Quick Facts
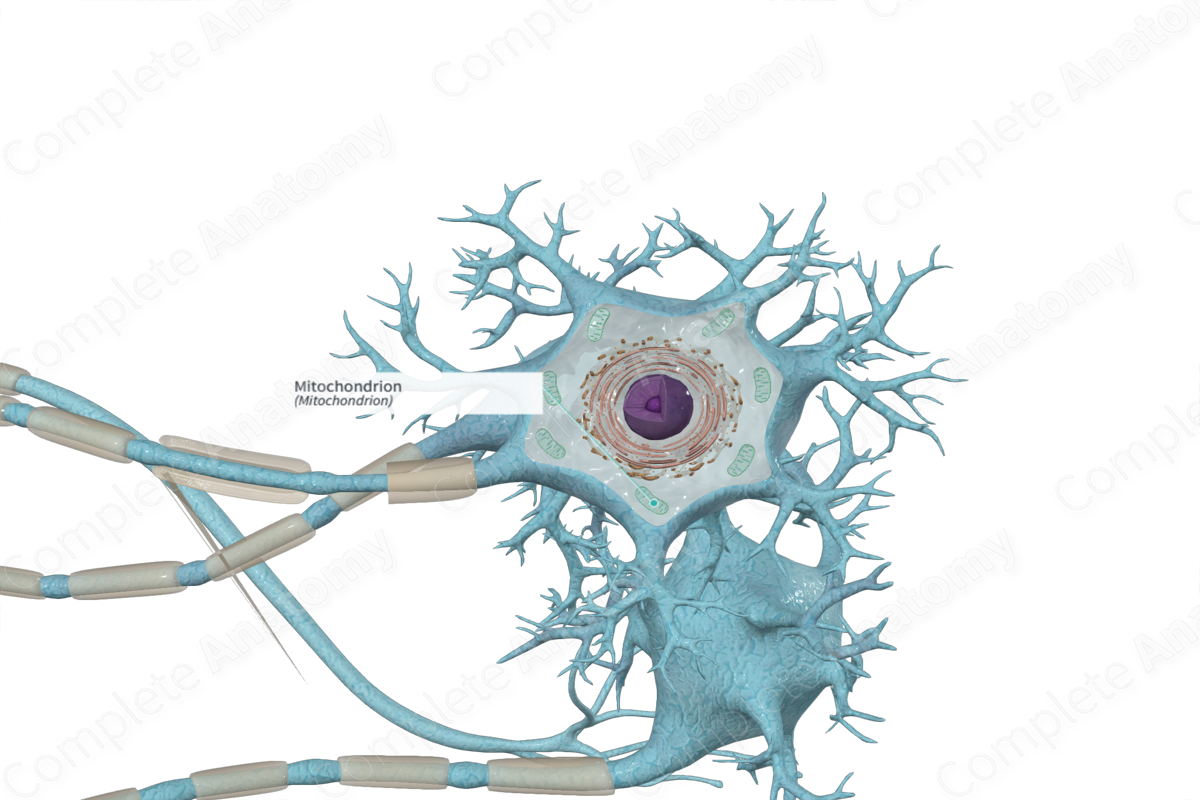
Mitochondria are the small spherical to rod-shaped cytoplasmic organelles, consisting of inner and outer bilayer membranes with a space between them. The inner membrane is infolded to form a series of projections (cristae), and the space between the cristae is filled by the mitochondrial matrix, which contains DNA, RNA, ribosomes, and granules. Mitochondria generate energy (in the form of ATP synthesis) by the oxidation of nutrients, and they contain the enzymes of the tricarboxylic acid (Krebs) cycle and for fatty acid oxidation and oxidative phosphorylation. In response to toxic insults, they release enzymes that cause apoptosis. Mitochondria can replicate independently and code for the synthesis of some of their proteins; inheritance of mitochondrial DNA is maternal, and mitochondrial DNA defects cause a variety of diseases (Dorland, 2011).
Structure and/or Key Features
The mitochondrion is a double membrane-bound organelle about 0.5-1 μm wide and up to 10 μm in length. The space between the inner and outer membrane is the intermembrane space.
Mitochondria occur in a variety of shapes and sizes. The only cells that lack mitochondria are erythrocytes (red blood cells) and terminal keratinocytes.
The outer membranes of the mitochondria are about 6–7 nm thick and have mitochondrial porins which are voltage-dependent anion channels. Ions, metabolites, and small molecules may enter the intermembrane space; however, they cannot pass through the inner mitochondrial membrane. In addition, the outer membrane possesses various receptors, for molecules that translocate in the intermembrane space, and various enzymes.
The inner mitochondrial membrane is thinner and rich in cardiolipin which is a phospholipid that makes the inner membrane impermeable to ions and less permeable to all other elements. The inner membrane invaginates to form long parallel stacks of membranous components called cristae that run perpendicular to the long axis of the mitochondrion and increase the surface area of the inner membrane. Cristae contain respiratory chain enzymes. Among these respiratory enzymes is ATP synthetase which is responsible for oxidative phosphorylation, a process of cellular respiration and the production of adenosine triphosphate (ATP), which is an energy-rich molecule.
Cristae that form parallel plates in mitochondria produce proteins, whereas in mitochondria that produce steroids, the cristae adopt a tubular form.
The numbers of mitochondria, as well as the number and complexity of the cristae, will correlate with the activity of the cell. Therefore, very active cells, such as a skeletal muscle fiber and a cardiomyocyte (cardiac muscle cell), will contain large numbers of mitochondria with extensive cristae.
The inner mitochondrial membrane surrounds the mitochondrial fluid (matrix) which contains mitochondrial DNA and RNA. The mitochondrial DNA encodes thirteen enzymes which are involved in the process of oxidative phosphorylation. It also contains two rRNAs, and twenty-two tRNAs that are involved in the translation of mitochondrial mRNA. In addition, mitochondria exhibit a complete system of proteins for protein and ribosomal synthesis. Mitochondrial proteins are formed both by mitochondrial and nuclear DNA.
Matrix granules that store Ca2+ are also housed within the matrix of the mitochondrion.
Mitochondria contribute to the acidophilia of the cytoplasm in cells where they aggregate in large numbers.
Anatomical Relations
The mitochondria are scattered throughout the cell body, dendrites, and axons. They are greater in number at the axon hillock, nodes of Ranvier, and presynaptic endings.
Function
The mitochondria are the power houses of the cell and produce chemical energy by producing high energy ATP molecules. The mitochondria are also able to induce apoptosis (Ross and Pawlina, 2006).
Clinical Correlates
Mutations in mitochondrial DNA result in a number of inherited disorders. Mitochondrial related diseases (mitochondrial myopathies) become most evident in tissues such as skeletal muscle that require large amounts of energy (ATP) generated by mitochondria.
Chronic progressive external ophthalmoplegia affects the inability to move the eyes due to weakening of extraocular muscles and the eyebrows. Leber hereditary optic neuropathy affects vision due to the degeneration of retinal ganglion cells and their axons as a result of mutations in the mitochondrial genome.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
Ross, M. H. and Pawlina, W. (2006) Histology: A text and atlas. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins.
