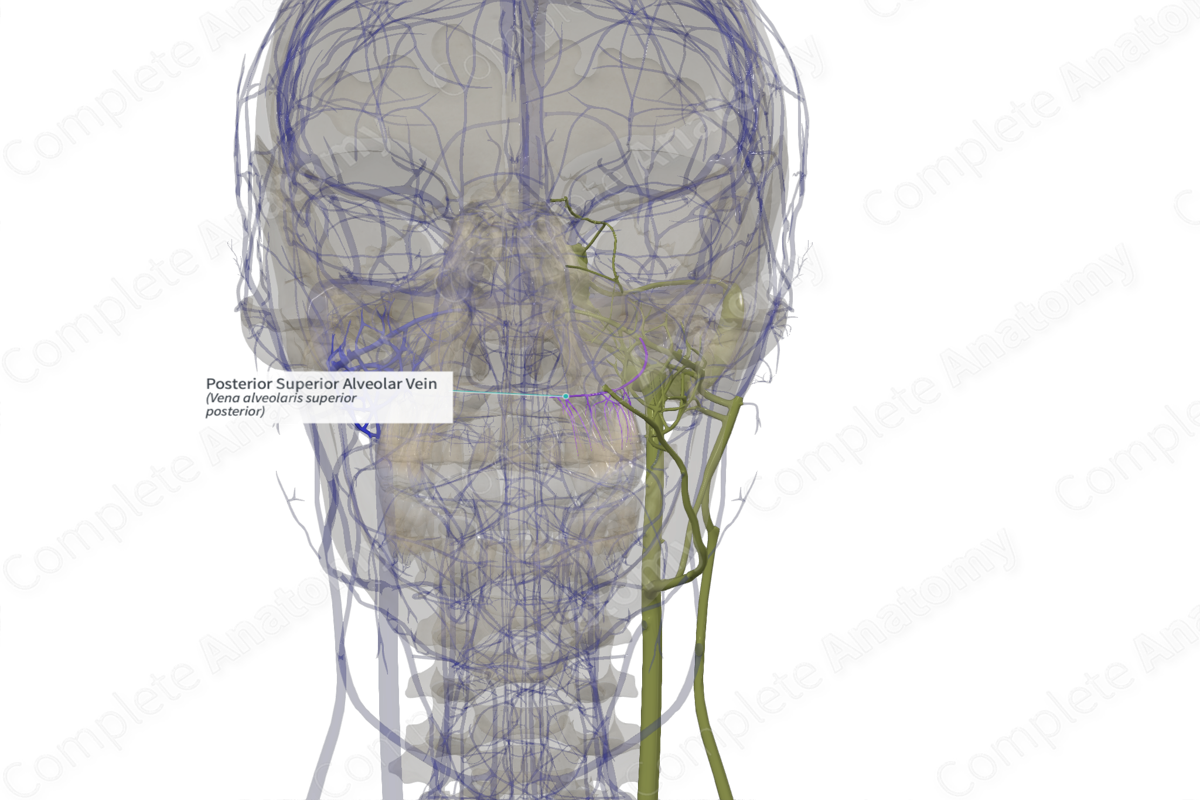
Posterior Superior Alveolar Vein (Left)
Vena alveolaris superior posterior
Read moreQuick Facts
Origin: Inside the maxilla.
Course: Emerges from maxillary tuberosity and passes through the pterygomaxillary fissure to join the maxillary artery inside the pterygopalatine fossa.
Tributaries: Venous tributaries come from the maxillary molar and premolar teeth and the maxillary air sinus.
Drainage: Maxillary molar and premolar teeth and the maxillary air sinus and the buccal mucosa.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The posterior superior alveolar vein arises as venous branches from the bony mandible, in areas around the maxillary molar and premolar teeth and the maxillary air sinus, and other venous branches from the buccal mucosa.
Course
The posterior superior alveolar vein emerges from the maxillary tuberosity and runs through the pterygomaxillary fissure to enter the pterygopalatine fossa, where it unites with the maxillary vein.
Tributaries
Venous tributaries of the posterior superior alveolar vein come from around the maxillary molar and premolar teeth and the maxillary air sinus and from the buccal mucosa.
Structures Drained
The posterior superior alveolar vein drains the molar and premolar areas of the maxilla, the maxillary air sinus, and buccal mucosa.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products


