent the flow of blood from deep to superficial.
List of Clinical Correlates
- Varicose veins
References
Caggiati, A., Mendoza, E., Murena-Schmidt, R. & Lattimer, C. R. (2014) Anatomy of the Superficial Veins, in Mendoza, E., Lattimer, C. R. & Morrison, N. (eds), Duplex Ultrasound of Superficial Leg Veins. Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 19-47.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Small Saphenous Vein

The small saphenous vein is located in the back of the lower limb and runs from the ankle upward until it joins the popliteal vein at the saphenopopliteal junction.




