Description
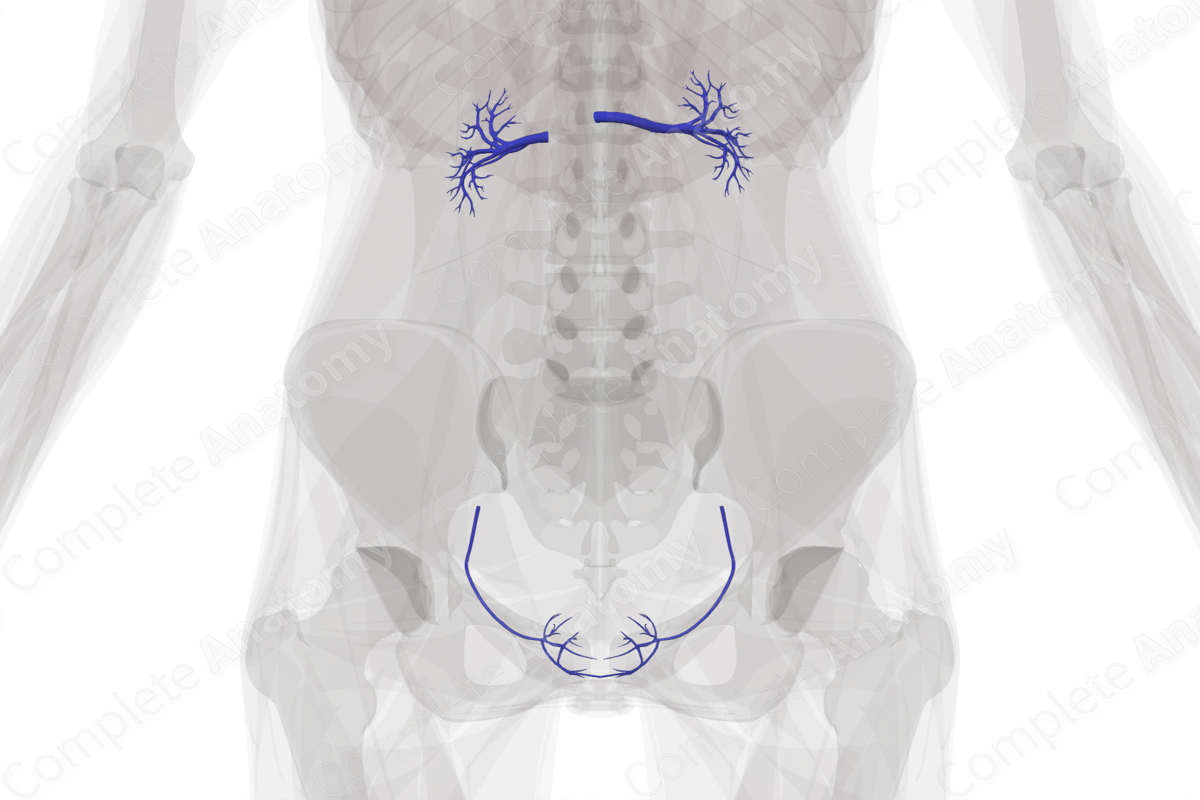
The urinary system consists of the kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra. The kidneys are drained by right and left renal veins, which drain into the inferior vena cava. The left renal vein is much longer than the right renal vein as it has to cross over the abdominal aorta. The ureters are drained segmentally by the ureteric veins which arise from the renal, gonadal, common iliac, internal iliac and uterine veins. The bladder is drained by the vesical venous plexus. The superior aspect of the plexus is drained into the superior vesical vein, and the inferior aspect of the plexus is drained into the inferior vesical vein. The urethra is drained by the vesical venous plexus and the internal pudendal vein.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





