Description
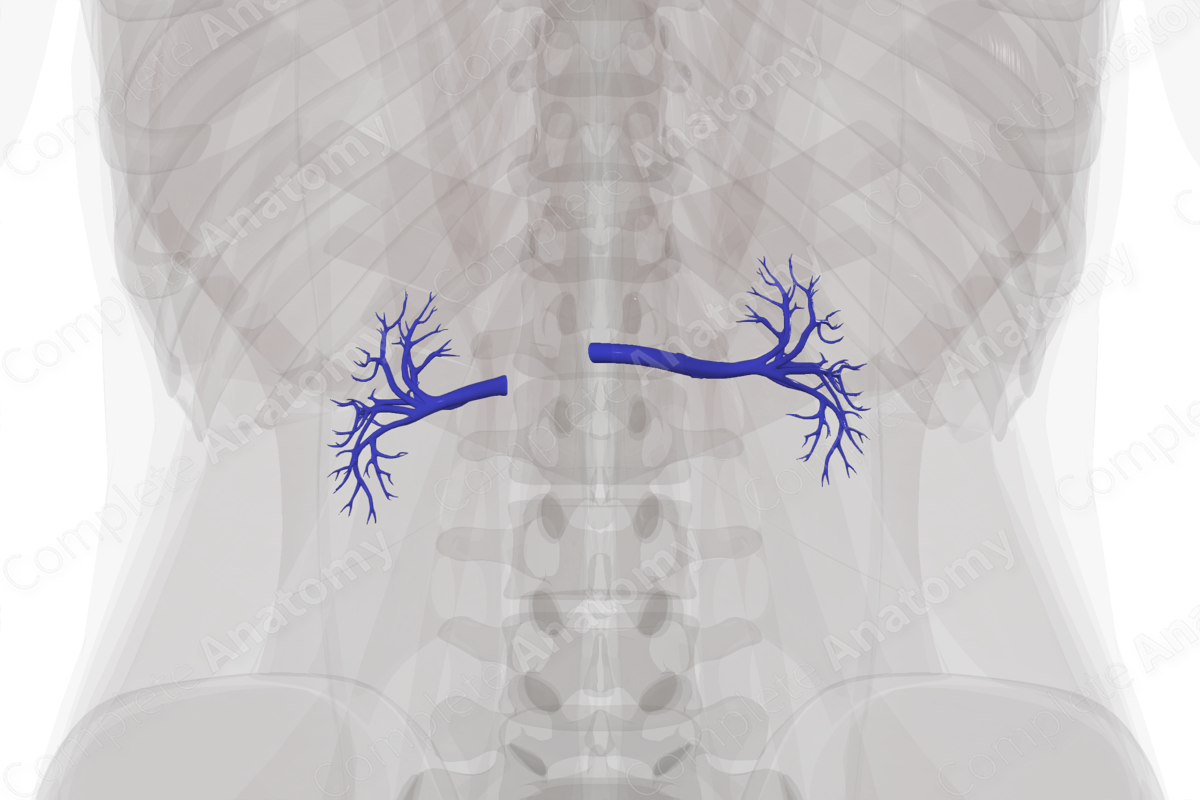
The venous drainage of the kidneys is achieved through paired, right and left renal veins. They are formed by the union of the posterior and anterior branches of the renal veins.
The longer left renal vein receives the left ovarian or the left testicular vein, the left suprarenal vein, and a communicating branch from the ascending lumbar vein as it travels horizontally to enter the inferior vena cava. Due to the location of the inferior vena cava on the right-hand side of the posterior abdominal wall, the right renal vein is three times shorter than the left renal vein and therefore does not receive any tributaries.
Related parts of the anatomy
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products
Renal Vein

A circumaortic left renal vein is an anatomic variant in which the left renal vein forms a ring around the aorta.




