Quick Facts
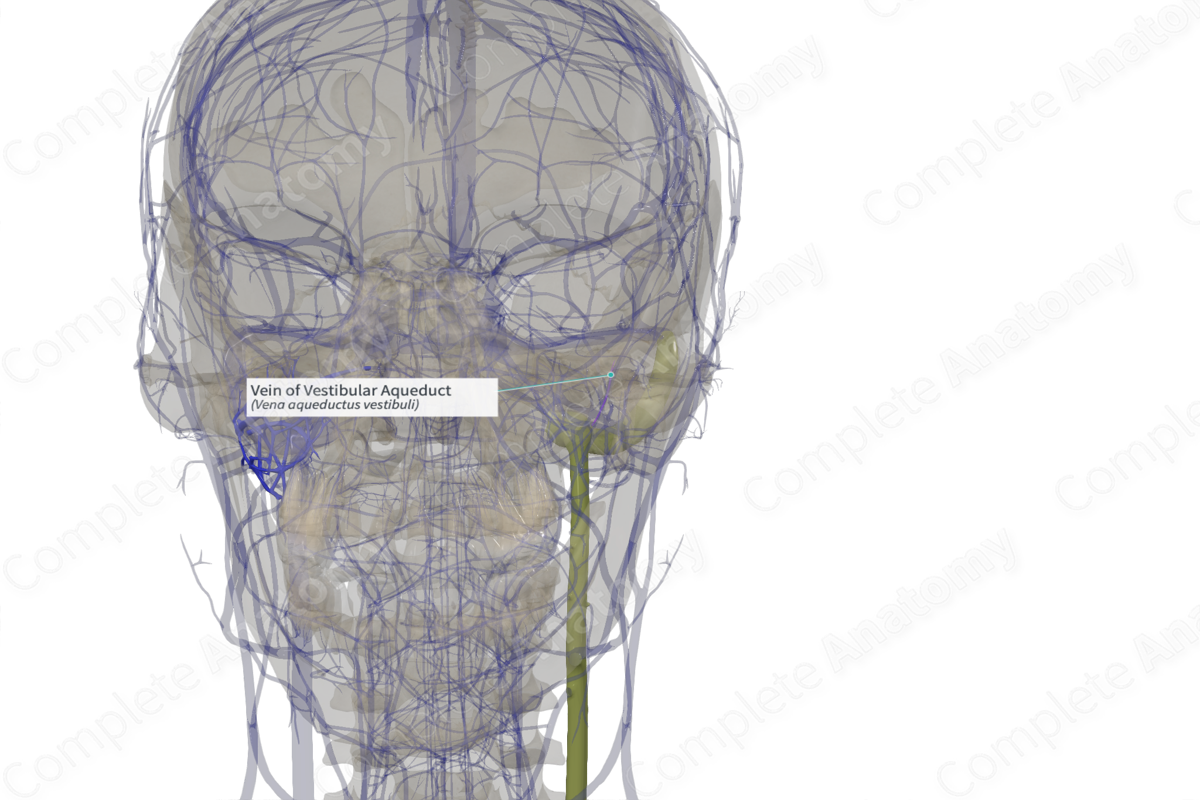
Origin: Union of various venous tributaries from the vestibule of the inner ear.
Course: Runs parallel to the vestibular aqueduct before draining into the inferior petrosal, sigmoid sinus, or superior bulb of internal jugular vein.
Tributaries: Small tributaries.
Drainage: Vestibule and semicircular canals.
Related parts of the anatomy
Origin
The vein of the vestibular aqueduct is formed by the union of venous tributaries draining the vestibule and semicircular canals of the internal ear (Standring, 2016).
Course
The vein of the vestibular aqueduct runs parallel to the vestibular aqueduct and the endolymphatic duct, prior to its opening into the inferior petrosal, sigmoid sinus, or the superior bulb of internal jugular vein.
Tributaries
The vein of the vestibular aqueduct receives the small veins draining the vestibule and the semicircular canals.
Structures Drained
The vein of the vestibular aqueduct drains blood from the vestibule and the semicircular canals.
References
Standring, S. (2016) Gray's Anatomy: The Anatomical Basis of Clinical Practice. Gray's Anatomy Series 41st edition edn.: Elsevier Limited.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products


