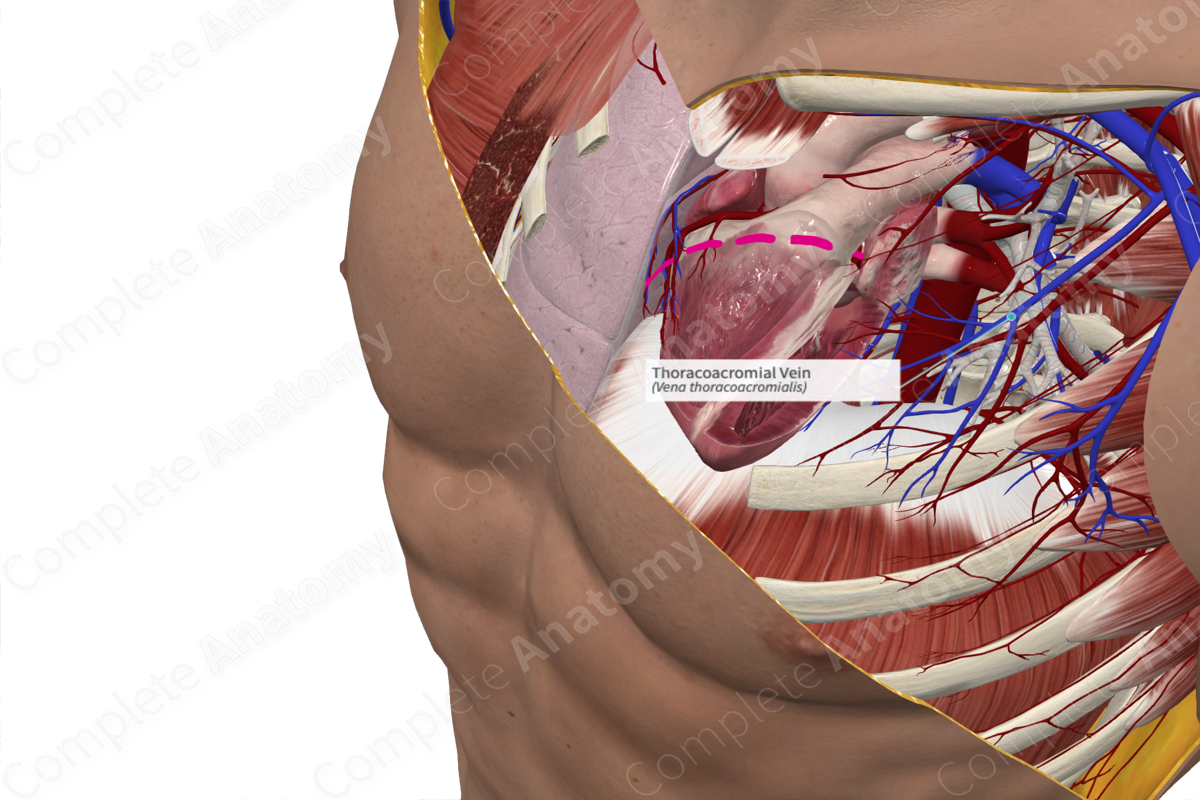
Quick Facts
Origin: The branches of this vein unite within the axilla.
Course: Short course to the axillary artery.
Tributaries: Deltoid, pectoral, acromial, and clavicular branches.
Drainage: Deltoid, pectoral, acromial, and clavicular regions.
Origin
Smaller veins unite to form the thoracoacromial vein. These include its deltoid, pectoral, acromial, and clavicular branches.
Course
The thoracoacromial vein forms at the superior end of the pectoralis minor muscle. It has a short course where it almost immediately unites with the axillary vein, at the level of the coracoid process of the scapula (Standring, 2016).
Tributaries
The thoracoacromial vein is formed by the union of the deltoid, pectoral, acromial, and clavicular branches.
Structures Drained
The thoracoacromial vein contributes to the venous drainage of the deltoid, pectoral, acromial, and clavicular regions.
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41 edn.: Elsevier Limit ed.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Vein

A venous sinus is a vein with a thin wall of endothelium that is devoid of smooth muscle to regulate its diameter.



