Quick Facts
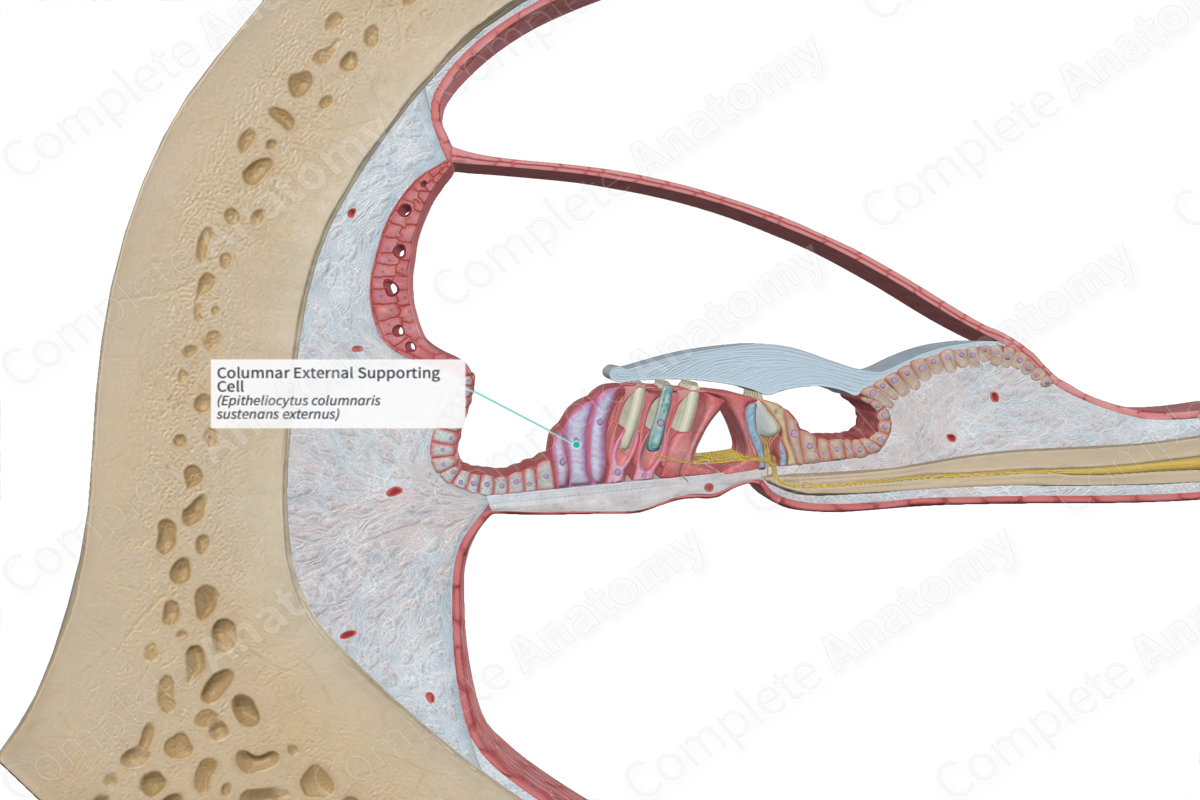
The columnar external supporting cells, of Hensen cells, are the tall supporting cells arranged in rows adjacent to the last row of outer phalangeal cells, constituting the outer border of the organ of Corti (Dorland, 2011).
Structure and/or Key Feature(s)
The columnar external supporting cells (Hensen’s cells or the outer border cells) are one of the three types of cells that form the supporting cells of the outer hair cells. The other cells include the outer pillar cells and the external phalangeal epithelial cells. They are arranged in numerous rows extending out toward the outer spiral sulcus. These border cells are oblong shaped, with the tallest cells nearest to the external phalangeal epithelial cells and outer hair cells. The columnar external supporting cells decrease in height as the rows move out toward the outer spiral sulcus.
Similar to the internal supporting cells, the apical surfaces of these cells are slanted, forming a gradual slope toward the outer hair cells. The slope of the surfaces of the shorter, outermost supporting cells is the steepest. The slope becomes less severe as it moves inwards and upwards. As the slope flattens, the apices of the taller cells become wider, with the innermost row of these border cells having a slight internal overhang in relation to their body.
The columnar external supporting cells have adherens and tight junctions which link them to the other columnar external supporting cells, as well as the other adjacent supporting cells. They communicate with each other via established gap junctions.
Anatomical Relations
The columnar external supporting cells are the most external epithelial cells of the organ of Corti. They are interjacent to the outer phalangeal epithelial cells and cuboid external supporting cells (Claudius’ cells).
Function
The columnar external supporting cells have a sturdy cytoskeleton that helps preserve the structural organization of the outer hair cells. They communicate effectively with the surrounding cells via gap junctions, allowing for an effective inflammatory response to be generated in the presence of damage or pathogens.
References
Dorland, W. (2011) Dorland's Illustrated Medical Dictionary. 32nd edn. Philadelphia, USA: Elsevier Saunders.
