Description
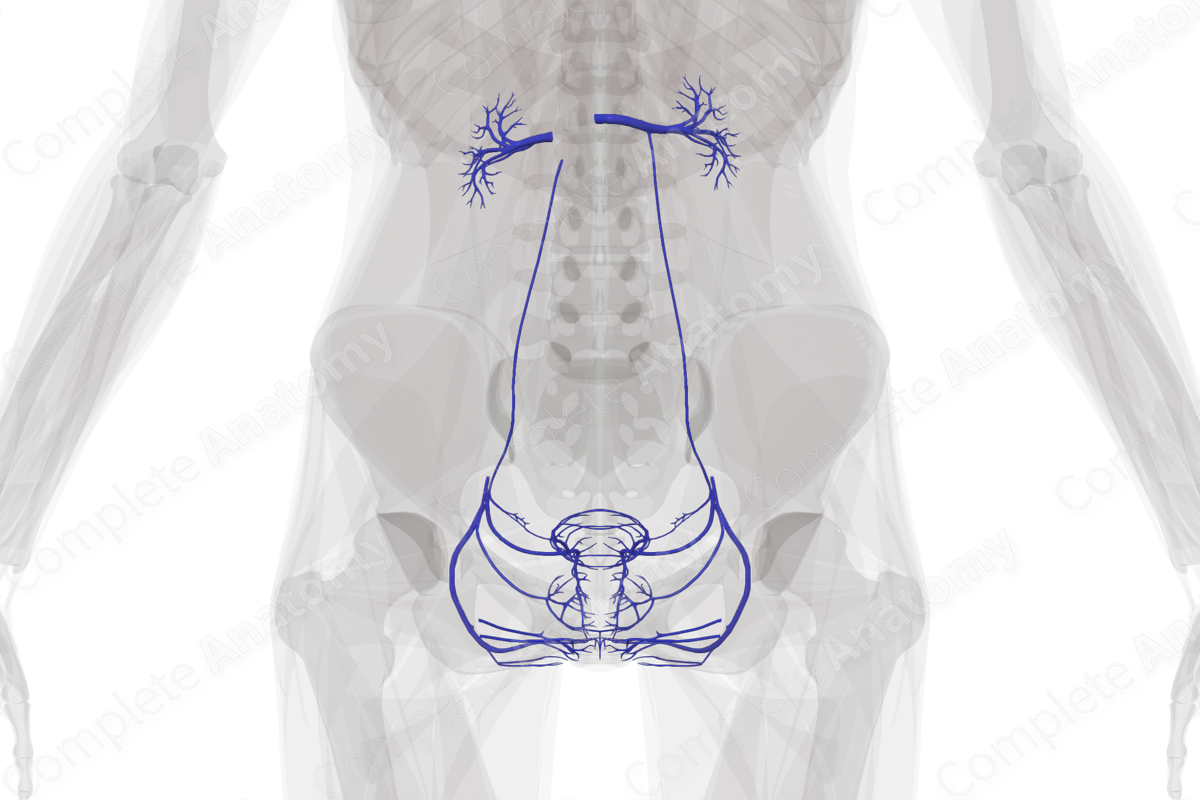
The kidneys are drained by paired left and right renal veins that drain directly into the inferior vena cava. The left renal vein is much longer than the right renal vein due to the position of the inferior vena cava on the right-hand side of the body. The ureters are drained segmentally as they descend from the abdomen into the pelvis. Multiple anastomoses are formed between superior and inferior segmental vessels. The bladder is drained by the vesical venous plexus. The superior aspect of the plexus is drained into the superior vesical vein, and the inferior aspect of the plexus is drained into the inferior vesical vein.
The testicular vein and the vein of the ductus deferens help to drain the testes, while the smaller pudendal, pampiniform, umbilical, and ductal veins drain the greater genital region. They drain into the femoral veins, the iliac veins, or their smaller regional tributaries.
Learn more about this topic from other Elsevier products





